The teacher-centered approach emphasizes authoritative instruction where educators direct the learning process, focusing on curriculum delivery and content mastery. In contrast, learner agency prioritizes student autonomy, encouraging active participation, self-directed learning, and critical thinking. Balancing these methods fosters a dynamic educational environment that nurtures both knowledge acquisition and independent problem-solving skills.
Table of Comparison
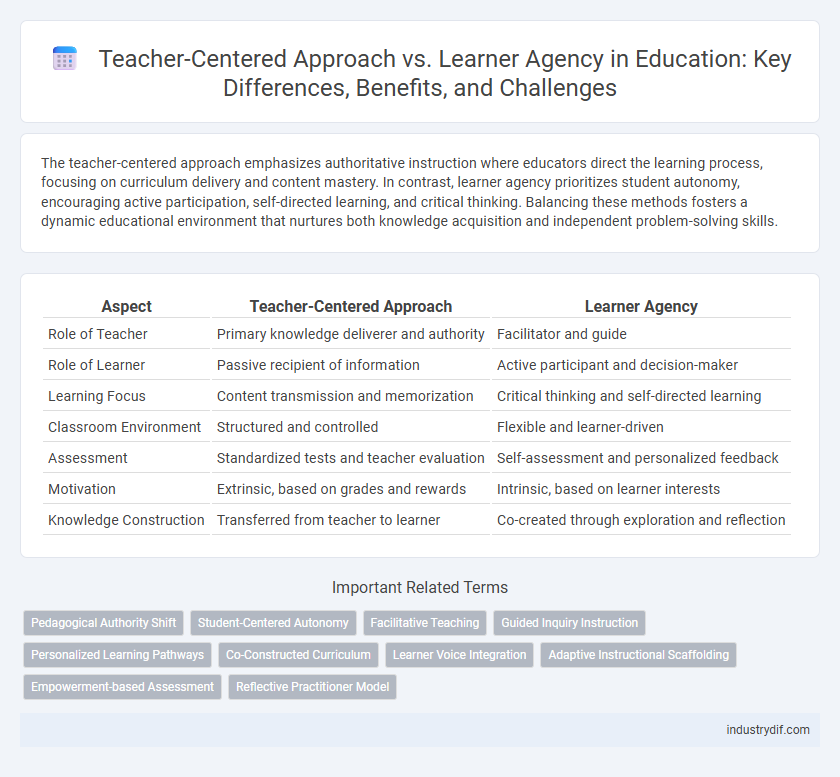
| Aspect | Teacher-Centered Approach | Learner Agency |
|---|---|---|
| Role of Teacher | Primary knowledge deliverer and authority | Facilitator and guide |
| Role of Learner | Passive recipient of information | Active participant and decision-maker |
| Learning Focus | Content transmission and memorization | Critical thinking and self-directed learning |
| Classroom Environment | Structured and controlled | Flexible and learner-driven |
| Assessment | Standardized tests and teacher evaluation | Self-assessment and personalized feedback |
| Motivation | Extrinsic, based on grades and rewards | Intrinsic, based on learner interests |
| Knowledge Construction | Transferred from teacher to learner | Co-created through exploration and reflection |
Defining Teacher-Centered Approach in Education
The teacher-centered approach in education emphasizes the instructor's role as the primary source of knowledge, where lessons are structured around lectures, direct instruction, and standardized assessments. This method prioritizes uniform content delivery and teacher authority, limiting student autonomy and active participation. Predominantly used in traditional classrooms, it contrasts sharply with learner agency by focusing on teacher-led goals and control over the learning environment.
Understanding Learner Agency in Modern Classrooms
Teacher-centered approaches prioritize structured content delivery and authority, often limiting student autonomy and engagement. Learner agency in modern classrooms emphasizes student voice, choice, and active participation, fostering critical thinking and personalized learning pathways. Embracing learner agency enhances motivation and deeper understanding by encouraging students to take ownership of their educational experience.
Historical Evolution: Teacher-Centered vs Learner-Centered Models
Teacher-centered approaches historically dominated education, emphasizing standardized curricula and authoritative instruction where teachers directed learning processes. Over time, the rise of constructivist theories shifted focus toward learner-centered models, promoting student autonomy, critical thinking, and active engagement. This evolution reflects a broader educational transformation from passive knowledge reception to fostering learner agency and personalized learning experiences.
Core Principles of Teacher-Centered Instruction
Teacher-centered instruction emphasizes structured lesson delivery, where educators act as primary knowledge sources, directing the learning process and maintaining classroom control. Core principles include clear objectives, systematic content presentation, and frequent assessments to gauge understanding. This approach ensures consistency and mastery of foundational knowledge, prioritizing teacher expertise over student autonomy.
Key Elements of Learner Agency and Student Empowerment
Learner agency emphasizes student autonomy, self-regulation, and active participation, fostering intrinsic motivation and personalized learning paths. Key elements include goal-setting, decision-making, and reflective practices that empower students to take ownership of their educational experiences. This approach contrasts with the teacher-centered model, where instruction is predominantly directed by educators, limiting opportunities for student empowerment and independent critical thinking.
Comparative Analysis: Learning Outcomes and Engagement
The teacher-centered approach often results in standardized learning outcomes with a focus on content mastery, yet may limit student engagement and critical thinking development. In contrast, learner agency promotes active participation, personalized learning paths, and higher motivation, leading to improved problem-solving skills and retention rates. Comparative studies indicate that environments fostering learner autonomy consistently enhance engagement levels and deeper conceptual understanding compared to traditional instructor-led models.
Advantages and Limitations of Teacher-Centered Pedagogy
Teacher-centered pedagogy provides structured, standardized instruction that ensures curriculum coverage and maintains classroom discipline, promoting efficient knowledge transmission. However, this approach often limits learner autonomy, suppresses creativity, and may hinder critical thinking development due to its passive student role. While effective for foundational skill acquisition, it may not foster learner agency or personalized educational experiences essential for 21st-century competencies.
Benefits and Challenges of Fostering Learner Agency
Fostering learner agency promotes student engagement, critical thinking, and personalized learning, enhancing motivation and long-term retention. Challenges include balancing curriculum requirements and providing adequate support for diverse learner needs, which can demand significant teacher adaptation. Despite these hurdles, empowering students to take ownership of their education cultivates autonomy and prepares them for lifelong learning.
Integrating Teacher Guidance with Student Autonomy
Integrating teacher guidance with student autonomy enhances learning outcomes by balancing structured instruction and independent exploration. This approach leverages the expertise of educators to scaffold complex concepts while empowering learners to take ownership of their educational journey, fostering critical thinking and self-regulation. Research shows that combining teacher-centered strategies with learner agency promotes engagement, motivation, and deeper comprehension in diverse educational settings.
Future Trends: Shifting Paradigms in Educational Practice
Emerging future trends in education emphasize a shift from the traditional teacher-centered approach toward enhancing learner agency, prioritizing student autonomy and personalized learning experiences. Technological advancements like AI-driven adaptive learning platforms enable educators to facilitate rather than dictate knowledge acquisition, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This paradigm shift aligns with global educational goals aiming to prepare learners for complex, dynamic environments by promoting self-directed learning and collaborative inquiry.
Related Important Terms
Pedagogical Authority Shift
The shift from a teacher-centered approach to learner agency redefines pedagogical authority by transferring control from instructors to students, enhancing autonomy and personalized learning experiences. This dynamic fosters critical thinking and engagement, as learners actively shape their educational paths rather than passively receiving knowledge.
Student-Centered Autonomy
Student-centered autonomy prioritizes learners' active participation and decision-making in the educational process, fostering critical thinking and intrinsic motivation. This approach contrasts with the traditional teacher-centered model by emphasizing personalized learning paths and empowering students to take ownership of their academic success.
Facilitative Teaching
Facilitative teaching prioritizes learner agency by creating environments where students actively construct knowledge through inquiry and collaboration, contrasting with the traditional teacher-centered approach that emphasizes direct instruction and passive reception. This method enhances critical thinking and autonomy, fostering deeper engagement and personalized learning outcomes.
Guided Inquiry Instruction
Guided Inquiry Instruction balances the Teacher-Centered Approach and Learner Agency by structuring learning through targeted questions while promoting student exploration and critical thinking. This method fosters deeper understanding and engagement by allowing learners to actively participate in their knowledge construction within a supportive framework.
Personalized Learning Pathways
Teacher-centered approaches often follow a standardized curriculum with limited flexibility, restricting learners' ability to customize their educational experiences. Personalized learning pathways empower students to take ownership of their progress by adapting content, pace, and assessment methods to individual needs and interests.
Co-Constructed Curriculum
A co-constructed curriculum balances the teacher-centered approach's structured guidance with learner agency's active participation, fostering personalized learning experiences that engage students in decision-making and content development. This collaborative model enhances critical thinking and motivation by integrating expert knowledge with learners' interests, promoting deeper understanding and ownership of the educational process.
Learner Voice Integration
Integrating learner voice in education shifts focus from the traditional teacher-centered approach to empowering students as active participants, fostering critical thinking and personalized learning experiences that enhance engagement and achievement. Research shows that when learners express their preferences and insights, educational outcomes improve through increased motivation and deeper understanding.
Adaptive Instructional Scaffolding
Adaptive instructional scaffolding enhances learner agency by tailoring support to individual student needs, promoting autonomy and deeper engagement. In contrast, the teacher-centered approach often limits this flexibility, emphasizing direct instruction and reducing opportunities for personalized learning and self-directed problem-solving.
Empowerment-based Assessment
Empowerment-based assessment in education shifts focus from traditional teacher-centered evaluation to fostering learner agency by prioritizing self-assessment and reflective practices that enhance student autonomy. This approach encourages active participation, critical thinking, and personal growth, leading to improved motivation and deeper understanding of learning outcomes.
Reflective Practitioner Model
The reflective practitioner model enhances learner agency by encouraging educators to critically assess their teaching methods and adapt strategies that prioritize student autonomy over traditional teacher-centered approaches. By fostering a dynamic environment where learners actively contribute to their educational journey, this model shifts the focus from mere knowledge transmission to collaborative inquiry and self-directed learning.
Teacher-Centered Approach vs Learner Agency Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com