Teacher certification provides a comprehensive and standardized validation of a teacher's qualifications and expertise, often required for formal employment in educational institutions. Microcredentials focus on specific skills or knowledge areas, enabling educators to demonstrate mastery in niche topics and adapt quickly to evolving teaching demands. Both certification and microcredentials enhance professional development but serve different purposes in recognizing teacher competency and specialization.
Table of Comparison
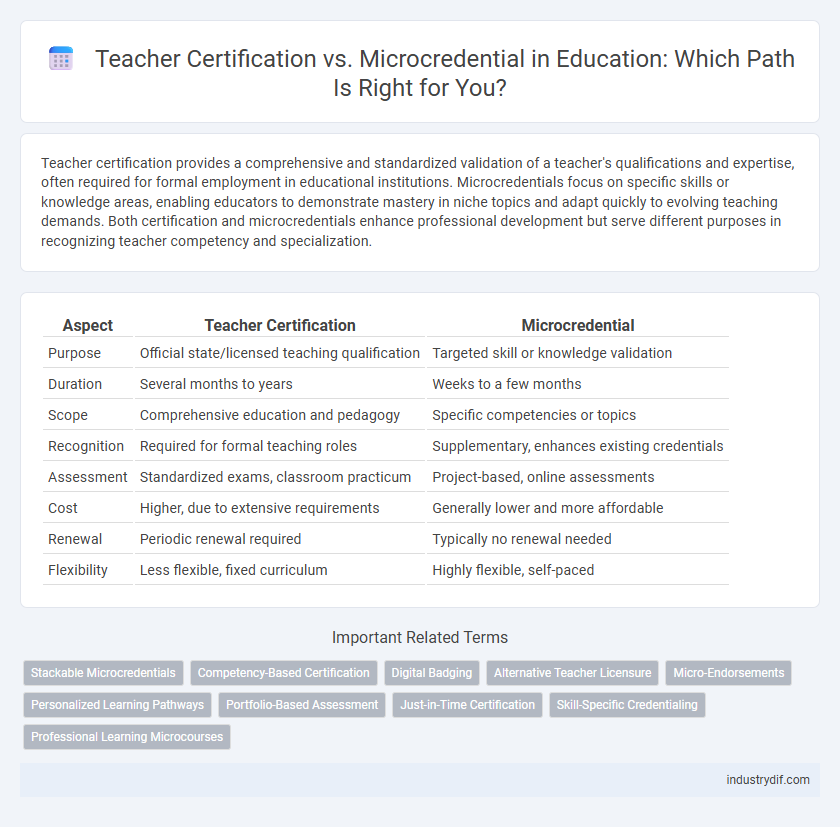
| Aspect | Teacher Certification | Microcredential |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Official state/licensed teaching qualification | Targeted skill or knowledge validation |
| Duration | Several months to years | Weeks to a few months |
| Scope | Comprehensive education and pedagogy | Specific competencies or topics |
| Recognition | Required for formal teaching roles | Supplementary, enhances existing credentials |
| Assessment | Standardized exams, classroom practicum | Project-based, online assessments |
| Cost | Higher, due to extensive requirements | Generally lower and more affordable |
| Renewal | Periodic renewal required | Typically no renewal needed |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, fixed curriculum | Highly flexible, self-paced |
Understanding Teacher Certification
Teacher certification establishes a standardized credential verifying educators' qualifications to teach specific subjects or grade levels, often requiring rigorous coursework, exams, and practical experience. This formal certification is typically mandated by state or national education authorities to ensure consistent teaching quality and compliance with educational standards. Understanding teacher certification is essential for educators seeking long-term employment and professional recognition within accredited institutions.
Defining Microcredentials in Education
Microcredentials in education represent focused, competency-based certifications that validate specific skills or knowledge areas, often complementing traditional teacher certification programs. Unlike comprehensive teacher certification, microcredentials offer targeted professional development through digital badges or certificates, enabling educators to demonstrate expertise in niche topics such as technology integration or classroom management. These credentials provide flexible, stackable learning opportunities aligned with evolving educational standards and personalized teacher growth pathways.
Key Differences Between Certification and Microcredentials
Teacher certification involves a formal process governed by state education boards that verifies a teacher's qualifications to instruct in specific grade levels or subjects, often requiring completion of a degree program and passing standardized exams. Microcredentials are specialized, competency-based credentials that recognize mastery of targeted skills or knowledge areas, typically earned through shorter, flexible learning experiences and digital badges. The key difference lies in certification's comprehensive, standardized validation of teaching eligibility versus microcredentials' focused, modular recognition of specific expertise or professional development.
Traditional Pathways: Teacher Certification Processes
Teacher certification processes typically require candidates to complete accredited education programs, supervised teaching experiences, and pass standardized exams to ensure comprehensive knowledge and practical skills in pedagogy. These traditional pathways emphasize state-mandated requirements, including coursework in educational theory, subject matter expertise, and classroom management. While time-intensive, certified teachers gain full licensure crucial for employment in public schools and eligibility for tenure.
Emerging Trends: Rise of Microcredentials
Microcredentials are rapidly gaining traction in education as flexible, skill-specific certifications that complement or even challenge traditional teacher certification pathways. Emerging trends highlight that educators pursue microcredentials to demonstrate targeted expertise in digital literacy, inclusive teaching, and classroom technology integration, aligning with evolving educational demands. This shift supports continuous professional development, enabling teachers to adapt swiftly to innovations and policy changes in education.
Benefits of Teacher Certification
Teacher certification establishes a standardized measure of expertise and competency, ensuring educators meet rigorous professional and academic criteria. Certified teachers gain access to higher salary scales, expanded career opportunities, and greater job security within public and private education systems. The credential also fosters trust among parents and administrators, reflecting a verified commitment to quality instruction and ongoing professional development.
Advantages of Earning Microcredentials
Earning microcredentials offers educators targeted skill validation in specific areas such as technology integration or classroom management, enabling personalized professional development. These credentials provide flexible, affordable learning opportunities that can be quickly acquired and immediately applied to enhance teaching effectiveness. Schools benefit from teachers holding microcredentials by gaining verified expertise aligned with evolving educational standards without the time and cost commitments of traditional certification.
Impact on Career Advancement
Teacher certification provides a formal and widely recognized qualification essential for securing stable teaching positions and advancing to higher roles within educational institutions. Microcredentials offer targeted skill validation that enhances specific competencies, making educators more adaptable and competitive in specialized areas like technology integration or inclusive education. Combining traditional certification with microcredentials can significantly accelerate career growth by demonstrating both foundational expertise and ongoing professional development.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Credential
Teacher certification often requires extensive time and financial investment, creating barriers for educators seeking career advancement or specialization. Microcredentials may lack widespread recognition and standardized quality assurance, limiting their acceptance in formal education systems. Both credentials face challenges in balancing accessibility, validation, and alignment with professional development needs in evolving educational landscapes.
Choosing the Right Path: Certification or Microcredential?
Choosing the right path between teacher certification and microcredentials depends on career goals and subject expertise. Teacher certification provides a comprehensive foundation and is often required for formal teaching positions, ensuring compliance with state regulations and educational standards. Microcredentials offer targeted, flexible skill development that supports ongoing professional growth and specialization in specific areas, making them ideal for educators seeking to enhance their expertise without pursuing full certification.
Related Important Terms
Stackable Microcredentials
Stackable microcredentials offer educators a flexible and personalized pathway to professional development by allowing them to accumulate specific skills and competencies that align with teacher certification standards. These credential bundles enable targeted expertise growth while providing recognized, incremental qualifications that can eventually support or supplement traditional certification requirements.
Competency-Based Certification
Competency-based teacher certification assesses educators through demonstrated skills and knowledge, providing a more personalized and flexible pathway compared to traditional certification methods. Microcredentials offer targeted recognition of specific competencies, enabling teachers to continuously update expertise and align with evolving educational standards.
Digital Badging
Digital badging offers educators a flexible, verifiable form of microcredential that highlights specific skills and competencies beyond traditional teacher certification. These digital credentials enable educators to showcase specialized expertise, enhance professional development, and adapt to rapidly evolving educational technologies.
Alternative Teacher Licensure
Alternative teacher licensure provides a flexible pathway for educators to enter the profession without traditional certification, often emphasizing microcredentials that verify specific skills or subject mastery. Microcredentials complement teacher certification by offering targeted professional development and demonstrating competency in specialized areas, accelerating career advancement in education.
Micro-Endorsements
Micro-endorsements provide educators with specialized, competency-based credentials that target specific skills or knowledge areas, offering flexibility beyond traditional teacher certification. These microcredentials enable teachers to demonstrate continuous professional development and adapt to evolving educational standards efficiently.
Personalized Learning Pathways
Teacher certification offers comprehensive validation of instructional skills and subject matter expertise, providing educators with formal recognition aligned with state standards. Microcredentials enable personalized learning pathways by allowing teachers to acquire targeted competencies and demonstrate mastery in specific areas, supporting ongoing professional growth and adaptability in diverse classroom environments.
Portfolio-Based Assessment
Teacher certification often requires comprehensive portfolio-based assessments that demonstrate mastery of pedagogical skills, classroom management, and curriculum development. Microcredentials utilize focused portfolio submissions to validate specific competencies, offering educators targeted recognition without the broad scope of traditional certification.
Just-in-Time Certification
Just-in-time certification offers educators targeted, flexible learning opportunities that align with immediate classroom needs, contrasting with traditional teacher certification's lengthy processes. Microcredentials provide skill-specific validation, enabling teachers to quickly adapt and demonstrate competencies without completing comprehensive certification programs.
Skill-Specific Credentialing
Teacher certification provides comprehensive validation of a candidate's qualifications and pedagogical knowledge, while microcredentials focus on skill-specific credentialing, enabling educators to demonstrate expertise in targeted areas such as technology integration or classroom management. Microcredentials offer flexible, stackable learning opportunities that support ongoing professional development tailored to evolving educational demands.
Professional Learning Microcourses
Professional learning microcourses offer educators targeted skill development through concise, competency-based modules, enhancing specific teaching practices without the extensive time commitment of traditional teacher certification programs. These microcredentials validate specialized expertise and facilitate continuous professional growth, complementing formal certification by addressing emerging educational technologies and methodologies.
Teacher Certification vs Microcredential Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com