Standardized testing offers a uniform metric to evaluate student achievement across diverse populations, emphasizing consistency and scalability. Performance-based assessment provides a deeper insight into student understanding by evaluating practical application and critical thinking skills in real-world contexts. Balancing both approaches can create a more comprehensive evaluation system that addresses varied learning styles and promotes meaningful educational outcomes.
Table of Comparison
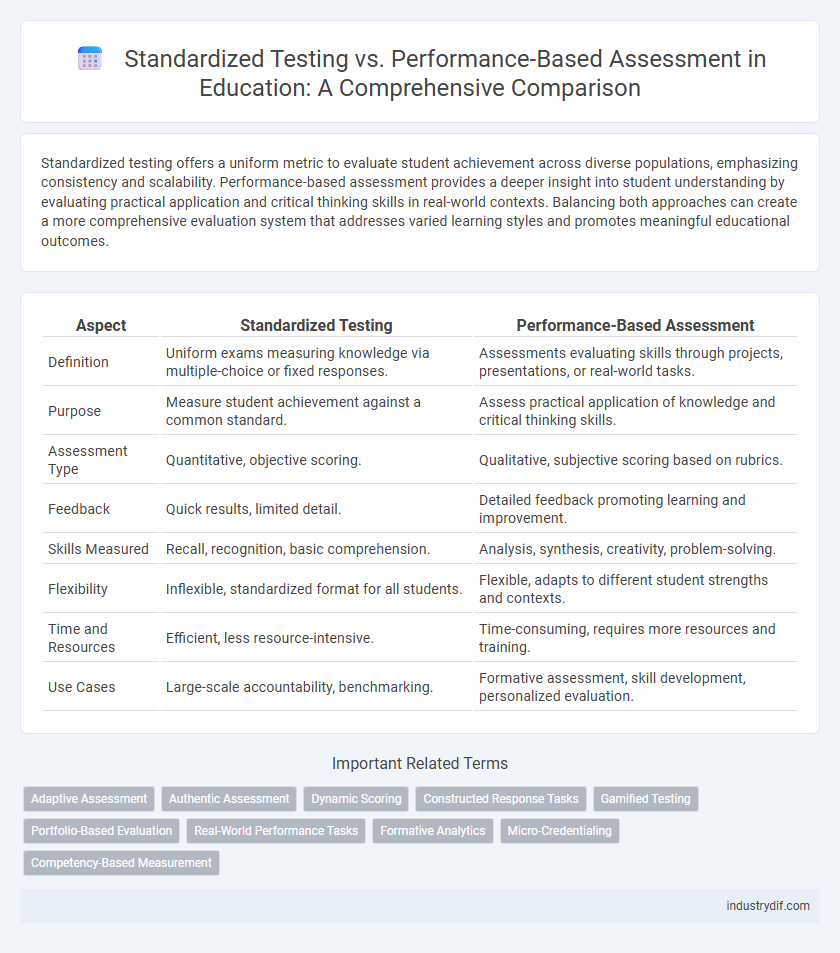
| Aspect | Standardized Testing | Performance-Based Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uniform exams measuring knowledge via multiple-choice or fixed responses. | Assessments evaluating skills through projects, presentations, or real-world tasks. |
| Purpose | Measure student achievement against a common standard. | Assess practical application of knowledge and critical thinking skills. |
| Assessment Type | Quantitative, objective scoring. | Qualitative, subjective scoring based on rubrics. |
| Feedback | Quick results, limited detail. | Detailed feedback promoting learning and improvement. |
| Skills Measured | Recall, recognition, basic comprehension. | Analysis, synthesis, creativity, problem-solving. |
| Flexibility | Inflexible, standardized format for all students. | Flexible, adapts to different student strengths and contexts. |
| Time and Resources | Efficient, less resource-intensive. | Time-consuming, requires more resources and training. |
| Use Cases | Large-scale accountability, benchmarking. | Formative assessment, skill development, personalized evaluation. |
Defining Standardized Testing and Performance-Based Assessment
Standardized testing refers to assessments administered and scored in a consistent, predetermined manner to measure students' knowledge and skills against uniform benchmarks, often involving multiple-choice or short-answer questions. Performance-based assessment evaluates students through real-world tasks and projects that demonstrate their ability to apply knowledge, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. These two methods differ fundamentally in structure, with standardized tests emphasizing uniformity and comparability, while performance-based assessments prioritize depth of understanding and practical application.
Historical Overview of Assessment Methods in Education
Standardized testing emerged in the early 20th century as a tool for objective measurement, enabling large-scale comparisons of student achievement through uniform multiple-choice exams. Performance-based assessments gained prominence in the late 20th century, emphasizing real-world tasks and critical thinking skills that reflect student learning more holistically. The evolution from traditional standardized tests to diverse evaluation methods highlights ongoing efforts to balance reliability, validity, and educational equity in assessment practices.
Key Differences: Standardized vs Performance-Based Assessment
Standardized testing relies on uniform procedures and multiple-choice or short-answer formats to measure student achievement across large populations, emphasizing consistency and comparability. Performance-based assessment evaluates students through tasks like projects, presentations, or portfolios, allowing demonstration of critical thinking, creativity, and application of knowledge in real-world contexts. The key difference lies in standardized tests prioritizing breadth and scalability, while performance assessments focus on depth and individualized skills assessment.
Advantages of Standardized Testing in Educational Systems
Standardized testing provides objective data that enables consistent measurement of student achievement across diverse populations, ensuring comparability and fairness. It facilitates large-scale analysis for policymakers to identify trends, allocate resources effectively, and hold schools accountable. The efficiency and scalability of standardized tests support timely evaluation of academic standards and curriculum effectiveness.
Benefits of Performance-Based Assessment for Student Learning
Performance-based assessment enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by requiring students to apply knowledge in real-world contexts. It provides personalized feedback, fostering deeper understanding and continuous improvement. This approach promotes student engagement and motivation by valuing creativity and individual learning styles.
Challenges and Criticisms of Standardized Testing
Standardized testing faces criticism for its limited ability to measure diverse student skills, often emphasizing rote memorization over critical thinking and creativity. Challenges include cultural bias, which can disadvantage minority students, and the pressure it places on educators and students, sometimes leading to teaching to the test rather than fostering deeper understanding. These issues raise concerns about the validity and fairness of standardized tests as the sole metric for student evaluation and educational accountability.
Limitations of Performance-Based Assessment Approaches
Performance-based assessments often face limitations related to subjective scoring and inconsistent reliability across different evaluators, which can compromise the fairness of results. These assessments also require significant time and resources for administration and evaluation, making them less feasible on a large scale compared to standardized tests. Furthermore, performance-based approaches may not fully capture knowledge breadth, focusing more on specific skills than comprehensive content mastery.
Impact on Teaching Strategies and Curriculum Design
Standardized testing often leads educators to prioritize test preparation, emphasizing rote memorization and narrow skill sets aligned with exam criteria. Performance-based assessment encourages the integration of critical thinking, problem-solving, and real-world application skills, prompting teachers to design curricula that foster deeper understanding and creativity. This shift impacts teaching strategies by promoting project-based learning, collaborative activities, and formative assessments that support diverse learning styles.
Equity and Accessibility Considerations in Assessment Practices
Standardized testing often presents barriers for students with diverse learning needs due to rigid formats and time constraints, limiting equitable access to demonstrating their knowledge. Performance-based assessments offer flexible evaluation methods that accommodate various learning styles and provide a more inclusive measure of student abilities. Equity-focused practices prioritize culturally responsive tasks and accessible formats, ensuring all students have fair opportunities to succeed in assessment.
Future Trends: Balancing Standardized and Performance-Based Assessment
Emerging trends in education emphasize integrating standardized testing with performance-based assessments to create a more holistic evaluation system. Advances in technology enable adaptive testing and real-time performance tracking, facilitating personalized learning paths and deeper insights into student competencies. Balancing these methods supports equitable assessment by combining objective measurement with authentic demonstrations of critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Related Important Terms
Adaptive Assessment
Adaptive assessment tailors questions to a student's ability level, offering a more personalized and accurate measure of learning compared to traditional standardized testing. This approach enhances engagement and provides real-time data to educators, enabling targeted instruction and improved student outcomes.
Authentic Assessment
Authentic assessment evaluates students through real-world tasks that demonstrate practical skills and critical thinking, contrasting with standardized testing's focus on multiple-choice questions and rote memorization. This approach fosters deeper learning by measuring how students apply knowledge in meaningful contexts, promoting engagement and long-term retention.
Dynamic Scoring
Dynamic scoring in performance-based assessments provides real-time evaluation of student skills, capturing critical thinking and problem-solving abilities more effectively than traditional standardized tests. This approach offers educators granular insights into student learning progression, enabling personalized feedback and adaptive instruction for improved educational outcomes.
Constructed Response Tasks
Constructed response tasks in performance-based assessments offer deeper insight into student understanding by requiring learners to generate original answers, unlike standardized testing which often relies on multiple-choice formats. These tasks promote critical thinking and problem-solving skills, providing educators with more nuanced data on student mastery and cognitive processes.
Gamified Testing
Gamified testing in education integrates game elements into standardized assessments, enhancing student engagement and motivation while providing real-time data on learning progress. This innovative approach contrasts with traditional performance-based assessments by combining objective measurement with interactive, adaptive challenges that promote deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Portfolio-Based Evaluation
Portfolio-based evaluation provides a comprehensive view of a student's skills by showcasing diverse work samples over time, emphasizing critical thinking and creativity rather than rote memorization. Evidence indicates this method enhances personalized learning and better aligns with real-world problem-solving compared to traditional standardized testing.
Real-World Performance Tasks
Performance-based assessments emphasize real-world performance tasks that measure students' ability to apply knowledge in practical scenarios, offering deeper insights into critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity compared to standardized testing's focus on memorization and multiple-choice formats. These authentic tasks simulate workplace and life challenges, enabling educators to assess skills like collaboration and communication that standardized tests often overlook.
Formative Analytics
Formative analytics in education leverages continuous data from both standardized testing and performance-based assessments to provide real-time insights into student learning progress. By analyzing patterns in test scores and authentic task performance, educators can tailor instruction to address individual needs, enhancing personalized learning and improving educational outcomes.
Micro-Credentialing
Micro-credentialing enhances personalized learning by allowing students to demonstrate specific competencies through performance-based assessments rather than traditional standardized testing. This approach supports skill mastery and real-world application, fostering continuous professional development and targeted achievement recognition.
Competency-Based Measurement
Competency-based measurement in education emphasizes assessing students' mastery of specific skills and knowledge through performance-based assessment rather than relying solely on standardized testing. This approach provides a more comprehensive evaluation of learners' abilities by integrating real-world tasks that demonstrate applied competence and critical thinking.
Standardized Testing vs Performance-Based Assessment Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com