University degrees provide comprehensive theoretical knowledge and widely recognized credentials essential for many professional careers, offering a broad educational foundation. Nanodegrees focus on specialized skills and practical experience tailored to rapidly evolving industries like technology, enabling faster career transitions and hands-on learning. Choosing between a university degree and a nanodegree depends on career goals, time availability, and the need for either in-depth academic study or targeted skill acquisition.
Table of Comparison
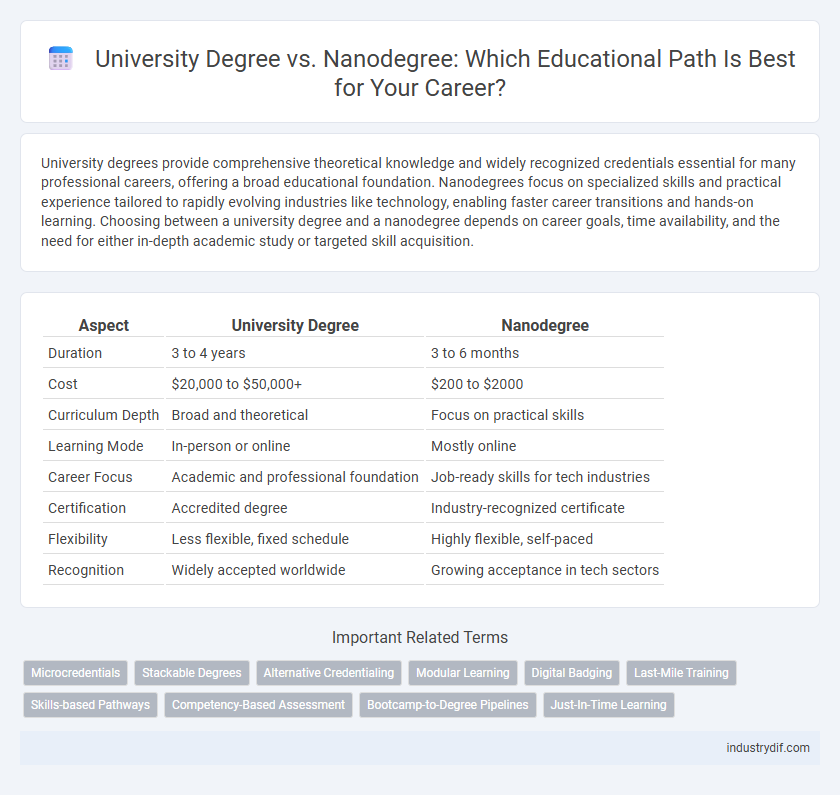
| Aspect | University Degree | Nanodegree |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | 3 to 4 years | 3 to 6 months |
| Cost | $20,000 to $50,000+ | $200 to $2000 |
| Curriculum Depth | Broad and theoretical | Focus on practical skills |
| Learning Mode | In-person or online | Mostly online |
| Career Focus | Academic and professional foundation | Job-ready skills for tech industries |
| Certification | Accredited degree | Industry-recognized certificate |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, fixed schedule | Highly flexible, self-paced |
| Recognition | Widely accepted worldwide | Growing acceptance in tech sectors |
Understanding University Degrees and Nanodegrees
University degrees typically involve comprehensive, multi-year programs that provide in-depth knowledge, critical thinking skills, and a broad educational foundation recognized worldwide by employers and institutions. Nanodegrees offer specialized, shorter-term learning focused on specific skills or industries, often developed in collaboration with tech companies, ideal for rapid upskilling and practical application. Understanding these differences helps learners choose between the depth and recognition of traditional degrees and the flexibility and targeted training of nanodegrees based on career goals.
Key Differences Between University Degrees and Nanodegrees
University degrees typically require several years of full-time study, offering comprehensive and in-depth knowledge across a broad academic curriculum, often recognized globally by employers and academic institutions. Nanodegrees are short-term, skill-focused programs designed for rapid acquisition of practical abilities, primarily delivered online and tailored to specific industries like technology and data science. Unlike university degrees, nanodegrees emphasize flexibility, affordability, and immediate job readiness but may lack the extensive accreditation and traditional academic rigor.
Curriculum Structure: Traditional vs. Digital Learning
University degrees offer comprehensive curriculum structures with in-depth theoretical foundations and a broad range of subjects spanning multiple years, emphasizing critical thinking and research skills. Nanodegrees provide highly specialized, modular digital learning experiences focused on practical skills and industry-relevant projects, often completed within months through online platforms. The traditional university approach prioritizes academic rigor and accreditation, while nanodegrees emphasize flexibility, real-time skill acquisition, and alignment with rapidly evolving job market demands.
Duration and Flexibility of Programs
University degrees typically require three to six years of full-time study, offering a structured curriculum with fixed schedules and limited flexibility. Nanodegrees, often completed within three to six months, provide highly flexible, self-paced online programs designed for accelerated learning and immediate application of skills. This makes nanodegrees ideal for working professionals seeking targeted education without committing to the lengthy timelines of traditional university programs.
Cost Comparison: University Degree vs. Nanodegree
University degrees often cost between $20,000 and $100,000 depending on the institution and program length, while nanodegrees typically range from $200 to $2,000, offering a more affordable and flexible learning option. University programs include additional expenses such as housing, textbooks, and campus fees, which nanodegrees usually exclude. The lower financial barrier of nanodegrees makes them accessible for learners seeking specialized skills without incurring significant debt.
Industry Recognition and Accreditation
University degrees offer widely recognized accreditation from established educational institutions, providing comprehensive knowledge and official certification valued by employers across industries. Nanodegrees, developed in partnership with leading tech companies, emphasize practical skills and current industry trends but may lack the broad accreditation and traditional academic rigor of university degrees. Employers in fast-evolving sectors like technology often prioritize nanodegree candidates for specific skill sets, while traditional degrees remain essential for roles requiring formal qualifications and recognized credentials.
Career Opportunities and Job Placement
University degrees provide comprehensive theoretical knowledge and are widely recognized by employers, offering strong career opportunities in traditional industries and roles requiring deep expertise. Nanodegrees, often developed in partnership with tech companies, focus on practical skills and emerging technologies, enabling faster job placement in rapidly evolving fields like data science, software development, and digital marketing. Employers increasingly value nanodegree holders for project-based experience and up-to-date skills, complementing or sometimes substituting formal university education in tech-driven career paths.
Skill Development: Depth vs. Specialization
University degrees provide comprehensive academic knowledge and critical thinking skills across a broad field, fostering deep understanding through extensive coursework and research. Nanodegrees focus on specialized skill development tailored to specific industry demands, offering practical, hands-on experience with targeted technology and tools. Employers often value nanodegrees for their relevance in rapidly evolving tech sectors, while traditional degrees remain crucial for foundational expertise and theoretical frameworks.
Admission Requirements and Accessibility
University degrees generally require high school diplomas, standardized test scores, and sometimes rigorous entrance exams, making admission more selective and time-consuming. Nanodegrees offer flexible enrollment with minimal prerequisites, emphasizing accessibility for working professionals and learners without formal academic backgrounds. This democratization of education through nanodegrees enables faster skill acquisition aligned with industry demands, contrasting with the structured and often competitive university admission processes.
Future Trends in Higher Education Credentials
University degrees and nanodegrees are reshaping higher education credentials, with nanodegrees gaining traction for their focused, skill-specific curricula aligned with rapidly evolving job markets. Future trends indicate a hybrid credential ecosystem where traditional degrees provide foundational knowledge while nanodegrees offer practical, tech-driven expertise tailored to emerging industries. Employers increasingly value nanodegree certifications for their demonstration of up-to-date competencies in fields like artificial intelligence, data science, and cybersecurity.
Related Important Terms
Microcredentials
University degrees provide comprehensive, accredited education often spanning multiple years, while nanodegrees emphasize microcredentials that deliver targeted skills and industry-relevant knowledge in shorter timeframes, enhancing career adaptability and lifelong learning. Microcredentials offer flexible, stackable certifications recognized by employers for specific competencies, making them a complementary alternative to traditional degree programs in the evolving job market.
Stackable Degrees
Stackable degrees combine traditional university degrees with nanodegrees to create flexible, career-focused learning pathways that enhance employability through targeted skill development. Employers increasingly value these hybrid credentials as they demonstrate both comprehensive theoretical knowledge and practical, up-to-date expertise in high-demand fields like data science and software development.
Alternative Credentialing
A University Degree traditionally offers comprehensive academic education with recognized accreditation and potential for broader career paths, while Nanodegrees provide targeted, skill-specific training designed for rapid workforce entry and adaptability in tech-driven industries. Alternative credentialing like Nanodegrees gains traction for flexibility, affordability, and alignment with evolving employer demands, challenging conventional higher education models.
Modular Learning
A university degree offers comprehensive modular learning through structured courses spanning multiple disciplines, ideal for in-depth academic knowledge and long-term career preparation. Nanodegrees focus on targeted, skill-specific modules designed for rapid mastery and immediate application in technology-driven industries, emphasizing flexibility and practical outcomes.
Digital Badging
Digital badging enhances nanodegrees by providing verifiable, skill-specific credentials that employers can instantly recognize, contrasting with traditional university degrees that offer broader academic validation but less granular evidence of competencies. Nanodegrees leverage digital badges to showcase mastery in emerging technologies and practical skills, aligning closely with workforce demands in fields like data science, programming, and digital marketing.
Last-Mile Training
University degrees provide comprehensive theoretical knowledge and broad academic foundations, while nanodegrees focus on last-mile training by offering targeted, practical skills directly aligned with industry demands. This specialized approach accelerates job readiness and bridges the gap between formal education and real-world application in technology and professional fields.
Skills-based Pathways
Skills-based pathways through nanodegrees emphasize practical, industry-relevant competencies often completed in months, contrasting with traditional university degrees that provide comprehensive academic theory over several years. Employers increasingly value the targeted skill sets and project-based learning from nanodegrees for rapid workforce entry and adaptability in evolving job markets.
Competency-Based Assessment
Competency-based assessment in university degrees emphasizes comprehensive subject mastery through theoretical exams and practical projects, while nanodegrees focus on demonstrating specific skills with real-world tasks and micro-credentials. This approach allows nanodegree holders to quickly validate job-ready competencies, complementing traditional degrees' broader academic foundation.
Bootcamp-to-Degree Pipelines
Bootcamp-to-degree pipelines offer a flexible alternative to traditional university degrees by providing intensive, skill-focused nanodegree programs that align with industry demands. These pathways accelerate career readiness through practical training while allowing credits to be transferred toward full university degrees, bridging practical experience with academic credentials.
Just-In-Time Learning
University degrees provide comprehensive foundational knowledge over several years, while nanodegrees offer targeted, Just-In-Time learning focused on specific skills for immediate application in fast-evolving industries like technology and data science. Employers increasingly value nanodegrees for their practical relevance and rapid adaptability, complementing traditional degrees with specialized, up-to-date expertise.
University Degree vs Nanodegree Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com