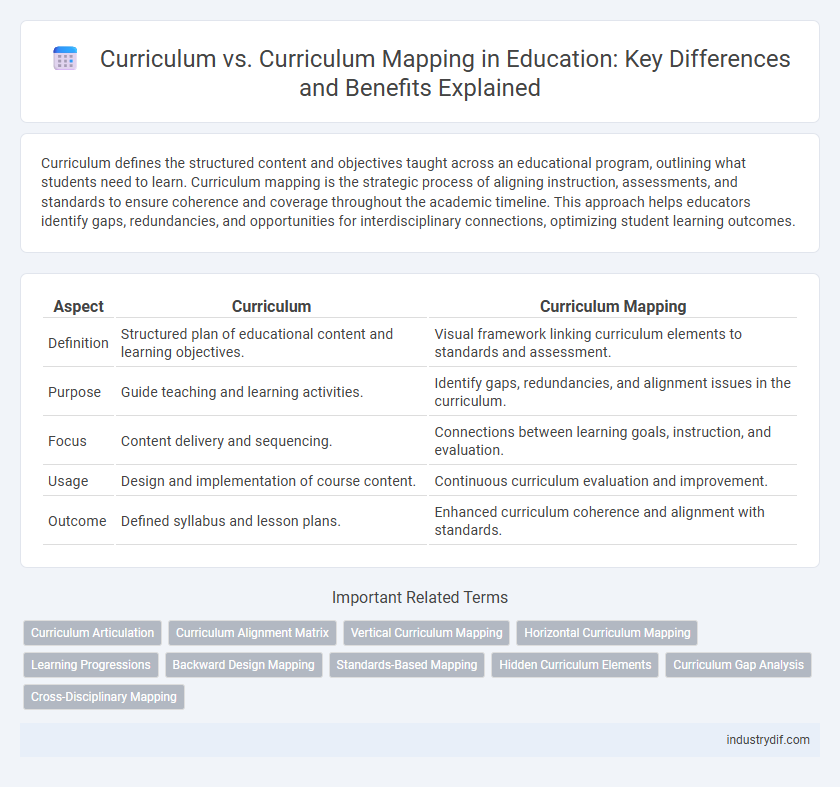
Curriculum defines the structured content and objectives taught across an educational program, outlining what students need to learn. Curriculum mapping is the strategic process of aligning instruction, assessments, and standards to ensure coherence and coverage throughout the academic timeline. This approach helps educators identify gaps, redundancies, and opportunities for interdisciplinary connections, optimizing student learning outcomes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Curriculum | Curriculum Mapping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured plan of educational content and learning objectives. | Visual framework linking curriculum elements to standards and assessment. |
| Purpose | Guide teaching and learning activities. | Identify gaps, redundancies, and alignment issues in the curriculum. |
| Focus | Content delivery and sequencing. | Connections between learning goals, instruction, and evaluation. |
| Usage | Design and implementation of course content. | Continuous curriculum evaluation and improvement. |
| Outcome | Defined syllabus and lesson plans. | Enhanced curriculum coherence and alignment with standards. |
Understanding Curriculum: Definition and Purpose
Curriculum refers to the structured set of educational content, learning objectives, and instructional materials designed to facilitate student learning and achievement within a specific grade or subject area. Curriculum mapping is the process of systematically aligning and visualizing curriculum components across different grades and subjects to ensure coherence, identify gaps, and support instructional planning. Understanding curriculum involves recognizing its role in defining what students need to learn, while curriculum mapping enhances curriculum implementation through strategic organization and assessment alignment.
What is Curriculum Mapping? An Overview
Curriculum mapping is a strategic process that visually aligns learning objectives, instructional materials, and assessments across grade levels and subjects to ensure coherence and continuity in education. This approach enables educators to identify gaps, redundancies, and misalignments within the curriculum, facilitating targeted improvements and fostering a more effective learning environment. By systematically documenting curriculum components, curriculum mapping supports data-driven decision-making and enhances communication among teachers, administrators, and stakeholders.
Key Differences Between Curriculum and Curriculum Mapping
Curriculum defines the overall educational content, learning objectives, and instructional materials for a course or program, outlining what students need to learn. Curriculum mapping is a strategic process that visually aligns and organizes these curriculum components to ensure coherence, coverage, and progression across grade levels or subjects. Key differences include curriculum as the foundational framework and curriculum mapping as the analytical tool used to identify gaps, redundancies, and alignment with standards.
The Role of Curriculum in Educational Planning
Curriculum serves as the foundational framework outlining the educational goals, content, and learning experiences necessary for student development, ensuring alignment with academic standards and institutional objectives. Curriculum mapping acts as a strategic tool that visually represents the delivery of curriculum components across grade levels and subjects, identifying gaps and redundancies to optimize instructional coherence. In educational planning, curriculum defines what is taught, while curriculum mapping provides critical data to refine teaching strategies and improve overall student outcomes.
Advantages of Implementing Curriculum Mapping
Curriculum mapping enhances instructional alignment by clearly outlining learning objectives and assessment methods, promoting consistency across grade levels. It facilitates data-driven decision making through continuous feedback and identification of gaps or redundancies in content coverage. Educators benefit from collaborative planning and resource sharing, resulting in improved student outcomes and streamlined curriculum updates.
Curriculum Development vs. Curriculum Mapping Process
Curriculum development involves designing, organizing, and structuring educational content, objectives, and assessments to align with learning standards and goals. Curriculum mapping process systematically visualizes and analyzes how curriculum components interconnect across grade levels or subjects, ensuring consistency and identifying gaps or redundancies. Effective curriculum mapping supports continuous improvement by providing educators with a clear overview of instructional alignment and student progression.
How Curriculum Mapping Enhances Instructional Alignment
Curriculum mapping improves instructional alignment by providing a detailed, visual representation of learning objectives, content, and assessments across grade levels and subjects, ensuring consistency and coherence. It enables educators to identify gaps, redundancies, and misalignments in the curriculum, which allows for targeted adjustments to better meet educational standards. This process fosters collaboration among teachers, promoting a unified approach that enhances student learning outcomes and achievement.
Challenges in Curriculum and Curriculum Mapping Practices
Curriculum challenges often arise from misalignment between learning objectives, teaching methods, and assessment practices, leading to gaps in student knowledge and inconsistent educational outcomes. Curriculum mapping faces difficulties such as lack of faculty collaboration, insufficient training, and the complexity of accurately reflecting course content, which can hinder its effectiveness as a tool for curriculum improvement. Effective integration of curriculum mapping requires ongoing professional development and institutional support to overcome resistance and ensure alignment with academic standards and student needs.
Tools and Technologies for Effective Curriculum Mapping
Curriculum mapping leverages digital tools such as learning management systems (LMS), specialized curriculum mapping software like Atlas and Rubicon, and data analytics platforms to align educational standards with lesson plans and assessments efficiently. These technologies enable educators to visualize curriculum gaps, ensure consistency across grade levels, and track student progress through real-time data integration. Implementing cloud-based collaboration tools enhances coordination among teachers, administrators, and stakeholders, resulting in a dynamic and adaptable curriculum framework.
Best Practices for Integrating Curriculum and Curriculum Mapping
Effective integration of curriculum and curriculum mapping involves aligning learning objectives with instructional activities and assessment methods to ensure coherence and consistency in education delivery. Utilizing digital tools for curriculum mapping enhances the visualization of curricular progress, enabling educators to identify gaps and redundancies efficiently. Engaging collaborative teams of teachers and curriculum specialists in ongoing review processes supports continuous improvement and ensures alignment with standards and student learning outcomes.
Related Important Terms
Curriculum Articulation
Curriculum articulation ensures seamless progression and coherence in learning objectives across grade levels, aligning curriculum content, skills, and assessments systematically. Curriculum mapping serves as a vital tool to visualize and organize this alignment, highlighting gaps and redundancies to optimize instructional planning and student outcomes.
Curriculum Alignment Matrix
A Curriculum Alignment Matrix visually links educational standards, learning objectives, and assessments to ensure cohesive instruction and measurable outcomes. Curriculum Mapping serves as an ongoing process to document and refine this alignment, enhancing curriculum coherence and instructional effectiveness.
Vertical Curriculum Mapping
Vertical curriculum mapping organizes learning objectives and content across grade levels to ensure coherence and progression, promoting skill development without gaps or redundancies. This method aligns standards, assessments, and instructional strategies vertically to create a seamless educational experience from early grades through advanced levels.
Horizontal Curriculum Mapping
Horizontal curriculum mapping aligns learning objectives, content, and assessments across the same grade level to ensure consistency and coherence in instruction. This process enhances collaboration among teachers by identifying gaps, overlaps, and opportunities for interdisciplinary integration within a single academic year.
Learning Progressions
Curriculum defines the structured content and objectives for student learning, while curriculum mapping visually organizes these elements to reveal learning progressions across grade levels, ensuring coherent skill development. Learning progressions in curriculum mapping help educators identify gaps and align instruction to foster continuous mastery of concepts from foundational to advanced stages.
Backward Design Mapping
Curriculum refers to the structured content and learning objectives designed for a course, while curriculum mapping involves the strategic alignment of these objectives across grade levels or courses to ensure coherence and rigor. Backward design mapping specifically starts with identifying desired learning outcomes and then planning instructional methods and assessments, creating a targeted and effective educational framework.
Standards-Based Mapping
Curriculum mapping aligns learning objectives, assessments, and instructional activities with educational standards to ensure coherent and targeted student learning outcomes. Standards-based curriculum mapping systematically tracks how each standard is addressed across grade levels, promoting consistency and mastery throughout the educational program.
Hidden Curriculum Elements
Curriculum encompasses the planned educational content and experiences, while curriculum mapping visually aligns and organizes these components across grade levels and subjects. Hidden curriculum elements, including implicit social norms, values, and attitudes, often remain unarticulated within official documents but profoundly influence student behavior and school culture.
Curriculum Gap Analysis
Curriculum gap analysis identifies missing or misaligned content in curriculum mapping, ensuring that learning objectives, standards, and assessments are cohesively integrated across grade levels and subjects. Effective curriculum mapping visualizes the instructional sequence, supporting curriculum gap analysis by highlighting inconsistencies and areas for enhancement in student learning progression.
Cross-Disciplinary Mapping
Curriculum mapping systematically aligns learning objectives, assessments, and instructional strategies across subjects to identify gaps and overlaps, fostering cohesive educational experiences. Cross-disciplinary mapping enhances this process by integrating themes and skills across multiple disciplines, promoting critical thinking and real-world application among students.
Curriculum vs Curriculum Mapping Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com