Fossil fuel generators operate by burning coal, oil, or natural gas, emitting significant greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change. Green hydrogen electrolyzers use renewable electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, producing clean fuel with zero carbon emissions. Transitioning from fossil fuel generators to green hydrogen electrolyzers enhances energy sustainability and supports global decarbonization efforts.
Table of Comparison
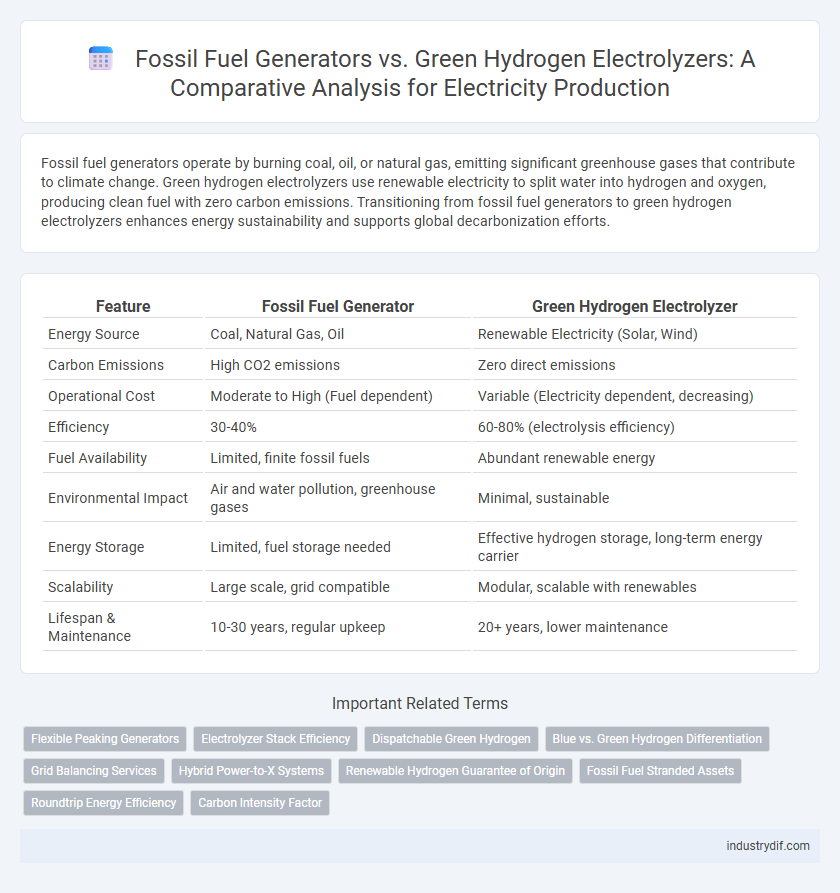
| Feature | Fossil Fuel Generator | Green Hydrogen Electrolyzer |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Coal, Natural Gas, Oil | Renewable Electricity (Solar, Wind) |
| Carbon Emissions | High CO2 emissions | Zero direct emissions |
| Operational Cost | Moderate to High (Fuel dependent) | Variable (Electricity dependent, decreasing) |
| Efficiency | 30-40% | 60-80% (electrolysis efficiency) |
| Fuel Availability | Limited, finite fossil fuels | Abundant renewable energy |
| Environmental Impact | Air and water pollution, greenhouse gases | Minimal, sustainable |
| Energy Storage | Limited, fuel storage needed | Effective hydrogen storage, long-term energy carrier |
| Scalability | Large scale, grid compatible | Modular, scalable with renewables |
| Lifespan & Maintenance | 10-30 years, regular upkeep | 20+ years, lower maintenance |
Introduction to Fossil Fuel Generators and Green Hydrogen Electrolyzers
Fossil fuel generators convert chemical energy from coal, natural gas, or oil into electricity by combustion, releasing significant carbon emissions. Green hydrogen electrolyzers use renewable energy sources such as wind or solar power to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, producing clean hydrogen fuel without CO2 emissions. The shift from fossil fuel generators to green hydrogen electrolyzers supports decarbonization and enhances sustainable energy systems.
How Fossil Fuel Generators Work
Fossil fuel generators produce electricity by burning coal, natural gas, or oil to heat water in a boiler, creating steam that drives a turbine connected to an electrical generator. The combustion process releases carbon dioxide and other pollutants, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental pollution. These generators are typically used for base-load power but face challenges due to fuel costs, regulatory pressures, and the shift toward renewable energy sources like green hydrogen electrolyzers.
Green Hydrogen Electrolyzer Technology Explained
Green hydrogen electrolyzer technology converts water into hydrogen and oxygen using renewable electricity, enabling carbon-neutral energy storage and fuel production. Unlike fossil fuel generators that emit greenhouse gases and rely on finite resources, electrolyzers produce clean hydrogen that can power industries, transport, and power grids sustainably. Advancements in proton exchange membrane (PEM) and alkaline electrolyzers improve efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, positioning green hydrogen as a critical solution for decarbonizing the energy sector.
Comparative Energy Efficiency
Fossil fuel generators typically convert fuel to electricity with efficiencies ranging from 33% to 40%, whereas green hydrogen electrolyzers achieve overall system efficiencies between 60% and 70% when paired with renewable energy sources. Electrolyzers convert electricity into hydrogen through water splitting, enabling storage and use in fuel cells with round-trip efficiencies around 40-45%. The higher operational efficiency and zero carbon emissions of green hydrogen systems make them a more sustainable alternative despite current infrastructure and scalability challenges.
Carbon Emissions and Environmental Impact
Fossil fuel generators emit approximately 0.7 to 2.0 kilograms of CO2 per kilowatt-hour, significantly contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. Green hydrogen electrolyzers produce almost zero direct carbon emissions, using renewable electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, thus offering a sustainable alternative. Transitioning to electrolyzers can reduce environmental impact by enabling decarbonization of power generation and lowering dependency on fossil fuels.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Operational Expenses
Fossil fuel generators typically incur lower upfront costs but face higher operational expenses due to fuel volatility and maintenance requirements. Green hydrogen electrolyzers demand significant initial capital investment driven by advanced technology and infrastructure needs, yet benefit from lower ongoing costs powered by renewable energy sources. Comprehensive cost analysis reveals shifting economics favoring green hydrogen as global carbon pricing and renewable adoption increase.
Grid Integration and Flexibility
Fossil fuel generators offer stable and controllable power output, facilitating straightforward grid integration and reliable baseload supply. Green hydrogen electrolyzers provide dynamic response capabilities, enabling grid flexibility by converting excess renewable energy into hydrogen for storage and later use. Integrating electrolyzers enhances grid stability by balancing intermittent renewables, supporting demand response, and enabling decarbonization of power systems.
Reliability and Energy Storage Capabilities
Fossil fuel generators offer consistent and high reliability with rapid start-up times, making them suitable for stable electricity supply but involve significant greenhouse gas emissions. Green hydrogen electrolyzers provide flexible energy storage capabilities by converting excess renewable electricity into hydrogen, enabling long-duration storage and grid balancing with zero direct emissions. Despite slower response times, hydrogen systems enhance renewable energy integration and improve overall energy system resilience through scalable storage solutions.
Future Trends and Technological Innovations
Fossil fuel generators face declining competitiveness as green hydrogen electrolyzers emerge with zero-emission power generation and scalable energy storage capabilities. Advances in proton exchange membrane (PEM) and solid oxide electrolyzer cells (SOEC) improve efficiency and reduce costs, accelerating green hydrogen adoption in power grids. Future trends highlight integration with renewable energy sources, supporting grid stability and decarbonization goals worldwide.
Regulatory and Policy Considerations
Regulatory frameworks for fossil fuel generators often include emissions caps and carbon pricing that increase operational costs, pushing industries toward cleaner alternatives like green hydrogen electrolyzers. Green hydrogen production benefits from evolving policies promoting renewable energy integration, investment subsidies, and mandates for decarbonization in power generation. Compliance with safety standards and grid interconnection requirements are rapidly adapting to accommodate electrolyzer technologies while addressing long-term sustainability goals.
Related Important Terms
Flexible Peaking Generators
Flexible peaking generators powered by fossil fuels provide rapid-response electricity during high-demand periods but generate significant carbon emissions, whereas green hydrogen electrolyzers enable clean, decarbonized power by producing hydrogen through renewable energy-driven electrolysis. Integrating green hydrogen as a peaking solution offers scalable, emission-free flexibility, reducing reliance on fossil fuel generators and supporting grid stability with sustainable energy storage.
Electrolyzer Stack Efficiency
Electrolyzer stack efficiency, which measures the ratio of chemical energy stored in hydrogen to the electrical energy input, typically ranges between 60% and 80%, outperforming fossil fuel generators that convert only about 33% to 45% of fuel energy into electricity. Higher stack efficiency in green hydrogen electrolyzers not only reduces operational costs but also lowers carbon emissions, making them a more sustainable and economically viable solution compared to conventional fossil fuel generators.
Dispatchable Green Hydrogen
Dispatchable green hydrogen electrolyzers provide a flexible and low-carbon alternative to fossil fuel generators by converting excess renewable electricity into hydrogen, enabling energy storage and on-demand electricity generation without greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike fossil fuel generators that rely on finite resources and emit significant CO2, green hydrogen systems enhance grid stability and decarbonize power supply through scalable, sustainable energy conversion.
Blue vs. Green Hydrogen Differentiation
Fossil fuel generators primarily rely on combustion of hydrocarbons, releasing significant CO2 emissions, whereas green hydrogen electrolyzers produce hydrogen through water electrolysis powered by renewable energy, resulting in zero direct emissions. Blue hydrogen, generated from natural gas with carbon capture and storage (CCS), offers lower emissions than traditional fossil fuels but remains carbon-intensive compared to the entirely clean process of green hydrogen production.
Grid Balancing Services
Fossil fuel generators provide reliable grid balancing services through fast ramp-up capabilities and consistent power output, but contribute to carbon emissions and environmental degradation. Green hydrogen electrolyzers offer flexible load management by adjusting hydrogen production in response to grid demand fluctuations, enabling renewable energy integration while supporting decarbonization goals.
Hybrid Power-to-X Systems
Hybrid power-to-X systems integrating fossil fuel generators with green hydrogen electrolyzers optimize grid stability and decarbonization by balancing intermittent renewable energy inputs with reliable backup power. This synergy enhances energy storage capabilities and reduces carbon emissions, supporting the transition to sustainable electricity infrastructure.
Renewable Hydrogen Guarantee of Origin
Renewable Hydrogen Guarantees of Origin (GHOs) certify green hydrogen produced via electrolysis powered by renewable energy, ensuring lower carbon emissions compared to fossil fuel generators that rely on combustion of coal, oil, or natural gas. These guarantees facilitate transparency and market trust, promoting the integration of green hydrogen electrolyzers into the power sector as a sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuel-based electricity generation.
Fossil Fuel Stranded Assets
Fossil fuel generators face increasing risks of becoming stranded assets due to global decarbonization policies and the rise of green hydrogen electrolyzers, which offer a cleaner alternative by producing zero-emission hydrogen through renewable energy-powered electrolysis. Investments in green hydrogen technology reduce dependency on carbon-intensive fossil fuels, mitigating financial losses tied to stranded fossil fuel infrastructure amid energy transition trends.
Roundtrip Energy Efficiency
Fossil fuel generators typically achieve roundtrip energy efficiencies around 30-40%, converting chemical energy in fuels directly into electricity with significant losses due to combustion and mechanical processes. Green hydrogen electrolyzers, combined with fuel cells for electricity regeneration, currently exhibit roundtrip efficiencies between 20-25%, limited by electrolysis and fuel cell conversion losses despite offering zero-carbon energy storage options.
Carbon Intensity Factor
Fossil fuel generators have a high carbon intensity factor, typically emitting around 0.9 to 2.2 kg of CO2 per kWh produced, depending on the fuel type and efficiency. Green hydrogen electrolyzers powered by renewable electricity achieve near-zero carbon intensity, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions in power generation.
Fossil Fuel Generator vs Green Hydrogen Electrolyzer Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com