Renewable energy sources such as solar and wind provide clean, sustainable power generation that reduces reliance on fossil fuels and lowers carbon emissions. Peer-to-peer energy trading enables consumers to directly buy and sell excess electricity generated from renewable installations, promoting local energy autonomy and efficient distribution. This decentralized approach not only maximizes the use of renewable energy but also empowers prosumers to participate actively in the energy market, driving innovation and resilience in the electricity grid.
Table of Comparison
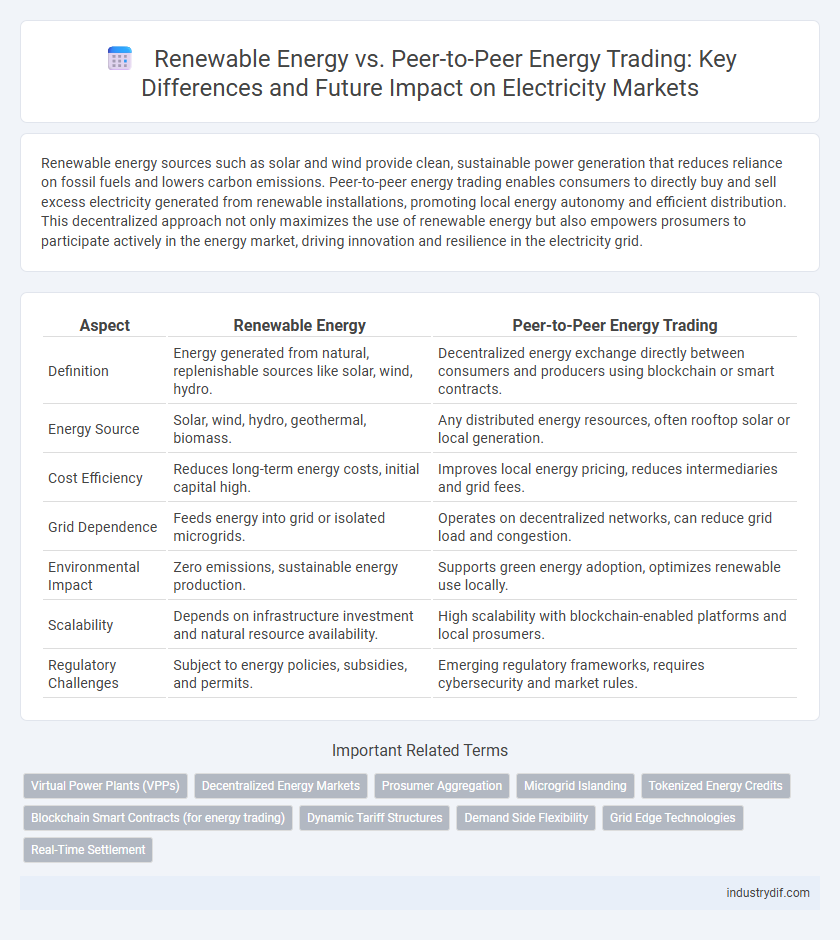
| Aspect | Renewable Energy | Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Energy generated from natural, replenishable sources like solar, wind, hydro. | Decentralized energy exchange directly between consumers and producers using blockchain or smart contracts. |
| Energy Source | Solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, biomass. | Any distributed energy resources, often rooftop solar or local generation. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces long-term energy costs, initial capital high. | Improves local energy pricing, reduces intermediaries and grid fees. |
| Grid Dependence | Feeds energy into grid or isolated microgrids. | Operates on decentralized networks, can reduce grid load and congestion. |
| Environmental Impact | Zero emissions, sustainable energy production. | Supports green energy adoption, optimizes renewable use locally. |
| Scalability | Depends on infrastructure investment and natural resource availability. | High scalability with blockchain-enabled platforms and local prosumers. |
| Regulatory Challenges | Subject to energy policies, subsidies, and permits. | Emerging regulatory frameworks, requires cybersecurity and market rules. |
Introduction to Renewable Energy in the Electricity Sector
Renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, and hydropower, play a critical role in transforming the electricity sector by reducing dependence on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Advances in technology and declining costs have accelerated the adoption of renewable energy systems, enabling more sustainable and decentralized electricity generation. This transition supports grid stability and fosters innovation in peer-to-peer energy trading platforms, which facilitate efficient energy distribution among prosumers.
Defining Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Energy Trading
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Energy Trading enables consumers to directly buy and sell surplus renewable energy, such as solar or wind power, without intermediaries, using blockchain or smart grid technologies. This decentralized approach enhances grid flexibility, promotes local energy generation, and increases renewable energy adoption by empowering prosumers to monetize excess electricity. P2P energy trading supports efficient energy distribution, reduces transmission losses, and helps balance supply and demand within localized networks.
Key Differences: Centralized Renewables vs. Decentralized P2P Models
Renewable energy systems primarily operate through centralized infrastructures like large-scale solar farms or wind parks, feeding power into the grid managed by utilities. Peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading leverages decentralized networks where individual consumers and prosumers directly exchange electricity using blockchain or smart contracts. This fundamental difference shifts control from centralized authorities to users, promoting local energy resilience and potentially lowering transaction costs.
Advantages of Renewable Energy Generation
Renewable energy generation offers significant environmental benefits by reducing carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels, promoting sustainable power supply. It leverages natural resources like solar, wind, and hydro, providing consistent and scalable electricity production with minimal operational costs. Furthermore, renewable energy enhances energy security by diversifying the power grid and decreasing vulnerability to market fluctuations in conventional energy prices.
Benefits of Peer-to-Peer Energy Exchange
Peer-to-peer energy trading enhances renewable energy utilization by enabling decentralized energy transactions directly between producers and consumers, reducing reliance on traditional utilities and cutting grid congestion. This system promotes higher energy efficiency and cost savings through localized energy exchange, incentivizing more households to invest in solar panels and other renewable sources. Blockchain technology ensures transparent, secure, and efficient transactions, fostering trust and accelerating the adoption of sustainable energy solutions.
Grid Integration Challenges for Renewables and P2P Trading
Renewable energy sources such as solar and wind face grid integration challenges due to their intermittent and variable nature, causing issues with voltage regulation, frequency control, and grid stability. Peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading introduces complexities in grid management by decentralizing energy transactions, requiring advanced grid coordination and real-time data analytics to maintain reliability. Both renewable integration and P2P trading demand robust grid infrastructure upgrades and smart grid technologies to optimize energy flow and ensure system resilience.
Regulatory Frameworks Impacting Both Models
Renewable energy adoption and peer-to-peer energy trading both face regulatory frameworks that shape market accessibility and grid integration. Policies such as feed-in tariffs, net metering, and energy trading licenses directly influence the scalability of decentralized solar and wind projects alongside P2P platforms. Regulatory clarity on grid balancing, consumer protection, and data privacy is crucial for fostering innovation and ensuring fair competition in both renewable energy generation and peer-to-peer energy exchanges.
Technological Enablers: Smart Grids and Blockchain
Smart grids revolutionize renewable energy integration by enabling real-time monitoring, demand response, and efficient energy distribution, enhancing grid stability and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Blockchain technology facilitates peer-to-peer energy trading by ensuring transparent, secure, and decentralized transactions between prosumers, promoting local energy exchange and grid resilience. Together, smart grids and blockchain drive a more flexible, efficient, and democratized electricity market by seamlessly connecting renewable energy sources with active consumer participation.
Environmental and Economic Implications
Renewable energy reduces carbon emissions by harnessing natural resources such as solar, wind, and hydropower, fostering environmental sustainability. Peer-to-peer energy trading enhances economic efficiency by enabling consumers to buy and sell excess renewable energy directly, lowering energy costs and increasing grid resilience. Together, these innovations drive a decentralized energy market that supports both ecological benefits and economic empowerment.
Future Trends: Merging Renewable Energy with Peer-to-Peer Trading
The future of electricity markets hinges on integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind with peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading platforms, enabling decentralized energy distribution. Blockchain technology and smart contracts are driving secure, transparent transactions among prosumers, enhancing grid resilience and energy efficiency. This merger supports sustainability goals by maximizing renewable energy utilization and reducing reliance on centralized power plants.
Related Important Terms
Virtual Power Plants (VPPs)
Virtual Power Plants (VPPs) aggregate distributed renewable energy resources such as solar panels and wind turbines to optimize energy production and delivery in peer-to-peer energy trading networks. By enabling real-time energy exchange and demand response, VPPs enhance grid stability, increase renewable penetration, and empower prosumers to monetize surplus electricity efficiently.
Decentralized Energy Markets
Renewable energy integration accelerates decentralized energy markets by enabling localized generation and consumption, reducing reliance on centralized grids. Peer-to-peer energy trading platforms leverage blockchain technology to facilitate transparent, efficient transactions among prosumers, enhancing grid resilience and energy democratization.
Prosumer Aggregation
Renewable energy integration benefits significantly from prosumer aggregation, which enhances grid stability and optimizes energy distribution by pooling resources from multiple producers and consumers. Peer-to-peer energy trading platforms facilitate this aggregation by enabling decentralized energy exchanges, increasing market efficiency and consumer empowerment while reducing reliance on centralized utilities.
Microgrid Islanding
Renewable energy integration enhances microgrid islanding by providing decentralized, sustainable power sources such as solar and wind, ensuring energy resilience during grid outages. Peer-to-peer energy trading within microgrids enables efficient energy distribution among prosumers, optimizing local energy use and supporting grid stability without reliance on the central grid.
Tokenized Energy Credits
Tokenized energy credits enable seamless peer-to-peer energy trading by digitally representing renewable energy generation, enhancing transparency and liquidity in decentralized electricity markets. These blockchain-based credits facilitate real-time transactions, incentivizing renewable energy production while reducing reliance on traditional utilities and grid constraints.
Blockchain Smart Contracts (for energy trading)
Blockchain smart contracts enable transparent, automated peer-to-peer energy trading by securely validating and executing transactions without intermediaries. This decentralized approach enhances the integration of renewable energy sources by facilitating real-time energy exchange and optimizing local energy distribution.
Dynamic Tariff Structures
Dynamic tariff structures in renewable energy systems enable real-time price adjustments based on supply and demand, enhancing grid efficiency and consumer savings. Peer-to-peer energy trading leverages these flexible tariffs to facilitate decentralized transactions, allowing prosumers to optimize revenue and promote sustainable energy distribution.
Demand Side Flexibility
Renewable energy integration enhances demand side flexibility by enabling consumers to adjust usage in response to variable supply, while peer-to-peer energy trading further optimizes this flexibility by allowing decentralized energy exchange directly between prosumers. This synergy reduces grid imbalances and promotes efficient energy distribution by leveraging real-time demand responsiveness and localized renewable generation.
Grid Edge Technologies
Renewable energy integration and peer-to-peer energy trading both leverage grid edge technologies such as smart inverters, advanced metering infrastructure, and blockchain-based platforms to enhance localized energy management and grid resilience. These innovations enable decentralized energy generation and real-time transactional capabilities, optimizing distribution, reducing transmission losses, and increasing the overall efficiency of electricity grids.
Real-Time Settlement
Renewable energy integration enhances peer-to-peer energy trading by enabling real-time settlement through blockchain technology, ensuring transparent and immediate transaction validation. This approach optimizes grid efficiency, reduces congestion, and incentivizes decentralized energy production with accurate, time-stamped energy exchange data.
Renewable Energy vs Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com