Smart meters provide real-time data on overall electricity consumption, enabling accurate billing and energy management. Energy disaggregation breaks down total energy use into specific appliances, offering detailed insights to optimize power usage and reduce waste. Combining both technologies enhances energy efficiency by delivering comprehensive consumption analysis.
Table of Comparison
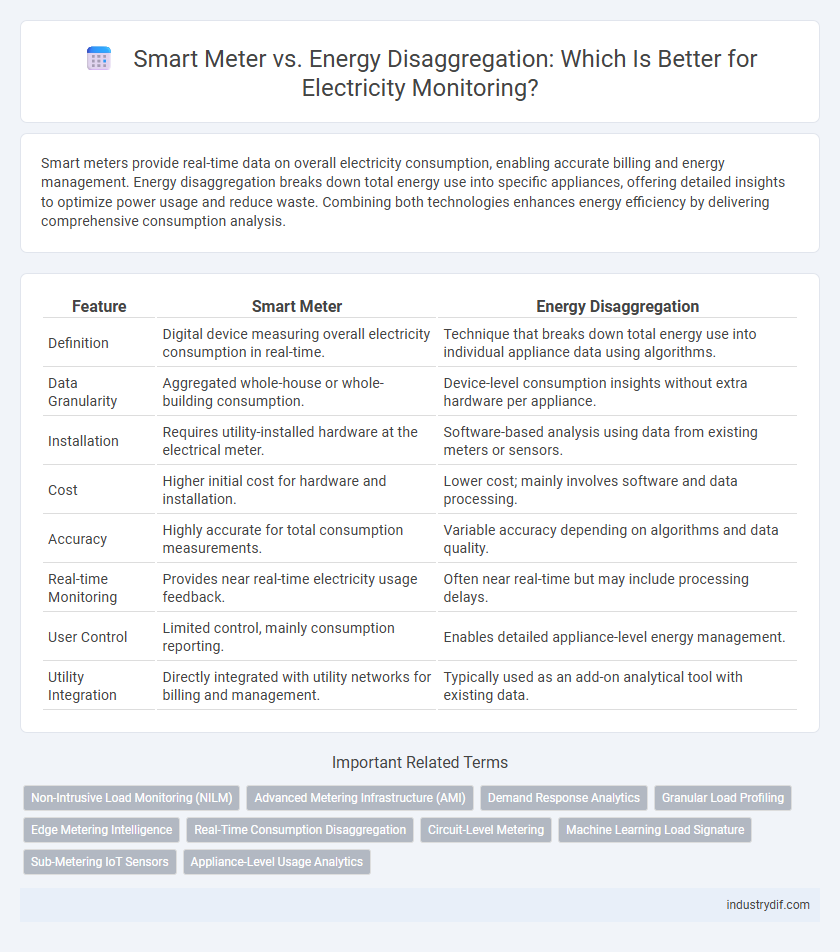
| Feature | Smart Meter | Energy Disaggregation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital device measuring overall electricity consumption in real-time. | Technique that breaks down total energy use into individual appliance data using algorithms. |
| Data Granularity | Aggregated whole-house or whole-building consumption. | Device-level consumption insights without extra hardware per appliance. |
| Installation | Requires utility-installed hardware at the electrical meter. | Software-based analysis using data from existing meters or sensors. |
| Cost | Higher initial cost for hardware and installation. | Lower cost; mainly involves software and data processing. |
| Accuracy | Highly accurate for total consumption measurements. | Variable accuracy depending on algorithms and data quality. |
| Real-time Monitoring | Provides near real-time electricity usage feedback. | Often near real-time but may include processing delays. |
| User Control | Limited control, mainly consumption reporting. | Enables detailed appliance-level energy management. |
| Utility Integration | Directly integrated with utility networks for billing and management. | Typically used as an add-on analytical tool with existing data. |
Introduction to Smart Meter Technology
Smart meter technology revolutionizes electricity management by providing real-time data on energy consumption through advanced digital communication systems. These devices enable precise monitoring, automated billing, and seamless integration with energy grids, enhancing efficiency and user control. Unlike energy disaggregation, which estimates individual appliance usage from aggregate data, smart meters capture detailed consumption at the source, improving accuracy and utility responsiveness.
Understanding Energy Disaggregation
Energy disaggregation utilizes advanced algorithms and machine learning to break down aggregate electricity consumption data from a single smart meter into individual appliance-level usage patterns. Unlike traditional smart meters that only provide total energy consumption, energy disaggregation offers detailed insights for optimizing energy efficiency and reducing costs. This technology supports targeted demand response strategies and enhances consumer awareness by identifying specific energy-intensive devices in real-time.
Core Differences Between Smart Meters and Energy Disaggregation
Smart meters provide real-time, aggregated electricity consumption data directly from the utility meter, enabling accurate billing and usage monitoring at the whole-house level. Energy disaggregation, or non-intrusive load monitoring (NILM), analyzes total electricity usage data to estimate individual appliance consumption without separate meters. The core difference lies in smart meters measuring total consumption with dedicated hardware, while energy disaggregation uses software algorithms to infer detailed appliance-level usage from aggregate data.
Data Collection and Analysis Methods
Smart meters collect real-time, granular electricity consumption data directly from households using automated sensors, enabling precise monitoring and billing. Energy disaggregation applies advanced algorithms and machine learning to analyze aggregated consumption data, separating total energy use into individual appliance-level insights without requiring additional hardware. While smart meters emphasize comprehensive data collection, energy disaggregation focuses on extracting detailed usage patterns through sophisticated data analysis methods.
Accuracy in Energy Consumption Monitoring
Smart meters provide direct and highly accurate real-time measurements of electricity usage at the household or device level through advanced metering infrastructure. Energy disaggregation techniques estimate individual appliance consumption by analyzing overall smart meter data using algorithms, often resulting in lower accuracy due to overlapping usage patterns and noise. For precise energy consumption monitoring, smart meters outperform energy disaggregation in delivering granular and reliable data critical for billing, demand response, and energy efficiency programs.
Benefits of Smart Meters for Utilities and Consumers
Smart meters enable utilities to gather real-time consumption data, improving grid management and demand forecasting while reducing operational costs. Consumers benefit from enhanced billing accuracy, detailed usage insights, and the ability to optimize energy consumption for cost savings. Unlike energy disaggregation, smart meters provide direct, continuous data collection, facilitating more responsive and efficient energy distribution.
Advantages of Energy Disaggregation in Detailed Monitoring
Energy disaggregation offers granular insights by breaking down total electricity consumption into individual appliance usage, enabling precise identification of energy-hungry devices. This detailed monitoring facilitates targeted energy-saving strategies and enhances demand response programs by providing real-time data on specific load patterns. Unlike smart meters that provide aggregate consumption data, energy disaggregation empowers consumers and utilities with actionable intelligence to optimize energy efficiency and reduce costs.
Integration with Home Automation Systems
Smart meters provide real-time energy consumption data through a single aggregated signal, enabling seamless integration with home automation systems for automated control and optimization. Energy disaggregation, or non-intrusive load monitoring, breaks down overall energy use into individual appliance-level data, offering deeper insights but requiring more complex software integration with smart home platforms. Combining smart meter data with energy disaggregation technology enhances predictive energy management and tailored automation based on specific device usage patterns.
Privacy and Security Considerations
Smart meters collect granular energy consumption data, raising privacy concerns due to the potential exposure of user habits and behaviors. Energy disaggregation techniques analyze aggregate consumption to infer appliance-level usage without requiring individual device sensors, offering enhanced privacy preservation by minimizing data granularity. Implementing robust encryption and anonymization protocols in both smart meter data transmission and energy disaggregation algorithms is essential to mitigate security vulnerabilities and protect consumer information.
Future Trends in Electricity Monitoring Technologies
Smart meter technology is evolving with improved data accuracy and real-time energy usage insights, driving smarter grid management and personalized consumer feedback. Energy disaggregation techniques are advancing through AI and machine learning, enabling detailed appliance-level consumption analysis without additional hardware. Future trends emphasize integrating these technologies with IoT platforms to enhance predictive maintenance, demand response, and energy efficiency at both residential and industrial scales.
Related Important Terms
Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring (NILM)
Smart meters provide detailed electricity consumption data by recording overall usage at short intervals, while Energy Disaggregation using Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring (NILM) analyzes aggregated energy data from a single point to identify individual appliance usage patterns. NILM leverages advanced algorithms and machine learning to decompose total household energy consumption into specific loads without installing multiple sensors, offering cost-effective and granular insights for energy management.
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) enables Smart Meters to provide real-time, interval-based energy consumption data, while energy disaggregation uses algorithms to break down this aggregate data into appliance-specific usage patterns. Integrating AMI with energy disaggregation enhances demand response strategies and empowers consumers with detailed insights for efficient energy management.
Demand Response Analytics
Smart meters provide granular real-time electricity usage data enabling demand response analytics to optimize grid load and reduce costs, while energy disaggregation decomposes aggregate consumption into appliance-level insights to enhance personalized demand response strategies. Combining smart meter data with advanced energy disaggregation techniques improves accuracy in analyzing consumption patterns for efficient demand response and grid stability.
Granular Load Profiling
Smart meters provide detailed electricity consumption data at regular intervals, enabling granular load profiling by capturing overall household or building energy use patterns. Energy disaggregation further enhances this data by breaking down total consumption into individual appliance usage, allowing for precise identification of energy-saving opportunities and improved demand response strategies.
Edge Metering Intelligence
Edge metering intelligence integrates smart meter data with advanced energy disaggregation techniques, enabling real-time analysis of individual appliance consumption directly at the meter. This localized processing reduces data transmission demands and enhances accuracy in identifying energy usage patterns for improved demand response and energy efficiency.
Real-Time Consumption Disaggregation
Smart meters provide real-time electricity consumption data by measuring total household usage, while energy disaggregation analyzes this aggregate data to identify individual appliance consumption patterns. Real-time consumption disaggregation enhances energy management by enabling precise monitoring and optimization of appliance-level electricity use without installing separate meters.
Circuit-Level Metering
Circuit-level metering enables detailed energy disaggregation by monitoring electricity consumption of individual circuits, offering more precise data compared to whole-home smart meters. This granular approach facilitates targeted energy efficiency measures and fault detection by isolating specific appliance or system usage within a building.
Machine Learning Load Signature
Smart meters provide precise, real-time electricity consumption data, enabling machine learning algorithms to analyze load signatures for accurate energy disaggregation at the appliance level. Machine learning techniques leverage these detailed consumption patterns to identify and classify individual device usage, enhancing energy efficiency and demand response strategies.
Sub-Metering IoT Sensors
Smart meters provide real-time, aggregated electricity consumption data at the household or building level, while energy disaggregation leverages sub-metering IoT sensors to break down this data into specific appliance-level usage patterns. Sub-metering IoT sensors enable precise monitoring and control of individual devices, enhancing energy efficiency, fault detection, and customized consumption insights beyond the capabilities of traditional smart meters.
Appliance-Level Usage Analytics
Smart meters provide real-time electricity consumption data at the whole-house level, while energy disaggregation techniques analyze aggregate data to identify appliance-level usage patterns. Appliance-level usage analytics enable consumers and utilities to optimize energy efficiency by pinpointing specific devices' consumption and behavior within the smart meter data.
Smart Meter vs Energy Disaggregation Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com