A wattmeter measures the instantaneous power consumption of an electrical circuit, providing real-time data for specific devices or loads. A smart meter, however, records overall energy usage over time and communicates this information remotely to utility providers for monitoring and billing. Smart meters enable enhanced energy management and dynamic pricing, whereas wattmeters are primarily used for detailed diagnostic or experimental purposes.
Table of Comparison
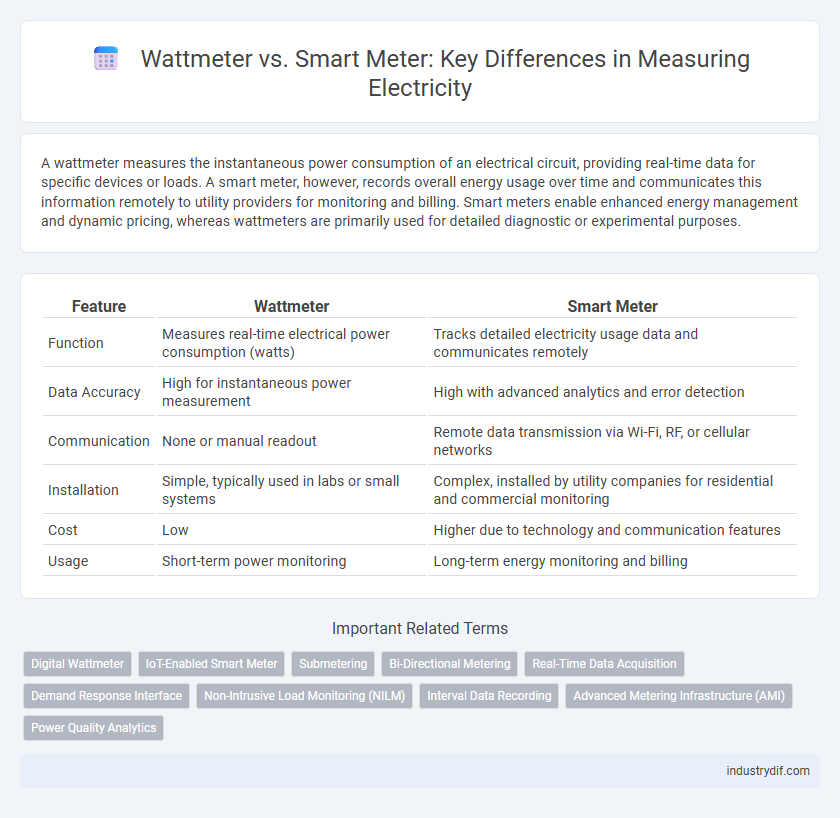
| Feature | Wattmeter | Smart Meter |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Measures real-time electrical power consumption (watts) | Tracks detailed electricity usage data and communicates remotely |
| Data Accuracy | High for instantaneous power measurement | High with advanced analytics and error detection |
| Communication | None or manual readout | Remote data transmission via Wi-Fi, RF, or cellular networks |
| Installation | Simple, typically used in labs or small systems | Complex, installed by utility companies for residential and commercial monitoring |
| Cost | Low | Higher due to technology and communication features |
| Usage | Short-term power monitoring | Long-term energy monitoring and billing |
Understanding Wattmeter: Definition and Functions
A wattmeter is an electrical instrument designed to measure the real power consumption in watts within an electrical circuit, providing precise energy usage data for various devices. It works by assessing both voltage and current while calculating the phase angle to determine actual power, distinguishing it from devices that measure only voltage or current individually. Commonly used in laboratories and industrial settings, wattmeters help optimize energy efficiency and electrical load management by delivering accurate power readings.
What is a Smart Meter? Key Features Explained
A smart meter is an advanced electronic device that records electricity consumption in real-time and communicates data directly to utility providers, enabling accurate billing and energy management. Key features include two-way communication, remote monitoring, and integration with home energy management systems for enhanced efficiency. Unlike traditional wattmeters, smart meters provide detailed usage data, fault detection, and support for demand response programs.
Core Differences Between Wattmeter and Smart Meter
A wattmeter measures real-time power consumption in watts, providing direct readings of electrical power used by a device or circuit. A smart meter records detailed energy usage over time, transmitting consumption data remotely for monitoring and billing purposes. Unlike wattmeters, smart meters integrate communication technologies and offer advanced analytics for energy management and grid optimization.
Measurement Accuracy: Wattmeter vs Smart Meter
Wattmeters provide precise real-time measurement of electrical power by directly measuring voltage and current with minimal latency, ensuring high accuracy in instantaneous readings. Smart meters offer comprehensive energy monitoring with built-in digital sensors that measure cumulative energy consumption and can detect power quality issues, but their real-time measurement accuracy may vary due to data aggregation and transmission intervals. The selection between wattmeter and smart meter depends on the requirement for exact instantaneous power measurement versus long-term consumption monitoring and data integration capabilities.
Installation and Maintenance: Comparative Analysis
Wattmeters require straightforward installation, often involving direct wiring to measure electrical power in a circuit, while smart meters demand more complex setup due to their advanced communication modules and integration with utility networks. Maintenance of wattmeters is minimal, typically limited to calibration checks, whereas smart meters necessitate regular firmware updates and diagnostic monitoring to ensure accurate data transmission and system compatibility. The higher installation and maintenance demands of smart meters are balanced by their ability to provide real-time consumption data and remote monitoring capabilities.
Data Collection and Communication Capabilities
Wattmeters measure electrical power consumption in real-time but have limited data storage and no communication capabilities, restricting their function to display-only devices. Smart meters collect detailed consumption data at frequent intervals, storing and transmitting this information via wireless or wired networks to utilities for remote monitoring and billing. Enhanced communication protocols in smart meters enable integration with smart grid systems, supporting dynamic energy management and user feedback.
Real-time Monitoring: Advantages of Smart Meters
Smart meters provide real-time monitoring of electricity consumption by transmitting data instantly to utilities and consumers, enabling accurate energy management and timely detection of anomalies. Unlike traditional wattmeters, smart meters facilitate dynamic pricing models and allow users to adjust usage patterns based on real-time electricity rates. This continuous data flow enhances grid reliability and supports demand-response programs, optimizing energy efficiency on a larger scale.
Cost Considerations: Initial Investment and ROI
Wattmeters generally incur a lower initial investment, making them cost-effective for basic energy measurement tasks. Smart meters require a higher upfront cost but offer enhanced data accuracy, remote monitoring capabilities, and detailed consumption analytics, improving long-term ROI through optimized energy management. Over time, the smart meter's ability to facilitate demand response programs and billing accuracy contributes to significant cost savings that surpass the initial expense.
Application Scenarios in Power Systems
Wattmeters are primarily used in power systems for precise measurement of real power in single-phase and balanced three-phase circuits, crucial for load monitoring and energy audits. Smart meters enable real-time monitoring, bidirectional communication, and remote management, making them ideal for advanced metering infrastructure, demand response programs, and integration with smart grids. While wattmeters provide foundational power consumption data, smart meters facilitate enhanced energy management, grid stability, and predictive maintenance in modern power distribution systems.
Future Trends: The Evolution from Wattmeter to Smart Meter
The transition from traditional wattmeters to advanced smart meters marks a significant evolution in electricity measurement technology, enabling real-time data monitoring and enhanced energy efficiency. Smart meters utilize digital communication to provide detailed insights into consumption patterns, facilitating demand response and integration with renewable energy sources. Future trends indicate widespread adoption of smart meters driven by smart grid developments and increasing emphasis on sustainable energy management.
Related Important Terms
Digital Wattmeter
A digital wattmeter precisely measures real-time power consumption by accurately capturing voltage and current waveforms, offering enhanced resolution compared to traditional analog wattmeters. Smart meters extend this functionality with integrated communication capabilities, enabling remote monitoring and detailed energy usage analytics for optimized electricity management.
IoT-Enabled Smart Meter
IoT-enabled smart meters provide real-time energy consumption data, remote monitoring, and enhanced grid management features, outperforming traditional wattmeters that only measure instantaneous power usage. These advanced smart meters leverage wireless connectivity and data analytics to optimize energy efficiency and support dynamic pricing models in modern electrical grids.
Submetering
Wattmeters measure electrical power consumption at a single point, providing real-time data essential for basic energy monitoring. Smart meters enable advanced submetering by collecting detailed usage data from multiple circuits or devices, facilitating precise energy allocation and efficient load management.
Bi-Directional Metering
Wattmeters measure real-time power consumption in a single direction, primarily tracking electricity usage, whereas smart meters enable bi-directional metering by recording both energy consumption and energy fed back into the grid from renewable sources like solar panels. This bi-directional capability facilitates accurate net metering, enhancing energy management and enabling dynamic billing based on actual energy flow.
Real-Time Data Acquisition
Wattmeters provide instantaneous power measurements by monitoring current and voltage, but smart meters enable real-time data acquisition with advanced communication capabilities, allowing continuous monitoring and remote transmission of energy consumption. Smart meters integrate IoT technology for detailed usage analytics, empowering consumers and utilities to optimize energy efficiency and grid management.
Demand Response Interface
A Wattmeter measures real-time electrical power consumption, providing basic demand data without communication capabilities, while a Smart Meter integrates a Demand Response Interface enabling two-way communication for dynamic load management and real-time energy usage optimization. Smart Meters facilitate automated demand response programs by sending consumption data and receiving utility signals to adjust power usage, enhancing grid efficiency and reducing peak demand.
Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring (NILM)
Wattmeters measure total electrical power consumption by directly connecting to a circuit, providing real-time usage in watts, but lack detailed appliance-level data. Smart meters equipped with Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring (NILM) algorithms analyze voltage and current waveforms to disaggregate consumption patterns, enabling precise identification of individual device energy usage without additional sensors.
Interval Data Recording
Wattmeters measure instantaneous power consumption without detailed interval data, while smart meters continuously record interval data, enabling precise monitoring of electricity usage over specific time periods. The interval data recording feature of smart meters supports advanced energy management, demand response, and accurate billing.
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
Wattmeters measure real-time electrical power consumption by recording watts, whereas smart meters, integral to Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI), provide two-way communication that enables remote monitoring, dynamic pricing, and grid management. AMI-linked smart meters enhance energy efficiency by offering granular consumption data and facilitating demand response programs.
Power Quality Analytics
Wattmeters provide basic measurement of active power consumption, whereas smart meters offer advanced power quality analytics such as voltage fluctuations, harmonic distortion, and real-time energy usage patterns. Smart meters enable detailed monitoring and diagnostics, improving energy efficiency and grid reliability beyond the simple wattage readings of traditional wattmeters.
Wattmeter vs Smart Meter Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com