Feature films deliver a complete and immersive storytelling experience in a single viewing, ideal for deep narrative and character development. Micro series break stories into short, episodic segments, perfect for capturing audience attention with concise, engaging content suitable for on-the-go entertainment. Choosing between feature film and micro series depends on audience preferences for either extended immersion or quick, episodic engagement.
Table of Comparison
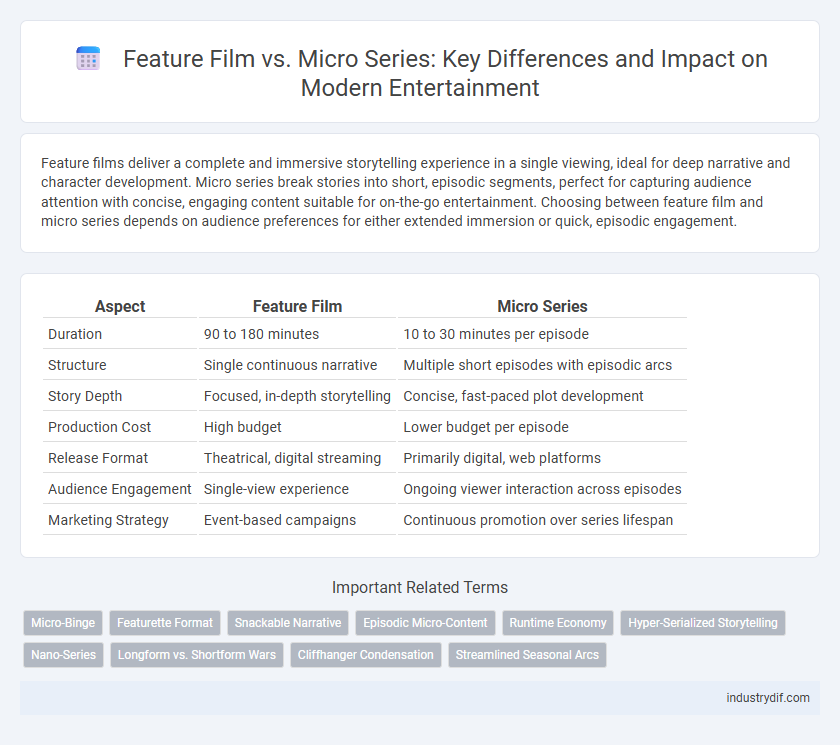
| Aspect | Feature Film | Micro Series |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | 90 to 180 minutes | 10 to 30 minutes per episode |
| Structure | Single continuous narrative | Multiple short episodes with episodic arcs |
| Story Depth | Focused, in-depth storytelling | Concise, fast-paced plot development |
| Production Cost | High budget | Lower budget per episode |
| Release Format | Theatrical, digital streaming | Primarily digital, web platforms |
| Audience Engagement | Single-view experience | Ongoing viewer interaction across episodes |
| Marketing Strategy | Event-based campaigns | Continuous promotion over series lifespan |
Defining Feature Film and Micro Series
Feature films typically have a runtime exceeding 60 minutes, designed for theatrical release and characterized by a self-contained narrative arc. Micro series are short-format episodic productions, often ranging from 5 to 20 minutes per episode, optimized for digital streaming platforms and mobile viewing. The distinction lies in length, distribution channels, and storytelling approach, where feature films offer a comprehensive cinematic experience, and micro series deliver concise, episodic content tailored for quick consumption.
Historical Evolution of Both Formats
Feature films have evolved from early silent shorts to complex narratives spanning over two hours, shaping cinematic storytelling with advancements in technology and audience expectations. Micro series emerged as a response to digital streaming demands, offering concise, episodic content that adapts to shorter attention spans and mobile viewing habits. Both formats reflect shifts in distribution platforms and consumer behavior, with feature films maintaining cultural prestige while micro series capitalize on accessibility and binge-watching trends.
Production Budgets and Resource Allocation
Feature films demand higher production budgets averaging $70 million due to extensive locations, special effects, and star talent, while micro series typically range from $500,000 to $3 million per episode, prioritizing concise storytelling and efficient resource allocation. Resource allocation in feature films heavily invests in pre-production and post-production phases, whereas micro series distribute resources evenly across shorter episodes to maintain consistent quality and audience engagement. Understanding these differences allows producers to strategically allocate budget and resources for optimal creative impact and financial viability.
Storytelling Structure and Narrative Pacing
Feature films typically follow a three-act structure delivering a complete narrative arc within 90 to 180 minutes, emphasizing concise character development and resolution. Micro series break stories into multiple short episodes, allowing for more flexible pacing, deeper character exploration, and episodic cliffhangers that sustain viewer engagement over time. The storytelling structure of micro series leverages serialized narratives, while feature films rely on a tightly woven plot designed for immersive, uninterrupted viewing.
Audience Engagement and Viewing Habits
Feature films typically deliver a complete narrative in one sitting, attracting viewers who prefer immersive, longer-form storytelling, resulting in intense but time-limited audience engagement. Micro series, with shorter episodes and flexible viewing options, cater to modern audiences seeking quick, episodic content ideal for multitasking or on-the-go consumption, fostering sustained engagement over time. Viewing habits increasingly favor micro series on digital platforms due to their adaptability, while feature films maintain appeal for theatrical and event-driven experiences.
Distribution Channels and Platform Preferences
Feature films often dominate theatrical releases and premium streaming platforms like Netflix and Amazon Prime Video, targeting audiences seeking a full narrative experience. Micro series gain traction on social media networks and short-form video platforms such as YouTube, TikTok, and Quibi, appealing to viewers favoring quick, episodic content. Distribution strategies prioritize feature films for established cinemas and subscription-based services, while micro series leverage mobile accessibility and viral sharing to reach niche, younger demographics.
Creative Freedom and Industry Constraints
Feature films often offer greater creative freedom due to longer runtimes and larger budgets, allowing filmmakers to develop complex narratives and detailed character arcs. Micro series face stricter industry constraints, including tighter production schedules and limited episode lengths that demand concise storytelling and more focused character development. Both formats require balancing creative ambitions with market demands, but feature films generally provide a broader canvas for artistic expression.
Marketing Strategies and Audience Reach
Feature films leverage wide theatrical releases and global streaming platforms to maximize audience reach through high-impact marketing campaigns, including star power and cinematic experiences. Micro series utilize targeted digital marketing strategies, such as social media engagement and niche platform distribution, to tap into specific demographics and build loyal online communities. The concise format of micro series allows for rapid content consumption and viral potential, contrasting with the prolonged, event-driven promotion typical of feature films.
Revenue Models and Monetization Potential
Feature films primarily generate revenue through box office sales, digital rentals, streaming rights, and international distribution, often commanding higher upfront investments and returns. Micro series leverage episodic content for steady monetization via subscription platforms, ad-supported streaming, and brand partnerships, maximizing viewer retention over time. Both models benefit from merchandising and licensing opportunities, but micro series offer greater flexibility for targeted advertising and audience engagement strategies.
Future Trends in Film and Series Production
Advancements in streaming technology and audience consumption patterns are driving a shift toward micro series, offering concise storytelling with high engagement suitable for mobile viewing. Feature films continue to evolve with immersive formats like virtual reality and interactive narratives, enhancing viewer experience and expanding creative possibilities. Hybrid models combining feature film quality and episodic micro series format are emerging as a dominant trend in future entertainment production.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Binge
Micro series offer compact storytelling with episodes typically under 10 minutes, enabling micro-binge viewing habits that fit seamlessly into busy lifestyles. Feature films, usually spanning 90 to 120 minutes, require longer continuous attention, whereas micro-bingeing allows audiences to consume multiple short episodes rapidly, enhancing engagement and retention in the entertainment experience.
Featurette Format
Featurettes, a hybrid format between feature films and micro series, typically run between 20 to 40 minutes, providing a concise yet immersive storytelling experience that fits modern digital consumption preferences. This format leverages cinematic production values and deep narrative arcs, making it ideal for streaming platforms targeting viewers seeking substantial content without committing to full-length feature films or episodic series.
Snackable Narrative
Feature films deliver immersive storytelling with complex plots and character development over 90+ minutes, whereas micro series offer snackable narratives divided into brief episodes, ideal for capturing audiences' attention in short viewing windows. Micro series leverage concise arcs and cliffhangers to maintain engagement on digital platforms, catering to evolving consumption habits favoring quick, impactful content.
Episodic Micro-Content
Episodic micro-content in micro series offers concise storytelling with bite-sized episodes, maximizing viewer engagement and adaptability across digital platforms compared to the extended narrative structure of feature films. This format leverages shorter runtimes and serialized plots to cater to modern audiences seeking quick, immersive entertainment experiences.
Runtime Economy
Feature films typically run between 90 to 180 minutes, offering a single, cohesive narrative arc that demands concentrated viewer attention, while micro series consist of multiple short episodes totaling 30 to 60 minutes, allowing for flexible consumption and episodic storytelling. The runtime economy of micro series maximizes engagement through bite-sized content, catering to audiences seeking quick, digestible entertainment compared to the extended immersive experience of feature films.
Hyper-Serialized Storytelling
Feature films deliver a complete narrative arc within a limited timeframe, providing a condensed yet impactful storytelling experience. Hyper-serialized micro series, by contrast, utilize fragmented episodic structures that develop complex characters and multi-layered plots over numerous short episodes, enhancing viewer engagement through continuous cliffhangers and thematic depth.
Nano-Series
Nano-series offer a concise storytelling format typically consisting of episodes under 10 minutes, providing an immersive alternative to traditional feature films and longer micro-series formats. This compact structure enables rapid content consumption and high engagement, appealing to audiences with limited time and a preference for bite-sized narrative arcs.
Longform vs. Shortform Wars
Feature films deliver immersive storytelling through extended runtime, allowing rich character development and complex plots, while micro series capitalize on shortform episodes to engage audiences with concise, episodic content suited for digital consumption. The ongoing longform vs. shortform wars highlight shifting viewer preferences, with streaming platforms balancing cinematic depth against binge-worthy brevity to capture diverse entertainment demands.
Cliffhanger Condensation
Feature films deliver a complete narrative arc within a limited timeframe, often building to a singular, impactful climax rather than multiple cliffhangers. Micro series employ cliffhanger condensation by breaking stories into brief, episodic segments designed to maintain viewer suspense and engagement consistently across installments.
Streamlined Seasonal Arcs
Feature films deliver a concise, impactful narrative with a singular, streamlined arc that resolves within a two-hour format, providing immediate emotional satisfaction. Micro series, by contrast, employ multiple compact episodes to develop streamlined seasonal arcs that maintain viewer engagement through focused plot progression and character development across a limited runtime.
Feature Film vs Micro Series Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com