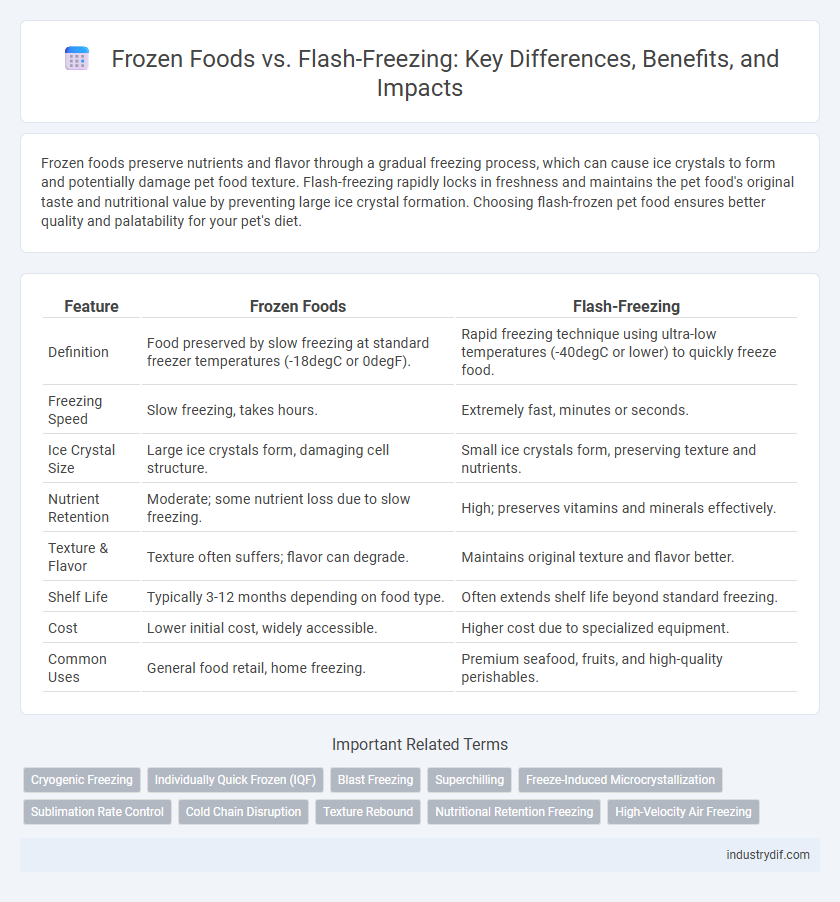
Frozen foods preserve nutrients and flavor through a gradual freezing process, which can cause ice crystals to form and potentially damage pet food texture. Flash-freezing rapidly locks in freshness and maintains the pet food's original taste and nutritional value by preventing large ice crystal formation. Choosing flash-frozen pet food ensures better quality and palatability for your pet's diet.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Frozen Foods | Flash-Freezing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Food preserved by slow freezing at standard freezer temperatures (-18degC or 0degF). | Rapid freezing technique using ultra-low temperatures (-40degC or lower) to quickly freeze food. |
| Freezing Speed | Slow freezing, takes hours. | Extremely fast, minutes or seconds. |
| Ice Crystal Size | Large ice crystals form, damaging cell structure. | Small ice crystals form, preserving texture and nutrients. |
| Nutrient Retention | Moderate; some nutrient loss due to slow freezing. | High; preserves vitamins and minerals effectively. |
| Texture & Flavor | Texture often suffers; flavor can degrade. | Maintains original texture and flavor better. |
| Shelf Life | Typically 3-12 months depending on food type. | Often extends shelf life beyond standard freezing. |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, widely accessible. | Higher cost due to specialized equipment. |
| Common Uses | General food retail, home freezing. | Premium seafood, fruits, and high-quality perishables. |
Understanding Frozen Foods: Industry Overview
Frozen foods represent a significant segment of the global food industry, accounting for over $250 billion in annual sales and driven by consumer demand for convenience and extended shelf life. Flash-freezing technology, developed in the 1930s, rapidly lowers the temperature of food items to preserve taste, texture, and nutritional value, minimizing ice crystal formation compared to conventional freezing. This innovation has revolutionized the supply chain by enabling year-round availability of seasonal produce and high-quality seafood, thereby boosting the frozen food market's growth and consumer acceptance.
What is Flash-Freezing? Key Concepts Explained
Flash-freezing is a rapid freezing process that preserves the texture, flavor, and nutritional value of food by quickly lowering its temperature to below -40degF (-40degC). Unlike traditional freezing, which forms large ice crystals that damage cell structures, flash-freezing creates tiny ice crystals, minimizing cellular damage and maintaining optimal quality. This technique is widely used in frozen food industries to ensure freshness and extend shelf life without compromising taste or nutrients.
Traditional Freezing vs Flash-Freezing: Core Differences
Traditional freezing slowly lowers food temperature, allowing larger ice crystals to form, which can damage cell structure and affect texture upon thawing. Flash-freezing rapidly freezes food at extremely low temperatures, preserving freshness, nutrient content, and texture by minimizing ice crystal size and preventing cellular damage. Consumers seeking superior taste and quality often prefer flash-frozen products over traditionally frozen alternatives due to enhanced preservation methods.
Impact on Nutritional Value: Frozen Foods vs Flash-Freezing
Flash-freezing preserves the nutritional value of foods more effectively than traditional freezing methods by rapidly lowering the temperature, which minimizes ice crystal formation and cellular damage. Frozen foods subjected to slow freezing often experience nutrient loss, particularly in vitamins C and B complex, due to prolonged exposure to ice crystals and enzymatic degradation. Scientific studies reveal that flash-frozen fruits and vegetables retain up to 90% of their original nutrient content, making them a superior choice for maintaining dietary quality.
Flavor and Texture Retention: Comparing Methods
Flash-freezing preserves food's cellular structure by rapidly lowering temperatures, resulting in superior flavor and texture retention compared to conventional frozen foods. Traditional freezing methods often cause ice crystals to form slowly, damaging cell walls and leading to mushy textures and diminished taste. Flash-frozen products like seafood and fruits maintain freshness closer to their original state, enhancing overall quality for consumers seeking premium frozen options.
Shelf Life and Storage Efficiency
Frozen foods maintain quality and nutritional value over extended shelf life through slow freezing methods, often resulting in larger ice crystals that may affect texture. Flash-freezing rapidly lowers food temperature, creating smaller ice crystals that better preserve cellular structure, enhancing flavor retention and texture while extending shelf life. Storage efficiency improves with flash-frozen products due to reduced spoilage and minimized freezer burn, allowing longer safe storage periods compared to traditionally frozen foods.
Food Safety Standards: Industry Best Practices
Frozen foods undergo traditional freezing processes that may allow ice crystal formation, potentially compromising texture and microbial safety. Flash-freezing involves rapid freezing at ultra-low temperatures, minimizing ice crystal size and preserving food quality and safety by inhibiting bacterial growth more effectively. Industry best practices mandate strict temperature controls, hygiene protocols, and regular safety audits to ensure compliance with food safety standards in both methods.
Common Applications in the Food Industry
Frozen foods often include ready-made meals, vegetables, fruits, and seafood, widely used for their convenience and extended shelf life in retail and food service sectors. Flash-freezing preserves texture and nutritional value efficiently, making it ideal for premium seafood, berries, and high-quality vegetables in upscale restaurants and gourmet food production. Both methods support supply chain efficiency but flash-freezing is preferred for maintaining freshness in delicate and perishable products.
Consumer Perceptions and Market Trends
Frozen foods dominate retail shelves due to convenience and extended shelf life, appealing to busy consumers seeking ready-to-eat options. Flash-freezing technology preserves nutritional value and texture better than traditional freezing, gradually shifting consumer perception toward higher-quality frozen products. Market trends indicate growing demand for flash-frozen items as health-conscious buyers prioritize freshness and product integrity.
Future Innovations in Frozen Foods Technology
Future innovations in frozen foods technology increasingly leverage flash-freezing methods to preserve nutritional quality and texture by rapidly lowering temperatures, minimizing ice crystal formation. Advanced cryogenic techniques and smart packaging sensors are emerging to enhance freshness monitoring and reduce food waste. Integration of AI-driven quality control systems promises more precise freezing protocols, improving the overall efficiency and sustainability of frozen food supply chains.
Related Important Terms
Cryogenic Freezing
Cryogenic freezing, a subset of flash-freezing, utilizes extremely low temperatures often below -150degC using liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide to rapidly freeze food, preserving texture and nutritional value better than conventional frozen foods. This method significantly reduces ice crystal size, preventing cellular damage and maintaining higher quality in meats, seafood, and fruits compared to standard freezing techniques.
Individually Quick Frozen (IQF)
Individually Quick Frozen (IQF) technology preserves the freshness and texture of frozen foods by rapidly freezing each piece separately, preventing clumping and maintaining quality during storage. Unlike traditional frozen foods that freeze in bulk, IQF ensures better portion control, reduced waste, and optimal retention of nutrients and flavor.
Blast Freezing
Blast freezing rapidly lowers the temperature of frozen foods, preserving texture, flavor, and nutritional value better than conventional frozen methods. This rapid freezing technique minimizes ice crystal formation, reducing cell damage and enhancing the quality and shelf life of frozen products.
Superchilling
Superchilling preserves frozen foods by lowering temperatures just below their initial freezing point, maintaining cellular structure and nutrient retention better than traditional flash-freezing methods. This technique extends shelf life while reducing ice crystal formation, enhancing texture and flavor quality in frozen food products.
Freeze-Induced Microcrystallization
Freeze-induced microcrystallization in frozen foods creates small ice crystals that preserve cellular structure and nutritional quality better than traditional freezing methods. Flash-freezing rapidly lowers the temperature, minimizing large ice crystal formation and enhancing texture, flavor, and shelf life of frozen produce.
Sublimation Rate Control
Flash-freezing minimizes sublimation rate by rapidly lowering food temperature, preserving texture and nutritional quality better than traditional frozen foods, which often experience higher sublimation leading to freezer burn. Controlled sublimation in flash-freezing maintains moisture retention and extends shelf life, ensuring optimal flavor and appearance in frozen food products.
Cold Chain Disruption
Frozen foods often suffer from quality degradation during cold chain disruption, leading to texture and flavor loss, whereas flash-freezing preserves cellular structure and nutritional value by rapidly lowering temperature. Maintaining an unbroken cold chain is critical for both methods, but flash-freezing's rapid temperature drop minimizes ice crystal formation, ensuring superior preservation even if minor disruptions occur.
Texture Rebound
Frozen foods often suffer from texture degradation due to slow ice crystal formation, whereas flash-freezing preserves cellular structure by rapidly freezing at extremely low temperatures, resulting in superior texture rebound upon thawing. This rapid freezing process minimizes ice crystal size, maintaining the food's original firmness and juiciness more effectively than conventional freezing methods.
Nutritional Retention Freezing
Flash-freezing preserves the nutritional content of food more effectively than traditional freezing methods by rapidly lowering the temperature and preventing large ice crystals from forming, which can damage cell structure and degrade vitamins. Studies show that flash-frozen fruits and vegetables retain higher levels of antioxidants, vitamins C and B, and minerals compared to conventionally frozen counterparts, ensuring superior nutritional retention.
High-Velocity Air Freezing
High-velocity air freezing, a critical technique in flash-freezing, rapidly lowers the temperature of frozen foods to preserve nutritional content, texture, and flavor better than conventional freezing methods. This process minimizes ice crystal formation within food cells by circulating extremely cold air at speeds exceeding 5 meters per second, ensuring superior quality and extended shelf life for frozen fruits, vegetables, seafood, and meats.
Frozen Foods vs Flash-Freezing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com