Free-range pet food offers natural ingredients sourced from animals raised in open environments, promoting animal welfare and nutrient-rich profiles. Cellular agriculture produces pet food by cultivating animal cells in labs, ensuring sustainable and cruelty-free alternatives with consistent quality. Both methods aim to enhance pet health while addressing ethical and environmental concerns.
Table of Comparison
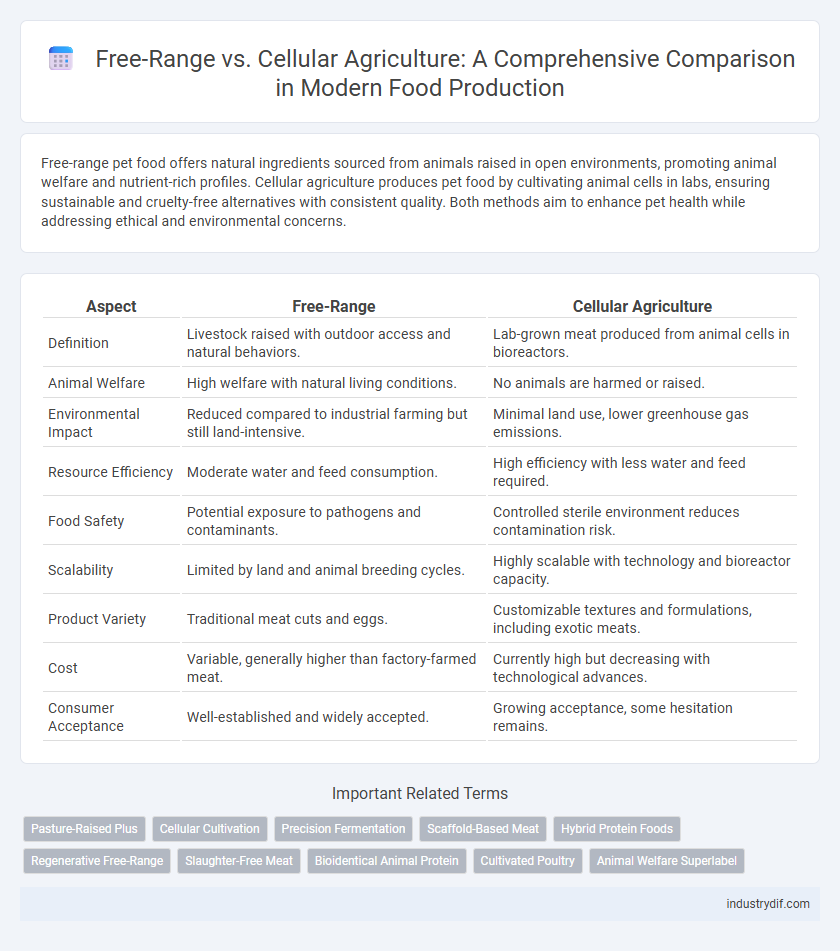
| Aspect | Free-Range | Cellular Agriculture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Livestock raised with outdoor access and natural behaviors. | Lab-grown meat produced from animal cells in bioreactors. |
| Animal Welfare | High welfare with natural living conditions. | No animals are harmed or raised. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced compared to industrial farming but still land-intensive. | Minimal land use, lower greenhouse gas emissions. |
| Resource Efficiency | Moderate water and feed consumption. | High efficiency with less water and feed required. |
| Food Safety | Potential exposure to pathogens and contaminants. | Controlled sterile environment reduces contamination risk. |
| Scalability | Limited by land and animal breeding cycles. | Highly scalable with technology and bioreactor capacity. |
| Product Variety | Traditional meat cuts and eggs. | Customizable textures and formulations, including exotic meats. |
| Cost | Variable, generally higher than factory-farmed meat. | Currently high but decreasing with technological advances. |
| Consumer Acceptance | Well-established and widely accepted. | Growing acceptance, some hesitation remains. |
Understanding Free-Range Food Production
Free-range food production emphasizes ethical animal welfare by allowing livestock to roam outdoors and access natural feed, promoting sustainability and higher nutritional quality. This method contrasts with cellular agriculture, which produces animal products through lab-grown cells without raising live animals. Understanding free-range practices highlights the environmental benefits of pasture-based farming, such as improved soil health and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
What Is Cellular Agriculture?
Cellular agriculture is an innovative food production method that cultivates animal cells in controlled environments to produce meat, dairy, and eggs without raising live animals. This technology uses tissue engineering and fermentation processes to create sustainable, animal-free products that reduce environmental impact and animal welfare concerns. Unlike free-range farming, cellular agriculture offers scalable solutions for high-quality protein with lower greenhouse gas emissions and land use.
Key Differences Between Free-Range and Cellular Agriculture
Free-range agriculture involves raising animals in open environments with natural access to outdoor spaces, ensuring animal welfare and traditional farming practices. Cellular agriculture produces meat and animal products through tissue engineering and cell culture without the need for live animals, offering a sustainable and ethical alternative. Key differences include environmental impact, with cellular agriculture reducing land and water use, and scalability, where free-range methods depend on land availability.
Animal Welfare: Free-Range vs Cellular Meat
Free-range animal farming provides animals with access to outdoor environments, allowing natural behaviors that enhance their welfare, while cellular agriculture produces meat from animal cells without raising or slaughtering animals, effectively eliminating animal suffering. Studies show free-range systems improve physical and psychological health compared to confined conditions, but still involve ethical concerns related to handling and lifespan. Cellular meat offers a scalable, cruelty-free alternative that could revolutionize animal welfare by removing the need for live animal husbandry altogether.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Free-range farming typically results in higher land use and greenhouse gas emissions due to methane produced by livestock, contributing significantly to environmental degradation. Cellular agriculture, involving lab-grown meat production, offers a reduced carbon footprint and minimizes land and water usage by eliminating the need for traditional grazing and feed crops. Studies indicate cellular agriculture could lower overall environmental impact, making it a more sustainable alternative for future food systems.
Food Safety and Quality Standards
Free-range food products generally adhere to stringent animal welfare and organic standards, ensuring minimal use of antibiotics and synthetic additives, which enhances food safety and natural quality. Cellular agriculture offers precise control over production environments, significantly reducing contamination risks and enabling consistent quality through lab-grown meat and dairy with standardized nutrient profiles. Comparing both, free-range emphasizes traditional safety and flavor authenticity, while cellular agriculture prioritizes innovative pathogen control and uniform product quality.
Consumer Perception and Acceptance
Consumer perception of free-range products often centers on animal welfare and naturalness, driving higher acceptance among environmentally conscious buyers. Cellular agriculture, while promising sustainability and ethical advantages, faces skepticism due to unfamiliarity and concerns over artificiality. Market adoption depends on transparency, education, and aligning product narratives with evolving consumer values on health and sustainability.
Cost and Scalability in Food Production
Free-range food production often incurs higher costs due to land, labor, and slower growth cycles, limiting scalability compared to cellular agriculture, which uses bioreactors to produce meat efficiently at scale. Cellular agriculture leverages technology to reduce resource consumption and accelerate production timelines, enabling greater output with lower environmental impact. Despite initial investment barriers, cellular agriculture presents a scalable and cost-effective alternative to traditional free-range methods for meeting rising global food demand.
Challenges Facing Each Method
Free-range farming faces challenges such as land use constraints, disease management, and environmental impacts including greenhouse gas emissions and soil degradation. Cellular agriculture grapples with high production costs, scalability issues, and consumer acceptance hurdles related to taste, texture, and ethical concerns. Both methods require innovation and investment to balance sustainability, animal welfare, and food security effectively.
Future Trends in Sustainable Protein Sources
Free-range animal farming offers ethical benefits by allowing animals natural living conditions, yet faces challenges in scalability and environmental impact. Cellular agriculture, producing lab-grown meat and dairy, promises efficient resource use, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and scalable protein production. Future trends in sustainable protein sources lean towards hybrid models integrating free-range practices with cellular agriculture innovations to meet global food demands sustainably.
Related Important Terms
Pasture-Raised Plus
Pasture-Raised Plus offers enhanced animal welfare by allowing livestock to graze freely on nutrient-rich pastures, contrasting with cellular agriculture's lab-grown protein that aims to reduce environmental impact and animal use. This sustainable farming method supports biodiversity, soil health, and provides consumers with ethically sourced, high-quality meat options.
Cellular Cultivation
Cellular cultivation in cellular agriculture offers a sustainable alternative to traditional free-range farming by producing meat directly from animal cells without raising and slaughtering animals. This innovative method reduces environmental impact, lowers greenhouse gas emissions, and enhances food security by enabling scalable, controlled production of high-quality protein.
Precision Fermentation
Precision fermentation in cellular agriculture enables the production of animal proteins without raising animals, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional free-range farming by reducing land use, greenhouse gas emissions, and ethical concerns. This technology allows for scalable, controlled synthesis of dairy, meat, and egg proteins, presenting a promising solution to meet global food demand while minimizing environmental impact.
Scaffold-Based Meat
Scaffold-based meat in cellular agriculture uses biocompatible structures to support the growth of cultured animal cells, enabling precise texture and nutrient control that mimics natural muscle tissue. This method contrasts with free-range meat production, which relies on traditional animal farming practices, impacting environmental sustainability and ethical considerations.
Hybrid Protein Foods
Hybrid protein foods combine free-range animal products with cellular agriculture techniques to enhance sustainability and animal welfare. These innovative foods reduce environmental impact while maintaining the taste and texture of traditional free-range meat.
Regenerative Free-Range
Regenerative free-range farming enhances soil health and biodiversity by allowing animals to graze naturally, promoting carbon sequestration and reducing reliance on synthetic inputs. Unlike cellular agriculture, which produces lab-grown meat through cellular culturing techniques, regenerative free-range supports ecosystem balance and long-term sustainability in food production.
Slaughter-Free Meat
Free-range meat comes from animals raised in natural environments with access to outdoor spaces, but it still involves traditional slaughter methods. Cellular agriculture produces slaughter-free meat by cultivating animal cells in laboratories, offering an ethical and sustainable alternative that eliminates animal harm while reducing environmental impact.
Bioidentical Animal Protein
Bioidentical animal protein produced through cellular agriculture offers a sustainable alternative to free-range meat by cultivating muscle cells without raising and slaughtering animals, reducing environmental impact and improving animal welfare. This method provides consistent nutritional profiles and can be engineered to replicate the exact molecular composition of traditionally sourced free-range proteins, meeting consumer demand for ethical and high-quality food sources.
Cultivated Poultry
Cultivated poultry, derived from cellular agriculture, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional free-range farming by reducing land use, greenhouse gas emissions, and animal welfare concerns. This innovative method involves growing animal cells in bioreactors, producing meat with the same texture and flavor as free-range poultry but with higher efficiency and scalability.
Animal Welfare Superlabel
Free-range farming promotes animal welfare by allowing livestock to roam freely outdoors, reducing stress and improving health compared to conventional methods. Cellular agriculture offers an ethical alternative by producing cultured meat without raising or slaughtering animals, further advancing the Animal Welfare Superlabel standards for cruelty-free food production.
Free-Range vs Cellular Agriculture Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com