Natural flavors in pet food offer familiar tastes derived from traditional plant and animal sources, ensuring pets enjoy meals that appeal to their senses. Cellular agriculture introduces lab-grown ingredients that replicate these flavors with potentially higher sustainability and ethical standards. Both approaches aim to enhance pet nutrition, but cellular agriculture may provide a more controlled and eco-friendly production method.
Table of Comparison
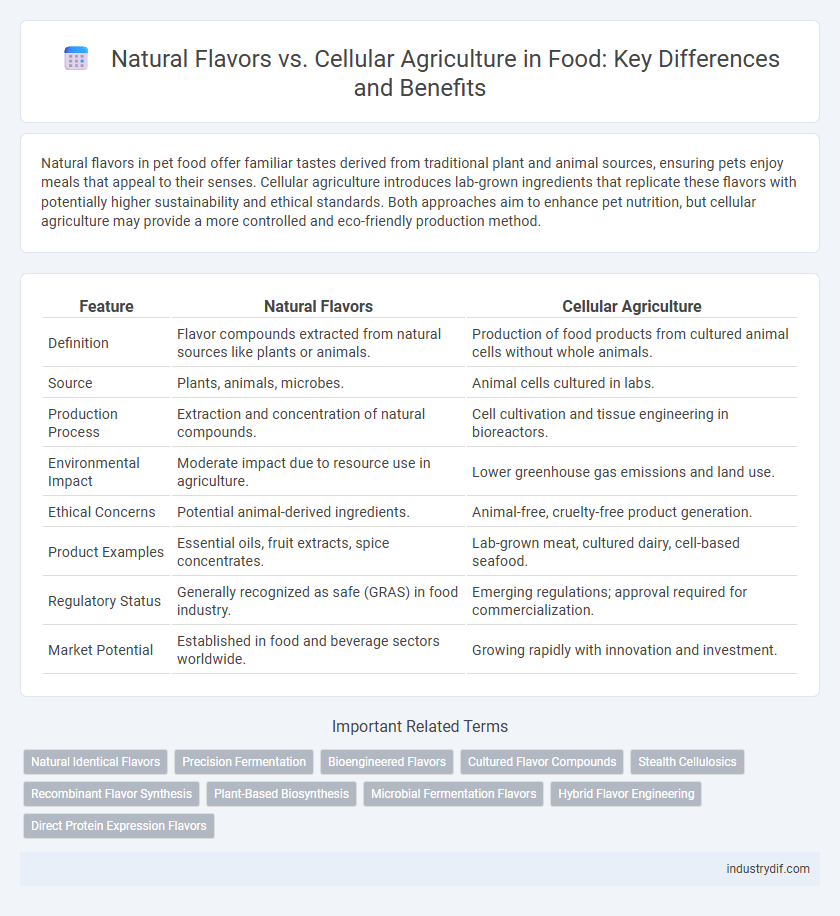
| Feature | Natural Flavors | Cellular Agriculture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Flavor compounds extracted from natural sources like plants or animals. | Production of food products from cultured animal cells without whole animals. |
| Source | Plants, animals, microbes. | Animal cells cultured in labs. |
| Production Process | Extraction and concentration of natural compounds. | Cell cultivation and tissue engineering in bioreactors. |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate impact due to resource use in agriculture. | Lower greenhouse gas emissions and land use. |
| Ethical Concerns | Potential animal-derived ingredients. | Animal-free, cruelty-free product generation. |
| Product Examples | Essential oils, fruit extracts, spice concentrates. | Lab-grown meat, cultured dairy, cell-based seafood. |
| Regulatory Status | Generally recognized as safe (GRAS) in food industry. | Emerging regulations; approval required for commercialization. |
| Market Potential | Established in food and beverage sectors worldwide. | Growing rapidly with innovation and investment. |
Understanding Natural Flavors: Definition and Sources
Natural flavors are complex mixtures derived from plant or animal sources, created to enhance food taste without synthetic chemicals. These flavors come from essential oils, fruit extracts, spices, or fermented products, retaining the original sensory properties of the source. Cellular agriculture, by contrast, produces food components like flavors or proteins through cell cultures, offering an alternative to traditional extraction methods while maintaining natural taste profiles.
What is Cellular Agriculture? An Overview
Cellular agriculture is an innovative food production method that cultivates animal cells directly to produce meat, dairy, and other products without raising animals. This technology enables sustainable, ethical, and scalable food manufacturing by replicating the cellular processes of traditional agriculture in controlled environments. Unlike natural flavors extracted from plants or animals, cellular agriculture focuses on growing real animal tissue, offering potential reductions in environmental impact and improved food security.
Production Process: Natural Flavors vs Cellular Agriculture
Natural flavors are derived through extraction and concentration of chemical compounds from plant or animal sources using solvents, distillation, or fermentation. Cellular agriculture produces food ingredients via cell cultures in bioreactors, harvesting proteins or fats without the need for whole organisms, focusing on scalability and sustainability. The production process of cellular agriculture offers precise control over molecular composition compared to the variable extraction methods used in natural flavor production.
Ingredient Transparency: Decoding Food Labels
Natural flavors often derive from plant or animal sources with limited transparency on the extraction process, making it challenging for consumers to fully understand ingredient origins. Cellular agriculture offers a clearer ingredient profile by producing food components through cell cultures, enabling detailed labeling of source materials and processing methods. Enhanced ingredient transparency in cellular agriculture supports informed consumer choices and aligns with growing demands for traceability and ethical food production.
Sustainability Impact: Comparing Environmental Footprints
Natural flavors derived from plants maintain a lower environmental footprint by minimizing resource-intensive processes and promoting biodiversity. Cellular agriculture, which cultivates animal products from cell cultures, offers significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, land use, and water consumption compared to traditional livestock farming. Both methods advance sustainable food production, yet cellular agriculture demonstrates greater potential for scalable environmental impact mitigation.
Health and Safety: Evaluating Risks and Benefits
Natural flavors, derived from plants or animals, undergo rigorous safety assessments to ensure they are free from allergens and contaminants. Cellular agriculture, involving lab-grown meat and dairy, offers controlled production environments that reduce exposure to pathogens and antibiotics commonly found in traditional farming. Both approaches present unique health benefits and safety challenges, necessitating ongoing evaluation to optimize consumer well-being and minimize potential risks.
Consumer Perception: Trends and Acceptance
Consumer perception of natural flavors remains anchored in the preference for authenticity and traditional food sources, with 65% of surveyed consumers expressing trust in labels indicating "natural." Cellular agriculture, producing flavors through cultured cells, faces growing interest but also skepticism due to unfamiliarity and concerns over processing methods, with acceptance rates varying significantly by region and demographic. Market trends indicate increasing openness among younger consumers, with 48% willing to try cellular agriculture products within the next five years, signaling shifting attitudes towards sustainable and innovative food technologies.
Regulatory Standards: Compliance and Labeling Requirements
Regulatory standards for natural flavors require strict compliance with ingredient transparency and safety assessments to ensure consumer protection, often mandating specific labeling that discloses source and processing methods. Cellular agriculture products face evolving regulatory frameworks, with agencies increasingly defining classification, safety evaluation, and labeling guidelines to distinguish lab-grown foods from conventional and natural flavors. Both sectors emphasize accurate labeling to maintain consumer trust, yet cellular agriculture demands more comprehensive oversight due to novel production techniques and potential allergenicity risks.
Industry Adoption: Key Players and Innovations
Natural flavors continue to dominate the food industry with key players like Givaudan, Firmenich, and Symrise driving innovations in sustainable extraction and formulation technologies. Cellular agriculture is rapidly gaining traction, with companies such as Eat Just, Memphis Meats, and Mosa Meat pioneering cultured meat and dairy proteins through advanced bioreactor systems. Industry adoption accelerates as major food corporations invest in partnerships and R&D to integrate cellular agriculture products alongside natural flavors for scalable, eco-friendly food solutions.
The Future of Flavor: Market Potential and Emerging Technologies
Natural flavors, derived from plant and animal sources, dominate the global food market due to consumer demand for authentic taste experiences. Cellular agriculture, an innovative technology producing flavors through cultured cells, presents a sustainable alternative that could revolutionize the flavor industry with scalable production and reduced environmental impact. Market projections estimate the cellular agriculture flavor sector will grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% by 2030, driven by advances in biotechnology and shifting consumer preferences towards clean-label and eco-friendly products.
Related Important Terms
Natural Identical Flavors
Natural identical flavors, derived through cellular agriculture, replicate traditional natural flavor compounds at a molecular level without using animal or plant extraction, offering sustainable and consistent alternatives to conventional natural flavors. This innovation reduces environmental impact and enhances flavor purity by utilizing biotechnology to produce identical flavor molecules in controlled conditions.
Precision Fermentation
Precision fermentation in cellular agriculture enables the production of natural flavors by programming microorganisms to biosynthesize specific compounds, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional extraction from plants or animals. This technology enhances flavor consistency, scalability, and reduces environmental impact compared to conventional natural flavor sources.
Bioengineered Flavors
Bioengineered flavors derived from cellular agriculture utilize cultured cells to produce authentic taste compounds without traditional farming, enhancing sustainability and consistency in natural flavor production. This innovative approach reduces environmental impact and resource use while delivering high-purity ingredients for the food industry.
Cultured Flavor Compounds
Cultured flavor compounds derived from cellular agriculture offer a sustainable and precise alternative to traditional natural flavors extracted from plants and animals, enabling the production of consistent, high-purity taste profiles. This innovative approach reduces reliance on seasonal crops and animal sources while enhancing flavor complexity through controlled microbial fermentation processes.
Stealth Cellulosics
Stealth Cellulosics utilizes advanced cellular agriculture techniques to produce natural flavors by cultivating plant-based cells rich in cellulose, enhancing flavor profiles while reducing reliance on traditional extraction methods. This innovative approach offers sustainable, scalable, and clean-label alternatives that meet consumer demand for natural and environmentally-friendly food ingredients.
Recombinant Flavor Synthesis
Recombinant flavor synthesis in cellular agriculture offers a sustainable alternative to traditional natural flavors by using engineered microorganisms to produce precise flavor compounds without relying on crop cultivation or extraction. This method reduces environmental impact, enhances flavor consistency, and enables scalable production of complex natural flavors such as vanillin, nootkatone, and saffron.
Plant-Based Biosynthesis
Plant-based biosynthesis leverages cellular agriculture techniques to produce natural flavors by using engineered microbes that convert plant-derived substrates into complex, authentic-tasting compounds, reducing reliance on traditional extraction methods. This innovative approach enhances sustainability and scalability while maintaining the chemical authenticity and sensory profile of natural flavors in food products.
Microbial Fermentation Flavors
Microbial fermentation flavors harness naturally occurring microorganisms to produce complex and authentic taste profiles, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional natural flavors derived directly from plants or animals. Cellular agriculture leverages microbial fermentation to create flavors with enhanced consistency and reduced environmental impact, revolutionizing the food industry by combining biotechnology with natural flavor production.
Hybrid Flavor Engineering
Hybrid Flavor Engineering combines natural flavors derived from traditional sources with cell-cultured ingredients produced through cellular agriculture, enhancing taste profiles while reducing environmental impact. This innovative approach leverages synthetic biology and fermentation techniques to create complex, sustainable flavors that mimic natural food compounds more precisely.
Direct Protein Expression Flavors
Direct Protein Expression Flavors leverage cellular agriculture to produce natural flavors by culturing specific proteins without traditional farming, ensuring higher purity and sustainability. These bioengineered flavors offer consistent quality and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional extraction methods from plants or animals.
Natural flavors vs Cellular agriculture Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com