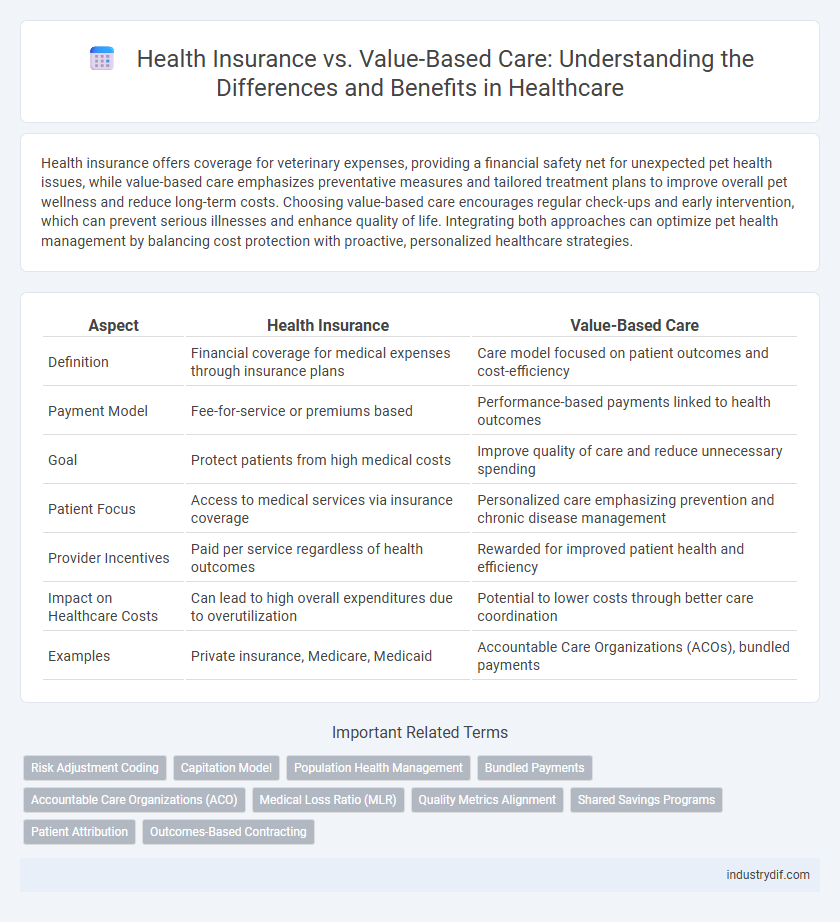
Health insurance offers coverage for veterinary expenses, providing a financial safety net for unexpected pet health issues, while value-based care emphasizes preventative measures and tailored treatment plans to improve overall pet wellness and reduce long-term costs. Choosing value-based care encourages regular check-ups and early intervention, which can prevent serious illnesses and enhance quality of life. Integrating both approaches can optimize pet health management by balancing cost protection with proactive, personalized healthcare strategies.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Health Insurance | Value-Based Care |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial coverage for medical expenses through insurance plans | Care model focused on patient outcomes and cost-efficiency |
| Payment Model | Fee-for-service or premiums based | Performance-based payments linked to health outcomes |
| Goal | Protect patients from high medical costs | Improve quality of care and reduce unnecessary spending |
| Patient Focus | Access to medical services via insurance coverage | Personalized care emphasizing prevention and chronic disease management |
| Provider Incentives | Paid per service regardless of health outcomes | Rewarded for improved patient health and efficiency |
| Impact on Healthcare Costs | Can lead to high overall expenditures due to overutilization | Potential to lower costs through better care coordination |
| Examples | Private insurance, Medicare, Medicaid | Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs), bundled payments |
Understanding Health Insurance: Traditional Models Explained
Traditional health insurance models rely on fee-for-service payments where providers are reimbursed for each test or procedure performed, leading to potential overutilization of services. These plans often emphasize coverage for a wide range of medical expenses but may lack incentives for improving patient outcomes or cost efficiency. Understanding these models highlights why cost control and quality improvement initiatives have driven the shift toward value-based care frameworks.
What Is Value-Based Care in Healthcare?
Value-based care in healthcare is a delivery model that prioritizes patient outcomes and cost-efficiency over the volume of services provided. It incentivizes providers to focus on preventive care, chronic disease management, and coordinated treatment plans to improve overall health while reducing unnecessary procedures. This approach contrasts with traditional health insurance payment models that reimburse based on service quantity rather than quality or effectiveness.
Key Differences Between Health Insurance and Value-Based Care
Health insurance primarily offers financial protection by covering medical expenses, whereas value-based care focuses on improving patient outcomes through coordinated and efficient healthcare delivery. Health insurance typically reimburses providers based on services rendered, while value-based care incentivizes providers to achieve better health results and reduce costs. The key differences lie in payment models, goals of care, and emphasis on cost versus quality metrics.
Payment Structures: Fee-for-Service vs Value-Based Payments
Fee-for-service payment structures reimburse healthcare providers for each service or procedure, often leading to higher costs without guaranteeing better outcomes. Value-based payments focus on rewarding providers based on patient health outcomes, encouraging efficient and effective care delivery. This model shifts incentives from quantity to quality, promoting long-term health improvements and cost containment.
Patient Outcomes: Impact of Value-Based Care vs Health Insurance
Value-based care prioritizes patient outcomes by incentivizing healthcare providers to deliver quality treatment that reduces hospital readmissions and improves chronic disease management. Health insurance primarily focuses on covering healthcare costs, which may not directly influence the effectiveness or quality of care received. Studies show that value-based care models lead to better patient satisfaction and health improvements compared to traditional health insurance systems.
Cost Implications for Providers and Patients
Health insurance impacts cost distribution between providers and patients by covering a wide range of services, often leading to higher premiums but predictable out-of-pocket expenses. Value-based care shifts the financial focus toward outcomes, incentivizing providers to reduce unnecessary treatments and lower overall costs, which can result in lower patient expenses and improved health quality. Providers benefit from value-based care through performance-based reimbursements, while patients experience cost savings linked to more efficient, personalized care delivery.
Provider Incentives: Aligning Goals in Each Model
Health insurance models typically incentivize providers through fee-for-service payments, promoting volume of care rather than patient outcomes. Value-based care aligns provider incentives to improve quality and efficiency, rewarding better health outcomes and cost containment. This alignment fosters coordinated care delivery, reducing unnecessary treatments and enhancing patient satisfaction.
Challenges in Transitioning to Value-Based Care
Transitioning to value-based care poses significant challenges such as aligning provider incentives with patient outcomes rather than service volume, which complicates traditional health insurance reimbursement models. Data integration and accurate risk adjustment require advanced health IT systems that many providers find costly and difficult to implement. Patient engagement also becomes crucial, demanding educational initiatives to shift focus from fee-for-service to value-driven care delivery.
Role of Technology in Health Insurance and Value-Based Care
Technology enhances health insurance by streamlining claims processing, enabling personalized policy management through data analytics, and improving fraud detection. In value-based care, advanced health IT systems facilitate real-time patient monitoring, data sharing among providers, and outcome-based payment models that focus on quality rather than quantity. Integration of electronic health records (EHR) and artificial intelligence (AI) tools drives efficiency and accuracy in both health insurance administration and value-based care delivery.
Future Trends: Integrating Value-Based Care with Health Insurance
Future trends in health insurance are increasingly focused on integrating value-based care models to enhance patient outcomes and cost efficiency. This shift involves insurers adopting value-based payment structures that reward providers for quality and patient satisfaction instead of service volume. Advanced data analytics and digital health platforms play a crucial role in supporting this integration by enabling real-time monitoring and personalized care plans.
Related Important Terms
Risk Adjustment Coding
Risk adjustment coding is critical in health insurance to ensure accurate compensation based on patients' health status and projected care costs, directly impacting provider reimbursement under value-based care models. Effective risk adjustment coding enhances data precision for population health management, aligning incentives to improve care quality while controlling costs.
Capitation Model
The capitation model in health insurance pays providers a fixed amount per patient regardless of services rendered, incentivizing efficient, preventive care under value-based care frameworks. This approach shifts financial risk to providers while promoting improved health outcomes and cost control by prioritizing patient wellness over service volume.
Population Health Management
Health insurance primarily covers individual medical expenses, whereas value-based care emphasizes population health management by incentivizing providers to improve health outcomes and reduce costs across defined patient groups. Integrating value-based care models with health insurance frameworks enhances preventative care, chronic disease management, and overall population wellness metrics.
Bundled Payments
Bundled payments in value-based care offer a fixed reimbursement for an entire episode of care, incentivizing providers to improve patient outcomes while controlling costs compared to traditional health insurance fee-for-service models. This approach reduces unnecessary treatments and enhances care coordination, leading to higher efficiency and better value in healthcare delivery.
Accountable Care Organizations (ACO)
Accountable Care Organizations (ACO) enhance the traditional Health Insurance model by emphasizing value-based care, where providers are incentivized to improve patient outcomes and reduce costs through coordinated care. This approach shifts the focus from fee-for-service payments to shared savings and quality metrics, driving more efficient resource utilization and better health management.
Medical Loss Ratio (MLR)
The Medical Loss Ratio (MLR) mandates health insurers to spend a minimum percentage of premium revenues on clinical services and quality improvement, promoting transparency and accountability in health insurance. Value-Based Care models leverage MLR by incentivizing providers to improve patient outcomes and reduce unnecessary costs, aligning financial practices with actual health benefits.
Quality Metrics Alignment
Health insurance plans increasingly emphasize quality metrics alignment to support value-based care models that reward providers for patient outcomes rather than service volume. Aligning payment structures with evidence-based quality indicators enhances patient satisfaction, reduces hospital readmissions, and lowers overall healthcare costs.
Shared Savings Programs
Shared Savings Programs align financial incentives between providers and payers by rewarding improved patient outcomes and cost efficiency, promoting value-based care over traditional fee-for-service health insurance models. These programs encourage healthcare providers to reduce unnecessary spending while maintaining high-quality care, driving sustainable healthcare savings and enhanced patient satisfaction.
Patient Attribution
Patient attribution in health insurance determines which provider is responsible for a patient's care, directly impacting reimbursement models and care coordination under value-based care systems. Accurate attribution improves health outcomes by aligning incentives for providers to focus on preventive care and chronic disease management, reducing costs and enhancing patient satisfaction.
Outcomes-Based Contracting
Outcomes-based contracting in health insurance aligns payment structures with the effectiveness of value-based care, emphasizing measurable patient health improvements and cost efficiency. This model incentivizes providers to deliver higher quality care by linking reimbursement to clinical outcomes rather than service volume.
Health Insurance vs Value-Based Care Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com