Hospital care provides pets with immediate access to specialized medical equipment and round-the-clock professional supervision, ensuring critical conditions are managed effectively. Hospital-at-home services offer a comfortable and familiar environment for pets, reducing stress and promoting faster recovery while still receiving expert veterinary attention. Choosing between the two depends on the severity of the pet's condition and the availability of appropriate medical resources at home.
Table of Comparison
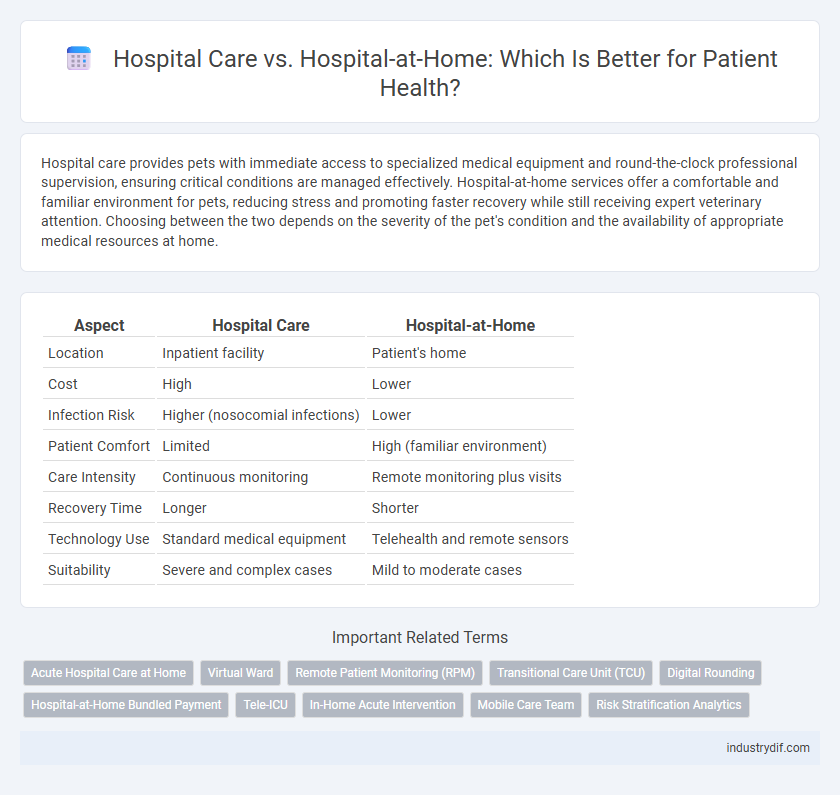
| Aspect | Hospital Care | Hospital-at-Home |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Inpatient facility | Patient's home |
| Cost | High | Lower |
| Infection Risk | Higher (nosocomial infections) | Lower |
| Patient Comfort | Limited | High (familiar environment) |
| Care Intensity | Continuous monitoring | Remote monitoring plus visits |
| Recovery Time | Longer | Shorter |
| Technology Use | Standard medical equipment | Telehealth and remote sensors |
| Suitability | Severe and complex cases | Mild to moderate cases |
Overview of Hospital Care and Hospital-at-Home Models
Hospital care involves patients receiving treatment within a traditional inpatient facility equipped with specialized medical staff, advanced diagnostic tools, and continuous monitoring to manage acute or chronic conditions. The hospital-at-home model delivers comparable healthcare services directly in a patient's home, leveraging telemedicine, remote monitoring devices, and coordinated care teams to ensure safety and effectiveness. Both models aim to optimize patient outcomes but differ fundamentally in setting, resource allocation, and patient experience.
Key Differences Between Hospital Care and Hospital-at-Home
Hospital care involves in-patient services within a traditional medical facility, offering immediate access to specialized equipment and multidisciplinary teams for acute conditions. Hospital-at-home provides equivalent acute care services in a patient's residence, leveraging remote monitoring technology and periodic healthcare professional visits to reduce hospital stay risks. Key differences include location of care, intensity of medical supervision, infection control, and patient comfort, with hospital-at-home promoting personalized recovery environments and lower healthcare costs.
Eligibility Criteria for Hospital-at-Home Services
Eligibility criteria for Hospital-at-Home services typically include patients requiring acute care without the need for intensive hospital resources, such as individuals with stable chronic conditions or recovering postoperative patients. Candidates must have a safe home environment, access to necessary medical equipment, and caregiver support to ensure continuous monitoring and treatment. Clinical assessments by healthcare professionals confirm that patients can receive equivalent care outside the hospital, reducing hospital stays while maintaining safety and effectiveness.
Clinical Outcomes: Hospital vs. Hospital-at-Home
Hospital-at-home programs demonstrate comparable or improved clinical outcomes compared to traditional hospital care, with reduced rates of hospital-acquired infections and fewer complications such as delirium and deep vein thrombosis. Studies indicate faster recovery times and higher patient satisfaction in hospital-at-home settings due to personalized care and a familiar environment. Mortality rates remain similar between both models, making hospital-at-home a viable alternative for appropriate patient populations.
Patient Experience and Satisfaction Comparisons
Hospital-at-Home programs often result in higher patient satisfaction by providing personalized care in a familiar environment, reducing the stress and discomfort associated with traditional hospital stays. Studies show that patients receiving hospital-at-home care report better pain management, increased comfort, and more effective communication with healthcare providers. Conversely, conventional hospital care may expose patients to more risks of hospital-acquired infections and longer recovery times, impacting overall patient experience negatively.
Cost Implications and Reimbursement Structures
Hospital-at-Home programs significantly reduce healthcare costs by minimizing overhead expenses such as facility maintenance and inpatient services, offering cost-effective alternatives to traditional hospital care. Reimbursement structures are evolving to accommodate these models, with Medicare and private insurers increasingly recognizing home-based acute care under value-based payment systems. This shift promotes financial sustainability while maintaining quality care through tailored reimbursements that incentivize efficient resource utilization in both settings.
Technology and Infrastructure Requirements
Hospital care traditionally depends on sophisticated onsite technology such as advanced imaging systems, centralized monitoring equipment, and extensive medical infrastructure to support complex procedures. Hospital-at-home models require integrated telehealth platforms, portable diagnostic devices, and robust remote monitoring systems to provide real-time patient data and maintain clinical standards in residential environments. Effective implementation mandates high-speed internet connectivity, secure data management, and adaptable medical equipment suitable for varied home settings.
Staffing and Workforce Considerations
Hospital care demands a broad team of specialized healthcare professionals onsite to manage complex medical needs and emergencies, requiring significant staffing resources and coordination. Hospital-at-home models rely on a flexible workforce of nurses, therapists, and remote physicians who provide personalized care in patients' homes, often improving staff efficiency and satisfaction. Workforce considerations include training for home-based care protocols, use of telehealth technology, and adapting staff roles to ensure quality and safety outside traditional hospital settings.
Challenges and Limitations of Hospital-at-Home
Hospital-at-Home programs face challenges including limited access to advanced diagnostic tools and specialized medical equipment available in traditional hospital settings. Patient safety concerns arise due to varying home environments and potential delays in emergency response compared to in-hospital care. Additionally, regulatory hurdles, reimbursement issues, and the need for robust caregiver support systems limit widespread adoption of Hospital-at-Home models.
Future Trends in Hospital and Home-Based Acute Care
Future trends in hospital and home-based acute care emphasize the integration of advanced telemedicine technologies and remote patient monitoring, enabling timely interventions without traditional hospital stays. Expanding hospital-at-home programs reduces healthcare costs while improving patient satisfaction and outcomes by offering personalized care in familiar environments. Predictive analytics and AI-driven decision support systems are transforming clinical workflows, supporting a shift toward decentralized acute care models that balance safety and efficiency.
Related Important Terms
Acute Hospital Care at Home
Acute hospital care at home delivers critical medical treatments traditionally provided in hospital settings, including intravenous therapy, oxygen support, and continuous monitoring, enabling patients to recover in familiar environments while reducing hospital-acquired infections. Studies indicate that hospital-at-home programs can decrease readmission rates by up to 30% and enhance patient satisfaction without compromising clinical outcomes.
Virtual Ward
Hospital-at-Home programs featuring Virtual Wards deliver acute care remotely, reducing the risk of hospital-acquired infections and enhancing patient comfort by enabling treatment in familiar home settings. These digitally supported Virtual Wards utilize real-time monitoring technologies and coordinated healthcare teams to provide continuous clinical oversight, matching hospital-level care standards while decreasing readmission rates and healthcare costs.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) enhances Hospital-at-Home programs by providing continuous, real-time health data, enabling early detection of complications and personalized care outside traditional hospital settings. This technology reduces hospital readmissions, lowers healthcare costs, and improves patient outcomes by facilitating timely interventions without the need for prolonged inpatient stays.
Transitional Care Unit (TCU)
Transitional Care Units (TCUs) bridge the gap between hospital care and Hospital-at-Home by providing specialized, short-term medical support for patients transitioning from acute hospitalization to home recovery. TCUs enhance patient outcomes by reducing readmission rates and enabling continuous monitoring with advanced telehealth technologies within a home-like environment.
Digital Rounding
Digital rounding in hospital care enhances real-time patient monitoring and staff communication through centralized dashboards, improving response times and clinical outcomes. In hospital-at-home models, digital rounding leverages telehealth and remote monitoring technologies to deliver personalized care, reduce readmission rates, and increase patient satisfaction outside traditional clinical settings.
Hospital-at-Home Bundled Payment
Hospital-at-Home bundled payment models streamline costs by combining all services into a single comprehensive fee, promoting efficient resource use and reducing unnecessary hospital admissions. This approach enhances patient outcomes through personalized, in-home medical care while lowering overall healthcare expenditures compared to traditional hospital care.
Tele-ICU
Tele-ICU technology enhances Hospital-at-Home services by providing continuous, remote monitoring of critical patients through advanced audiovisual and data analytics systems, ensuring expert care comparable to traditional hospital ICU settings. This integration reduces hospital stays, decreases infection risks, and improves patient outcomes by delivering timely interventions without the need for physical ICU admission.
In-Home Acute Intervention
In-home acute intervention through Hospital-at-Home programs offers patients timely access to medical care with reduced risk of hospital-acquired infections and increased comfort in familiar surroundings. Studies show that this model improves patient outcomes, decreases emergency readmissions, and lowers overall healthcare costs compared to traditional hospital care.
Mobile Care Team
Mobile care teams in hospital-at-home programs provide personalized medical treatment, monitoring, and support, enabling patients to receive high-quality hospital-level care in the comfort of their own homes. This approach reduces hospital stay durations, lowers risk of hospital-acquired infections, and improves patient satisfaction compared to traditional hospital care.
Risk Stratification Analytics
Risk stratification analytics in hospital care enables precise identification of patients requiring intensive inpatient services, optimizing resource allocation and improving outcomes; hospital-at-home models leverage these analytics to safely manage lower-risk patients remotely, reducing hospital congestion and costs while maintaining quality care. Advanced algorithms analyze clinical, demographic, and biometric data to dynamically classify patient risk, facilitating tailored interventions that prevent complications and readmissions in both traditional and home-based care settings.
Hospital Care vs Hospital-at-Home Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com