Inpatient care provides pets with round-the-clock monitoring and immediate access to advanced medical interventions within a hospital setting, ideal for critical or complex conditions. Hospital-at-home services offer a comfortable, stress-free environment for pets to recover with professional veterinary oversight, minimizing exposure to hospital-related infections and reducing anxiety. Choosing between these options depends on the pet's health status, treatment complexity, and the owner's preference for care setting and convenience.
Table of Comparison
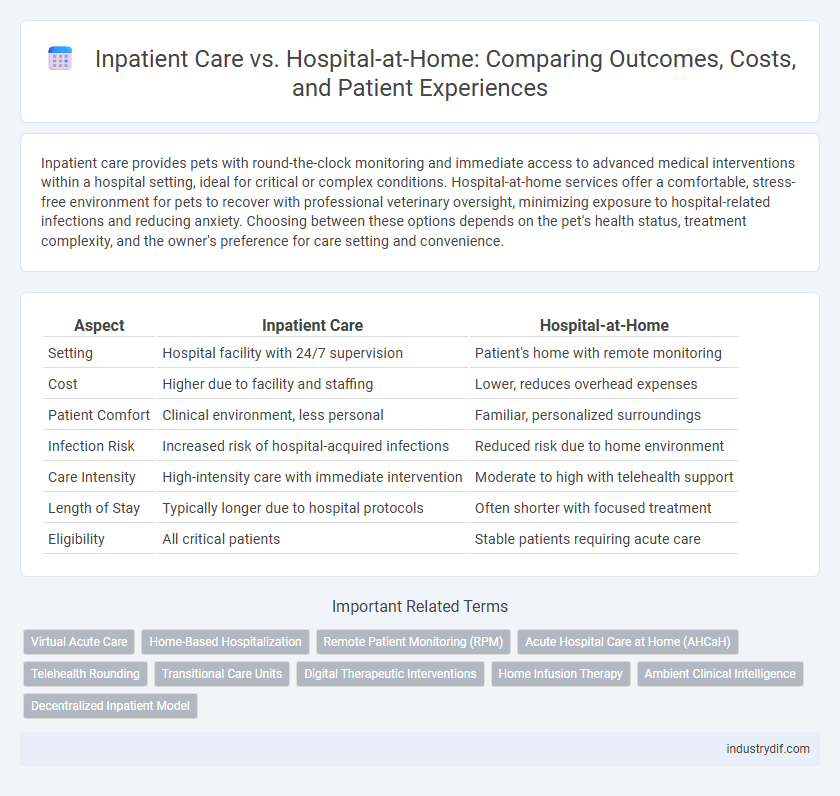
| Aspect | Inpatient Care | Hospital-at-Home |
|---|---|---|
| Setting | Hospital facility with 24/7 supervision | Patient's home with remote monitoring |
| Cost | Higher due to facility and staffing | Lower, reduces overhead expenses |
| Patient Comfort | Clinical environment, less personal | Familiar, personalized surroundings |
| Infection Risk | Increased risk of hospital-acquired infections | Reduced risk due to home environment |
| Care Intensity | High-intensity care with immediate intervention | Moderate to high with telehealth support |
| Length of Stay | Typically longer due to hospital protocols | Often shorter with focused treatment |
| Eligibility | All critical patients | Stable patients requiring acute care |
Overview of Inpatient Care
Inpatient care involves admitting patients to a hospital where they receive continuous, 24-hour medical attention and monitoring, typically for severe or complex conditions requiring specialized equipment and constant supervision. This level of care supports surgeries, intensive treatments, and emergency interventions within a controlled clinical setting to ensure patient safety and effective recovery. Hospitals utilize multidisciplinary teams including physicians, nurses, and therapists to deliver comprehensive treatment plans during the inpatient stay.
What Is Hospital-at-Home?
Hospital-at-Home is an innovative healthcare model that delivers acute, hospital-level care to patients within the comfort of their own homes, utilizing advanced medical technology and remote monitoring. This approach reduces the need for traditional inpatient stays, decreasing risks of hospital-acquired infections and promoting faster recovery through personalized care in familiar surroundings. By providing comprehensive services such as intravenous therapy, diagnostic testing, and continuous clinical supervision, Hospital-at-Home ensures safety and quality comparable to conventional inpatient care.
Patient Eligibility Criteria
Patient eligibility criteria for inpatient care typically include severe or acute medical conditions requiring continuous monitoring, complex diagnostic procedures, or specialized treatments not feasible at home. Hospital-at-Home programs select patients based on stable vital signs, manageable symptoms, and the presence of a supportive home environment to ensure safety and effective care delivery. Both models assess medical stability, risk factors, and the potential for rapid intervention when determining the most appropriate care setting.
Key Differences in Care Delivery
Inpatient care involves patients receiving treatment within a hospital setting, allowing continuous monitoring by medical professionals and access to advanced medical equipment. Hospital-at-home programs deliver similar acute care services in a patient's residence, emphasizing comfort and reducing exposure to hospital-related infections. The key differences lie in the care environment, with inpatient care offering centralized, intensive resources, whereas hospital-at-home prioritizes personalized care and convenience while maintaining clinical safety standards.
Safety and Quality Standards
Inpatient care ensures comprehensive monitoring with immediate access to emergency services, meeting rigorous hospital safety protocols and accreditation standards. Hospital-at-home programs replicate clinical quality by employing skilled healthcare professionals and utilizing advanced remote monitoring technologies to maintain patient safety. Both models adhere to stringent quality frameworks, but hospital-at-home offers personalized care while reducing risks associated with hospital-acquired infections.
Cost Comparison and Reimbursement
Hospital-at-Home programs typically reduce costs by 20-40% compared to traditional inpatient care due to lower facility fees and resource utilization. Reimbursement models for Hospital-at-Home are evolving, with Medicare and private insurers increasingly recognizing its cost-effectiveness and offering comparable payment rates. Cost savings are driven by factors like shorter lengths of stay, reduced readmissions, and minimized overhead expenses in home-based care settings.
Patient Outcomes and Satisfaction
Inpatient care often provides intensive monitoring and immediate access to medical interventions, which can be critical for severe conditions but may increase risks of hospital-acquired infections and patient stress. Hospital-at-home programs deliver acute care in the comfort of a patient's home, showing comparable or improved patient outcomes, including reduced readmission rates and enhanced satisfaction due to personalized care and familiar surroundings. Studies indicate that patients receiving hospital-at-home services report higher satisfaction levels and faster recovery times, emphasizing the model's effectiveness in managing select acute illnesses.
Technology and Remote Monitoring
Hospital-at-home programs leverage advanced remote monitoring technologies, including wearable devices and telehealth platforms, to continuously track patients' vital signs and health status outside traditional inpatient settings. These digital tools enable real-time data transmission to healthcare providers, facilitating timely interventions and personalized care while reducing hospital stay duration. Integration of AI-driven analytics further enhances patient outcomes by predicting complications early, making hospital-at-home a technologically advanced alternative to conventional inpatient care.
Staffing Models and Resource Allocation
Inpatient care staffing models typically involve a fixed team of healthcare professionals providing continuous, on-site support, while hospital-at-home programs allocate resources dynamically with remote monitoring and intermittent in-person visits. Resource allocation in inpatient care is centered on dedicated hospital infrastructure and technology, contrasting with hospital-at-home approaches that leverage telehealth tools and community-based services to optimize efficiency. Effective staffing in hospital-at-home models depends on integrating virtual care teams and mobile healthcare providers to ensure patient safety and quality outcomes outside traditional hospital settings.
Future Trends in Acute Care Settings
Future trends in acute care settings emphasize a shift towards Hospital-at-Home models, leveraging telemedicine, remote monitoring, and advanced digital health tools to provide high-quality inpatient care outside traditional hospitals. This approach reduces hospital-acquired infections, lowers healthcare costs, and improves patient satisfaction by delivering personalized treatment in familiar environments. Integration of artificial intelligence and data analytics further optimizes patient outcomes and resource allocation, signaling a transformative evolution in inpatient care delivery.
Related Important Terms
Virtual Acute Care
Virtual acute care in hospital-at-home models delivers supervised medical treatment remotely, reducing the need for traditional inpatient care and lowering risks of hospital-acquired infections. Advanced telemedicine technologies and remote monitoring enable timely interventions and continuous patient assessment, enhancing recovery outcomes outside conventional hospital settings.
Home-Based Hospitalization
Home-based hospitalization offers comprehensive inpatient care within the comfort of a patient's residence, utilizing advanced telemedicine, remote monitoring, and coordinated healthcare teams to manage acute conditions effectively. This model reduces hospital-associated risks such as infections and promotes faster recovery times while maintaining the clinical standards of traditional inpatient care.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) enhances Hospital-at-Home programs by enabling continuous surveillance of vital signs and health metrics, reducing the need for traditional inpatient care. RPM technologies facilitate early detection of complications and timely interventions, improving patient outcomes while lowering hospital readmission rates and healthcare costs.
Acute Hospital Care at Home (AHCaH)
Acute Hospital Care at Home (AHCaH) delivers comprehensive inpatient-level treatment within patients' residences, leveraging advanced remote monitoring and telehealth technologies to manage acute medical conditions typically requiring hospitalization. This model reduces hospital admissions and associated risks while maintaining clinical quality through daily virtual assessments and coordinated home healthcare services.
Telehealth Rounding
Telehealth rounding in hospital-at-home programs leverages advanced remote monitoring and video consultations to provide continuous inpatient-level care, reducing hospital stays and enhancing patient comfort. This approach improves clinical outcomes by enabling real-time data access and multidisciplinary team collaboration while minimizing infection risk and healthcare costs.
Transitional Care Units
Transitional Care Units (TCUs) provide a critical bridge between inpatient care and hospital-at-home models, offering medically supervised environments designed to support patients recovering from acute illness while reducing hospital readmissions. These units leverage coordinated care plans and remote monitoring technologies to enhance patient outcomes, improve comfort, and lower healthcare costs.
Digital Therapeutic Interventions
Digital therapeutic interventions in hospital-at-home programs deliver personalized, evidence-based treatments remotely, enhancing patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs compared to traditional inpatient care. Integration of wearable sensors and telehealth platforms enables continuous monitoring and real-time adjustments, fostering effective management of chronic conditions outside conventional hospital settings.
Home Infusion Therapy
Home Infusion Therapy within Hospital-at-Home programs offers patients the ability to receive complex intravenous medications safely in their residences, reducing risks of hospital-acquired infections and improving comfort. This approach enhances treatment adherence and patient outcomes by leveraging advanced portable infusion devices and remote monitoring technologies compared to traditional inpatient care.
Ambient Clinical Intelligence
Ambient Clinical Intelligence enhances Hospital-at-Home models by integrating real-time biometric monitoring and AI-driven analytics, reducing the need for traditional Inpatient Care admissions. This technology improves patient outcomes and clinical workflow efficiency while maintaining the safety and quality standards of in-hospital treatment.
Decentralized Inpatient Model
The decentralized inpatient model, exemplified by hospital-at-home programs, delivers acute care traditionally provided in hospitals directly to patients' homes using remote monitoring technologies and mobile healthcare teams. This approach reduces hospital stays, lowers infection risks, and enhances patient comfort while maintaining clinical outcomes comparable to conventional inpatient care.
Inpatient Care vs Hospital-at-Home Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com