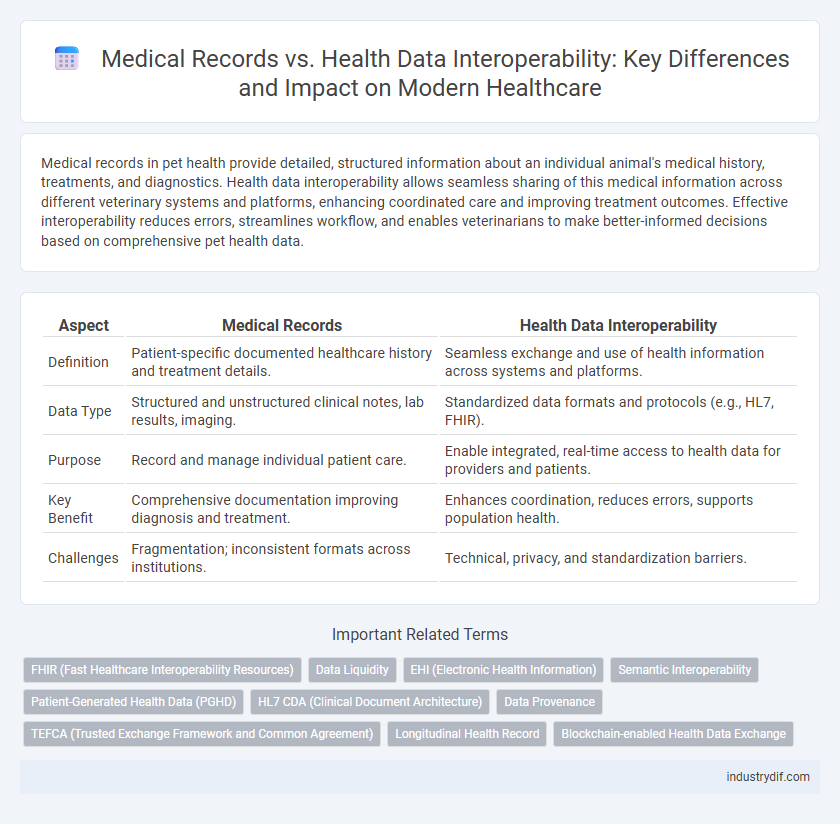
Medical records in pet health provide detailed, structured information about an individual animal's medical history, treatments, and diagnostics. Health data interoperability allows seamless sharing of this medical information across different veterinary systems and platforms, enhancing coordinated care and improving treatment outcomes. Effective interoperability reduces errors, streamlines workflow, and enables veterinarians to make better-informed decisions based on comprehensive pet health data.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Medical Records | Health Data Interoperability |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Patient-specific documented healthcare history and treatment details. | Seamless exchange and use of health information across systems and platforms. |
| Data Type | Structured and unstructured clinical notes, lab results, imaging. | Standardized data formats and protocols (e.g., HL7, FHIR). |
| Purpose | Record and manage individual patient care. | Enable integrated, real-time access to health data for providers and patients. |
| Key Benefit | Comprehensive documentation improving diagnosis and treatment. | Enhances coordination, reduces errors, supports population health. |
| Challenges | Fragmentation; inconsistent formats across institutions. | Technical, privacy, and standardization barriers. |
Understanding Medical Records: Definitions and Components
Medical records are comprehensive documents that store patient-specific information, including medical history, diagnoses, treatment plans, medications, immunization dates, allergies, radiology images, and laboratory test results. Health data interoperability emphasizes seamless exchange and integration of these records across diverse healthcare systems to improve patient care continuity and data accuracy. Understanding the definitions and components of medical records is essential for optimizing interoperability, ensuring that electronic health records (EHRs) capture and communicate structured clinical data effectively.
What is Health Data Interoperability?
Health data interoperability is the ability of different healthcare information systems, devices, and applications to access, exchange, integrate, and cooperatively use data in a coordinated manner, ensuring seamless patient care. Unlike medical records, which are typically static and confined to a single provider or system, interoperable health data enables real-time sharing of comprehensive patient information across multiple platforms. This facilitates improved clinical decision-making, reduced errors, and enhanced healthcare outcomes by promoting data accuracy and availability.
Key Differences Between Medical Records and Health Data Interoperability
Medical records are structured documents containing a patient's medical history, diagnoses, treatments, and test results, primarily used by healthcare providers for clinical care. Health data interoperability refers to the seamless exchange and integration of health information across different healthcare systems and platforms, enabling real-time access and improved care coordination. The key difference lies in medical records being static, individual datasets, whereas interoperability emphasizes dynamic, standardized data sharing to enhance healthcare efficiency and patient outcomes.
Importance of Accurate Medical Records in Healthcare
Accurate medical records are crucial for ensuring effective communication among healthcare providers and delivering timely, personalized patient care. High-quality medical records reduce errors, improve diagnosis accuracy, and facilitate seamless health data interoperability across different systems and platforms. Enhanced interoperability supports comprehensive patient histories, leading to better clinical decisions and improved health outcomes.
The Role of Interoperability in Modern Health Systems
Interoperability in modern health systems enables seamless exchange and integration of medical records and health data, improving clinical decision-making and patient outcomes. Standardized data formats and APIs facilitate real-time access to comprehensive patient information across diverse healthcare providers and electronic health record (EHR) systems. Enhanced interoperability reduces errors, lowers costs, and supports population health management through efficient data aggregation and analysis.
Data Standards Driving Health Data Interoperability
Data standards such as HL7 FHIR and SNOMED CT are pivotal in driving health data interoperability by enabling seamless exchange and integration of medical records across diverse health information systems. These standards ensure consistent data formats and terminologies, enhancing accuracy and accessibility for clinical decision-making and patient care coordination. Adoption of universal data standards significantly reduces errors, improves data sharing efficiency, and supports comprehensive health analytics and population health management.
Challenges in Integrating Medical Records with Interoperable Systems
Integrating medical records with health data interoperability systems encounters significant challenges due to variations in data standards, formats, and terminologies used across healthcare providers. Inconsistent Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems and lack of standardized APIs hinder seamless data exchange, leading to incomplete patient information and increased risk of errors in clinical decision-making. Security and privacy concerns further complicate integration efforts, necessitating robust encryption and compliance with regulations such as HIPAA to protect sensitive health information.
Privacy and Security Concerns in Health Data Exchange
Medical records and health data interoperability raise critical privacy and security concerns, as sensitive patient information must be protected from unauthorized access and cyber threats during data exchange. Robust encryption protocols, stringent access controls, and compliance with regulations like HIPAA are essential to ensure data confidentiality and integrity. Interoperability solutions must balance seamless data sharing with rigorous safeguards to prevent breaches and maintain patient trust.
Benefits of Achieving Full Health Data Interoperability
Full health data interoperability enables seamless sharing of patient medical records across healthcare providers, which improves care coordination and reduces errors. It enhances clinical decision-making by providing real-time access to comprehensive health information, leading to better patient outcomes. Interoperability also supports population health management and streamlines administrative workflows, resulting in cost savings and increased operational efficiency.
Future Trends in Medical Records and Data Interoperability
Future trends in medical records emphasize seamless health data interoperability through blockchain technology, enhancing data security and patient control. Advanced artificial intelligence algorithms are expected to facilitate real-time data integration across diverse healthcare systems, improving diagnostic accuracy and personalized treatment plans. Standardization initiatives, such as FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), will drive widespread adoption of interoperable medical records, enabling efficient information exchange and fostering collaborative care models.
Related Important Terms
FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources)
FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) revolutionizes medical records management by enabling seamless health data interoperability across diverse healthcare systems, improving patient care coordination. This standardized framework supports real-time data exchange using API-driven resources, enhancing accuracy, accessibility, and efficiency in electronic health records (EHRs).
Data Liquidity
Medical records are structured documents containing patient history, diagnoses, and treatments, while health data interoperability enables seamless exchange and integration of diverse health information across systems. Data liquidity enhances patient care by allowing real-time access and use of comprehensive health data, improving clinical decision-making and coordination among providers.
EHI (Electronic Health Information)
Electronic Health Information (EHI) interoperability enables seamless exchange of medical records across diverse healthcare systems, improving clinical decision-making and patient outcomes. Standardizing data formats and adopting HL7 FHIR protocols are critical to achieving comprehensive health data interoperability beyond isolated medical records.
Semantic Interoperability
Semantic interoperability in health data ensures that medical records are accurately understood and integrated across diverse healthcare systems, enabling precise communication of clinical information. Effective semantic interoperability supports seamless exchange, reduces errors, and enhances patient outcomes by harmonizing terminologies and data formats within electronic health records (EHRs).
Patient-Generated Health Data (PGHD)
Patient-Generated Health Data (PGHD) enhances medical records by providing real-time, personalized insights directly from patients, improving health data interoperability through seamless integration with electronic health records (EHRs) and facilitating comprehensive, patient-centered care. Effective interoperability platforms standardize PGHD formats and ensure secure data exchange, empowering clinicians with accurate, up-to-date information for informed decision-making and improved health outcomes.
HL7 CDA (Clinical Document Architecture)
HL7 CDA (Clinical Document Architecture) provides a standardized framework for medical records, enabling consistent formatting and exchange of clinical documents across diverse healthcare systems. Enhancing health data interoperability through HL7 CDA facilitates seamless integration, improved patient care coordination, and accurate clinical decision-making by ensuring comprehensible and structured health information exchange.
Data Provenance
Data provenance in medical records ensures accurate tracking of patient information origin, enhancing trust and reliability in health data interoperability systems. Precise documentation of data sources supports seamless integration across healthcare platforms, optimizing patient care and clinical decision-making.
TEFCA (Trusted Exchange Framework and Common Agreement)
TEFCA (Trusted Exchange Framework and Common Agreement) establishes standardized protocols to enhance health data interoperability by facilitating seamless and secure exchange of medical records across diverse healthcare systems. This framework reduces data silos, improving real-time access to comprehensive patient information and enabling better coordinated care.
Longitudinal Health Record
Longitudinal Health Records integrate medical records and health data interoperability by compiling patient information across multiple healthcare providers over time, enabling comprehensive and continuous care management. Enhanced interoperability standards, such as HL7 FHIR, facilitate seamless data exchange, improving accuracy and accessibility of longitudinal patient histories.
Blockchain-enabled Health Data Exchange
Blockchain-enabled health data exchange enhances medical records interoperability by providing a secure, decentralized platform that ensures data integrity, patient privacy, and real-time access across healthcare providers. This technology supports seamless sharing of health information while reducing errors and administrative costs, ultimately improving clinical decision-making and patient outcomes.
Medical Records vs Health Data Interoperability Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com