Telemedicine offers remote consultations for a wide range of pet health issues, including general illnesses, behavioral concerns, and chronic disease management. Teledentistry specifically targets dental care, allowing veterinarians to assess oral health, provide preventative advice, and recommend treatments for pets without an in-person visit. Both services improve access to specialized care and reduce stress for pets by minimizing travel and in-clinic wait times.
Table of Comparison
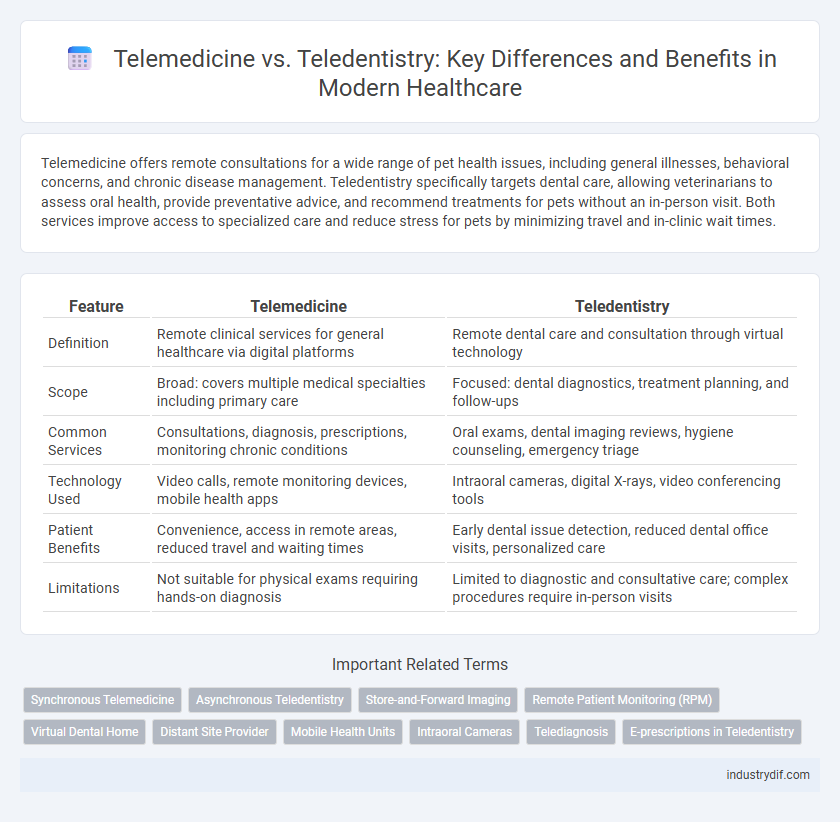
| Feature | Telemedicine | Teledentistry |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Remote clinical services for general healthcare via digital platforms | Remote dental care and consultation through virtual technology |
| Scope | Broad: covers multiple medical specialties including primary care | Focused: dental diagnostics, treatment planning, and follow-ups |
| Common Services | Consultations, diagnosis, prescriptions, monitoring chronic conditions | Oral exams, dental imaging reviews, hygiene counseling, emergency triage |
| Technology Used | Video calls, remote monitoring devices, mobile health apps | Intraoral cameras, digital X-rays, video conferencing tools |
| Patient Benefits | Convenience, access in remote areas, reduced travel and waiting times | Early dental issue detection, reduced dental office visits, personalized care |
| Limitations | Not suitable for physical exams requiring hands-on diagnosis | Limited to diagnostic and consultative care; complex procedures require in-person visits |
Defining Telemedicine and Teledentistry
Telemedicine refers to the delivery of healthcare services remotely through digital communication technologies, enabling diagnosis, treatment, and patient monitoring without in-person visits. Teledentistry is a specialized subset of telemedicine that focuses on dental care, including virtual consultations, oral health assessments, and remote dental consultations. Both telemedicine and teledentistry utilize video conferencing, mobile apps, and digital imaging to enhance access to medical and dental services.
Core Technologies in Telemedicine vs Teledentistry
Telemedicine primarily utilizes video conferencing, mobile health apps, and remote monitoring devices to deliver a wide range of healthcare services, enabling real-time patient-doctor interaction and continuous health tracking. Teledentistry employs specialized imaging technologies such as intraoral cameras, digital X-rays, and CAD/CAM systems to provide precise dental diagnostics and treatment planning remotely. Both fields rely heavily on secure data transmission protocols and cloud-based electronic health records to maintain patient privacy and streamline care coordination.
Clinical Applications and Use Cases
Telemedicine encompasses a broad range of clinical applications including remote diagnosis, chronic disease management, mental health counseling, and follow-up care through video consultations and digital monitoring tools. Teledentistry specializes in dental care delivery, focusing on virtual consultations for oral health assessments, orthodontic evaluations, and post-operative follow-ups using intraoral camera transmission and digital imaging. Both modalities improve access to healthcare services, but teledentistry addresses specific needs like cavity detection, periodontal monitoring, and dental hygiene education remotely.
Patient Access and Engagement
Telemedicine enhances patient access by offering virtual healthcare services across diverse medical specialties, improving convenience and reducing travel barriers. Teledentistry specifically targets oral health, providing remote dental consultations, screenings, and follow-ups, which increases engagement for patients in underserved or rural areas. Both platforms leverage technology to facilitate timely communication and continuous care, but teledentistry uniquely addresses the niche needs of dental health, boosting patient adherence through tailored digital interactions.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Telemedicine and teledentistry face distinct regulatory and legal considerations, with telemedicine broadly governed by state medical boards and HIPAA compliance, while teledentistry must also adhere to dental board regulations and specific licensure requirements across jurisdictions. Both practices require strict patient consent protocols and secure data transmission standards to protect patient privacy under HIPAA and state-specific telehealth laws. Understanding differences in malpractice coverage, prescribing authority, and cross-state licensing is crucial for healthcare providers implementing these digital services.
Data Security and Privacy in Virtual Care
Telemedicine and teledentistry both utilize digital platforms to deliver healthcare, yet data security and privacy in virtual care remain paramount concerns across these fields. Encryption protocols, secure patient authentication, and compliance with HIPAA regulations are critical for protecting sensitive health information transmitted during virtual consultations. While telemedicine often involves broader health data, teledentistry requires specialized safeguards for dental records and imaging, emphasizing tailored cybersecurity measures to uphold patient confidentiality.
Cost Implications for Providers and Patients
Telemedicine generally offers lower setup and operational costs for providers due to broader applicability and existing infrastructure, while teledentistry may require additional specialized equipment and training, increasing initial expenses. Patients benefit from telemedicine's wide range of covered services and lower co-pays, whereas teledentistry can lead to cost savings primarily through reduced travel and quicker access to dental consultations. Both models aim to reduce overall healthcare expenses, but cost-effectiveness varies based on service type, technology adoption, and reimbursement policies.
Overcoming Barriers to Adoption
Telemedicine and teledentistry both address healthcare access challenges, but overcoming barriers to adoption requires targeted strategies specific to each field. Telemedicine faces technological literacy and infrastructure gaps, while teledentistry must tackle insurance coverage limitations and patient-provider trust issues. Implementing user-friendly platforms, expanding broadband access, and improving reimbursement policies are critical for increasing utilization and acceptance across diverse populations.
Patient Outcomes and Satisfaction Metrics
Telemedicine and teledentistry both enhance patient outcomes through improved access and timely care, yet teledentistry specifically addresses oral health issues with tailored remote diagnostics and treatment plans. Patient satisfaction metrics reveal that teledentistry often achieves higher scores in convenience and clarity of communication due to its specialized focus on dental concerns. Studies indicate telemedicine broadly reduces hospital readmissions, while teledentistry significantly decreases emergency dental visits, reflecting distinct impacts on patient health and experience.
Future Trends and Innovations in Digital Health
Telemedicine and teledentistry are rapidly evolving with advancements in AI-powered diagnostics, virtual reality for patient consultations, and enhanced remote monitoring tools. Integration of wearable devices and real-time data analytics is transforming personalized care in both fields, improving patient outcomes and accessibility. Future innovations will prioritize interoperability, augmented reality-assisted procedures, and expanded mobile health platforms to streamline digital health services.
Related Important Terms
Synchronous Telemedicine
Synchronous telemedicine enables real-time video consultations between patients and healthcare providers, facilitating immediate diagnosis and treatment across various medical specialties. In teledentistry, synchronous methods allow dentists to assess oral health, provide consultations, and guide patients during live virtual appointments, improving access to dental care without in-person visits.
Asynchronous Teledentistry
Asynchronous teledentistry enables patients to send dental images and medical histories to dentists for evaluation without real-time interaction, improving access to oral healthcare in remote areas. This method contrasts with general telemedicine by specializing in dental diagnostics and treatment planning, reducing appointment delays and optimizing resource allocation.
Store-and-Forward Imaging
Store-and-forward imaging in telemedicine allows healthcare providers to securely share medical images such as X-rays and MRIs for remote diagnosis and consultation, improving patient care efficiency. In teledentistry, this technology enables dentists to exchange dental images and records asynchronously, facilitating timely treatment planning without the need for synchronous patient visits.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) in telemedicine involves continuous health data collection through connected devices to manage chronic conditions and improve patient outcomes, while teledentistry utilizes RPM specifically for dental health by remotely monitoring oral conditions and treatment progress. Both fields leverage real-time biometric data and patient feedback to enhance personalized care, but teledentistry emphasizes dental imaging and symptom tracking to prevent oral diseases effectively.
Virtual Dental Home
Telemedicine expands healthcare access through remote clinical services, while teledentistry specifically targets oral health via digital platforms. The Virtual Dental Home model leverages teledentistry by enabling dental hygienists to collect patient data in community settings, which dentists then review remotely to provide timely, efficient care.
Distant Site Provider
Telemedicine and teledentistry both utilize distant site providers to deliver healthcare services remotely, but telemedicine covers a broad range of medical specialties while teledentistry specifically addresses oral health care, including diagnosis, consultation, and treatment planning. Distant site providers in telemedicine connect with patients through video conferencing, remote monitoring, and electronic health records, whereas teledentistry providers focus on dental imaging and patient education to improve access to dental care in underserved areas.
Mobile Health Units
Mobile health units equipped for telemedicine provide comprehensive medical consultations, remote diagnostics, and real-time patient monitoring, enhancing access to healthcare in underserved areas. In contrast, mobile teledentistry units focus on oral health services, offering virtual dental screenings, preventive care, and emergency consultations, which significantly reduce barriers to dental care in remote communities.
Intraoral Cameras
Intraoral cameras enhance telemedicine and teledentistry by providing high-resolution, real-time visuals for remote diagnosis and treatment planning, improving patient outcomes and accessibility to dental care. These devices enable dentists to detect cavities, lesions, and other oral health issues accurately during virtual consultations, bridging the gap between traditional in-office exams and digital healthcare services.
Telediagnosis
Teledentistry leverages telemedicine principles to provide remote telediagnosis for dental conditions, enabling dentists to assess oral health using digital imaging and patient data without in-person visits. This technology enhances early detection of dental issues, improves access to specialist consultations, and facilitates timely treatment planning, especially in underserved or rural areas.
E-prescriptions in Teledentistry
E-prescriptions in teledentistry streamline dental care by enabling remote prescription of medications such as antibiotics and pain relievers, reducing the need for in-person visits. This digital approach enhances patient convenience and adherence to treatment plans while maintaining safety through secure electronic health records and pharmacy integration.
Telemedicine vs Teledentistry Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com