Records management involves the systematic control of official documents and data throughout their lifecycle, ensuring accuracy, accessibility, and compliance. Digital twins create dynamic, real-time virtual replicas of physical assets or processes, enabling simulation, monitoring, and predictive analysis. While records management focuses on archival and retrieval of static information, digital twins emphasize continuous data integration for operational optimization.
Table of Comparison
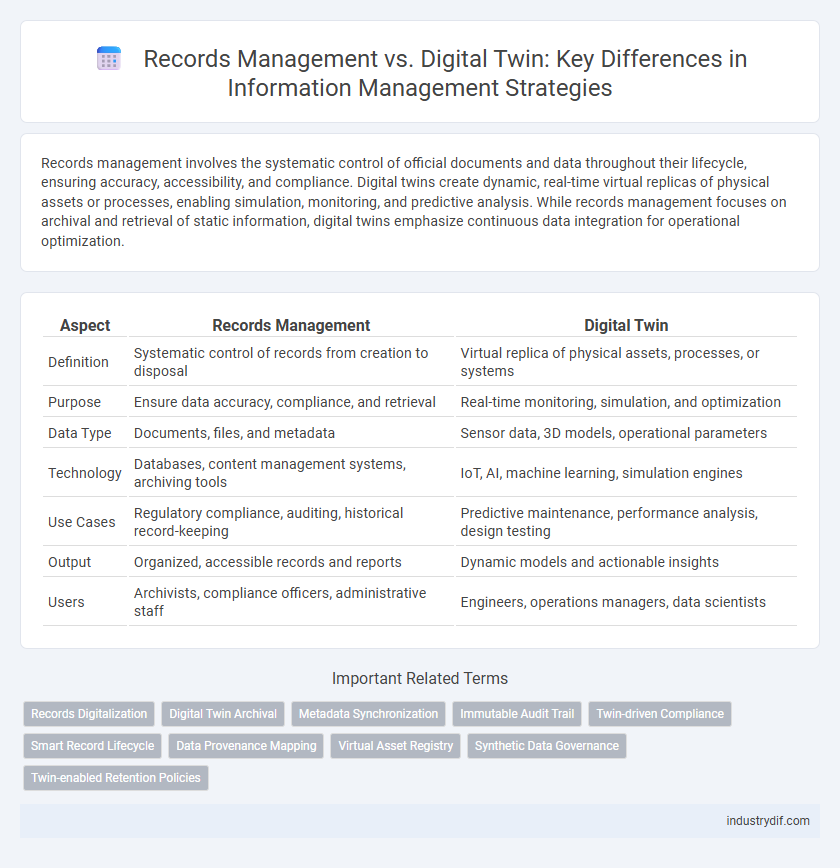
| Aspect | Records Management | Digital Twin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic control of records from creation to disposal | Virtual replica of physical assets, processes, or systems |
| Purpose | Ensure data accuracy, compliance, and retrieval | Real-time monitoring, simulation, and optimization |
| Data Type | Documents, files, and metadata | Sensor data, 3D models, operational parameters |
| Technology | Databases, content management systems, archiving tools | IoT, AI, machine learning, simulation engines |
| Use Cases | Regulatory compliance, auditing, historical record-keeping | Predictive maintenance, performance analysis, design testing |
| Output | Organized, accessible records and reports | Dynamic models and actionable insights |
| Users | Archivists, compliance officers, administrative staff | Engineers, operations managers, data scientists |
Introduction to Records Management and Digital Twin
Records Management involves systematically capturing, organizing, and maintaining documents and data to ensure accessibility, compliance, and security throughout their lifecycle. Digital Twin technology creates real-time, virtual replicas of physical assets or systems for simulation, monitoring, and optimization purposes. Integrating Records Management with Digital Twin platforms enhances data accuracy, operational efficiency, and decision-making in asset-intensive industries.
Core Concepts: Understanding Records Management
Records management involves the systematic control of an organization's records throughout their lifecycle, ensuring accuracy, accessibility, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical assets or processes, primarily used for simulation and real-time monitoring. Understanding records management is crucial for maintaining data integrity and legal accountability, providing a foundation that complements the dynamic, real-time data utilization found in digital twin technology.
Core Concepts: Understanding Digital Twin Technology
Digital twin technology creates a dynamic, real-time digital replica of physical assets or systems, enabling continuous monitoring and simulation to optimize performance. In contrast, records management focuses on the systematic control, storage, and retrieval of static documents and data for compliance and organizational efficiency. Digital twins integrate IoT sensors and advanced analytics, offering predictive insights beyond traditional records management's archival approach.
Key Differences: Records Management vs Digital Twin
Records management involves the systematic control and maintenance of documents and data to ensure compliance, accessibility, and preservation over time. Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical assets or systems, enabling real-time monitoring, simulation, and optimization through data integration and analytics. Key differences include records management focusing on information governance and lifecycle management, while digital twins emphasize dynamic, real-time interaction and predictive insights in operational environments.
Data Lifecycle: Creation, Storage, and Retrieval
Records Management ensures data lifecycle integrity through systematic creation, secure storage, and efficient retrieval, emphasizing compliance and long-term preservation. Digital Twin technology focuses on real-time data creation, dynamic storage, and immediate retrieval to mirror physical assets, supporting predictive analysis and operational optimization. Integrating both approaches enhances data accuracy, accessibility, and lifecycle management across physical and digital environments.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Records management ensures security and compliance by maintaining accurate, auditable documentation that adheres to regulatory standards such as GDPR and HIPAA. Digital twins enhance security through real-time monitoring and predictive analytics but require robust encryption and access controls to protect sensitive operational data. Both systems demand comprehensive governance frameworks to mitigate risks and ensure compliance with industry-specific regulations.
Integration with Enterprise Systems
Records management integrates with enterprise systems by ensuring secure, compliant data storage and streamlined access across platforms, enhancing operational efficiency. Digital twin technology connects with enterprise systems through real-time data synchronization, enabling predictive analytics and performance optimization of physical assets. Together, they create a cohesive framework where historical records support digital twin insights, fostering informed decision-making and improved asset lifecycle management.
Use Cases in Modern Industries
Records management ensures systematic organization, storage, and retrieval of critical business documents, facilitating compliance and audit readiness across industries such as healthcare, finance, and legal sectors. Digital twins create virtual replicas of physical assets or processes, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and performance optimization in manufacturing, energy, and smart cities. Combining records management with digital twin technology enhances decision-making by linking historical data with live operational insights, driving innovation and operational efficiency.
Challenges and Limitations Compared
Records management faces challenges such as physical storage constraints, data retrieval inefficiencies, and risks of document deterioration or loss. Digital twins encounter limitations related to high implementation costs, complex integration with existing systems, and data accuracy depending on sensor reliability. Both approaches struggle with ensuring data security and maintaining up-to-date information for effective decision-making.
Future Trends in Records Management and Digital Twin
Future trends in records management emphasize integration with digital twin technologies to enhance data accuracy, real-time monitoring, and predictive analytics. Implementing AI-driven automation and blockchain ensures secure, immutable records that synchronize seamlessly with digital twins for improved lifecycle management. Emerging standards focus on interoperability and scalability, enabling comprehensive decision-making across industries using combined datasets from records management systems and digital twin environments.
Related Important Terms
Records Digitalization
Records management leverages digitalization to convert physical documents into structured electronic formats, enhancing accessibility, searchability, and compliance across organizational systems. Digital twins complement this process by creating dynamic virtual replicas of records management infrastructures, enabling real-time monitoring, data synchronization, and predictive analysis for business continuity and operational efficiency.
Digital Twin Archival
Digital Twin archival involves the systematic preservation of dynamic, real-time data models that replicate physical assets, enabling accurate historical analysis and lifecycle management. Unlike traditional records management, which focuses on static documents, Digital Twin archives integrate continuous sensor data and simulation outputs to support predictive maintenance and operational insights.
Metadata Synchronization
Records management ensures accurate metadata synchronization by systematically cataloging and preserving document attributes, which enhances data integrity and compliance. Digital twin technology integrates real-time operational metadata with physical asset data, enabling dynamic updates and improved decision-making across systems.
Immutable Audit Trail
Records management ensures a trustworthy immutable audit trail by securely preserving historical documents with strict version control and tamper-evident features. Digital twins, while offering real-time data integration and simulation, rely on underlying records management systems to maintain an unalterable audit trail for compliance and accountability.
Twin-driven Compliance
Records management ensures accurate documentation and regulatory compliance through systematic control of physical and digital records, while digital twin technology enhances twin-driven compliance by providing real-time, dynamic simulations of assets and processes for predictive auditing and risk mitigation. Integrating digital twins with records management enables continuous monitoring, automated compliance reporting, and improved decision-making in complex regulatory environments.
Smart Record Lifecycle
Smart Record Lifecycle integrates records management principles with digital twin technology to enhance data accuracy, accessibility, and compliance throughout an asset's lifecycle. By synchronizing physical records with real-time digital replicas, organizations achieve improved decision-making, risk reduction, and streamlined regulatory adherence.
Data Provenance Mapping
Records management ensures accurate data provenance mapping by systematically tracking document origination, modifications, and custodianship throughout the information lifecycle. Digital twin technology enhances provenance mapping by creating dynamic virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling real-time data integration and comprehensive historical traceability.
Virtual Asset Registry
Records management systematically organizes and preserves physical and digital documents to ensure compliance and accessibility, while a digital twin creates a dynamic virtual asset registry that mirrors real-time data and operational states of physical assets. Integrating digital twin technology enhances asset lifecycle tracking and predictive maintenance by providing up-to-date, interactive virtual models, surpassing traditional records management limitations.
Synthetic Data Governance
Records management ensures the systematic control of physical and digital records for compliance and retrieval, while digital twins utilize real-time virtual representations of assets to enhance operational insights. Synthetic data governance in digital twins enables secure, privacy-compliant data generation by simulating real-world scenarios without exposing sensitive information.
Twin-enabled Retention Policies
Twin-enabled retention policies leverage digital twin technology to enhance records management by automating data classification and lifecycle tracking based on real-time asset performance and operational conditions. Integrating digital twins with records management systems ensures precise retention schedules, reduces compliance risks, and optimizes storage by dynamically adjusting policies according to the twin's evolving digital footprint.
Records Management vs Digital Twin Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com