A boss directs tasks and enforces rules to achieve specific goals, often focusing on performance and results. A culture steward nurtures the workplace environment by promoting shared values, encouraging collaboration, and fostering employee engagement. Effective management balances authoritative leadership with cultural stewardship to build a motivated, cohesive team.
Table of Comparison
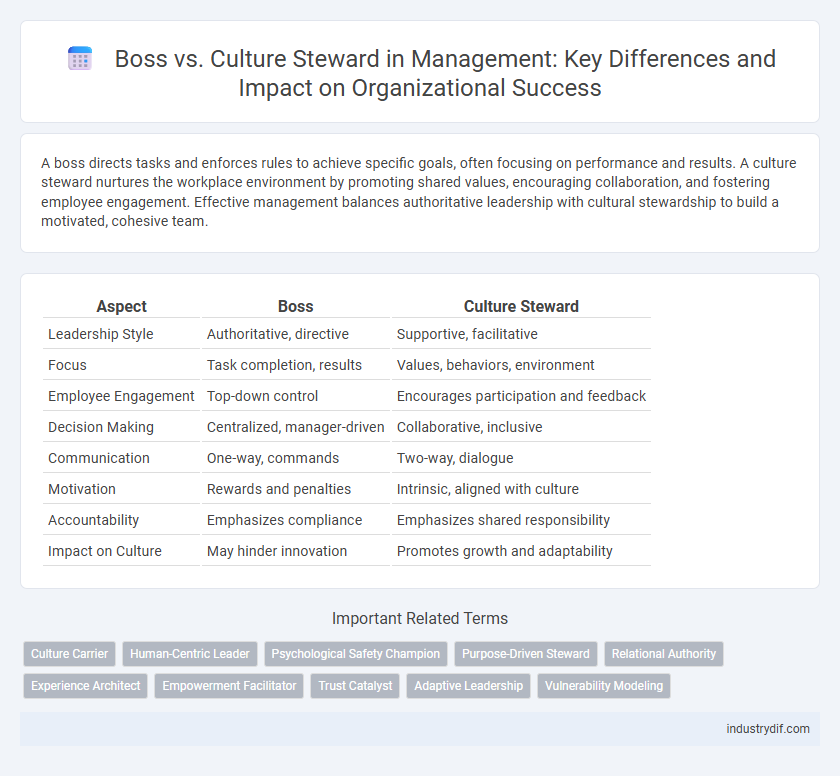
| Aspect | Boss | Culture Steward |
|---|---|---|
| Leadership Style | Authoritative, directive | Supportive, facilitative |
| Focus | Task completion, results | Values, behaviors, environment |
| Employee Engagement | Top-down control | Encourages participation and feedback |
| Decision Making | Centralized, manager-driven | Collaborative, inclusive |
| Communication | One-way, commands | Two-way, dialogue |
| Motivation | Rewards and penalties | Intrinsic, aligned with culture |
| Accountability | Emphasizes compliance | Emphasizes shared responsibility |
| Impact on Culture | May hinder innovation | Promotes growth and adaptability |
Defining Boss vs Culture Steward
A boss primarily enforces rules and directs employees to achieve organizational goals, relying on authority and control. In contrast, a culture steward nurtures a supportive environment by modeling values, fostering collaboration, and encouraging employee engagement. Effective leaders balance both roles to drive performance while sustaining a positive workplace culture.
Key Characteristics of a Boss
A boss typically exercises authoritative control, prioritizing task completion and enforcing rules to maintain order and productivity. They often rely on positional power to direct employees and make decisions unilaterally. Key characteristics include decisiveness, accountability for results, and a clear hierarchy that emphasizes command and compliance.
Essential Traits of a Culture Steward
A Culture Steward embodies empathy, effective communication, and consistency, guiding teams to align with organizational values and purpose. They prioritize psychological safety and inclusivity, fostering an environment where innovation and collaboration flourish. Unlike traditional bosses who focus primarily on authority and control, Culture Stewards inspire intrinsic motivation and nurture long-term employee engagement.
Leadership Styles: Command vs Influence
Boss leadership relies heavily on command tactics, enforcing rules through authority and top-down directives that prioritize control and compliance. Culture Stewards emphasize influence by fostering collaboration, trust, and shared values, encouraging employee engagement and intrinsic motivation. Effective leadership balances command for clear expectations with influence to inspire commitment and innovation within organizational culture.
Decision-Making Approaches Compared
Bosses typically rely on authoritative decision-making, emphasizing control and quick resolutions to drive short-term results. Culture stewards prioritize inclusive and collaborative decision-making, fostering shared values and long-term organizational alignment. This approach enhances employee engagement and adaptability by integrating diverse perspectives into strategic choices.
Impact on Employee Engagement
A boss often drives task completion through authority and directive management, which can limit employee autonomy and reduce engagement levels. In contrast, a culture steward fosters a supportive environment that emphasizes shared values, collaboration, and recognition, significantly enhancing employee motivation and commitment. This stewardship approach leads to higher retention rates and sustained organizational performance by deeply engaging employees in the company's mission.
Effects on Organizational Culture
A boss typically enforces rules and drives short-term results, often creating a top-down organizational culture marked by compliance and fear of failure. A culture steward actively shapes and nurtures core values, fostering collaboration, trust, and long-term commitment among employees. This stewardship leads to higher employee engagement, innovation, and sustained organizational success.
Navigating Change: Boss vs Culture Steward
Navigating change requires a shift from the traditional boss mindset to a culture steward approach that emphasizes collaboration, empathy, and adaptability. While bosses often rely on authority and directives to enforce change, culture stewards foster an environment where employees feel valued and are empowered to contribute to transformation initiatives. This shift enhances organizational resilience and drives sustainable growth during periods of change.
Talent Retention and Development
Effective talent retention and development hinge on leadership that prioritizes culture stewardship over authoritative boss-like management. Culture stewards cultivate environments where employees feel valued, supported, and motivated to grow, thereby reducing turnover and enhancing skill progression. Organizations with strong culture stewards report higher employee engagement and accelerated internal talent development compared to those led primarily by directive bosses.
Future Trends in Leadership Roles
Future trends in leadership emphasize a shift from the traditional boss model to culture stewardship, prioritizing empathy, inclusivity, and employee empowerment. Leaders act as culture stewards by fostering environments that support innovation, collaboration, and continuous learning, aligning organizational values with evolving workforce expectations. This approach enhances employee engagement and drives long-term success in dynamic, competitive markets.
Related Important Terms
Culture Carrier
A culture carrier actively embodies and reinforces organizational values, serving as a role model who influences team behavior and mindset more effectively than a traditional boss focused solely on authority. This approach fosters trust, collaboration, and engagement, driving sustainable performance and long-term cultural alignment within the company.
Human-Centric Leader
A human-centric leader acts as a culture steward by prioritizing employee well-being, fostering trust, and promoting open communication, which drives engagement and innovation. Unlike traditional bosses who focus on directives and control, culture stewards cultivate environments where collaboration and personal growth thrive.
Psychological Safety Champion
A Culture Steward fosters psychological safety by promoting open communication and validating diverse perspectives, ensuring team members feel secure and valued. Unlike a traditional boss who may prioritize control, a Psychological Safety Champion empowers collaboration and innovation through trust and empathy.
Purpose-Driven Steward
A purpose-driven steward prioritizes cultivating a mission-aligned organizational culture that empowers employees and drives sustainable success, contrasting with a traditional boss who often emphasizes authority and control. This leadership approach integrates core values and long-term vision into daily operations, fostering engagement, innovation, and accountability across teams.
Relational Authority
Relational authority in management emphasizes influence built through trust, empathy, and collaboration, distinguishing a culture steward from a traditional boss who relies on positional power and directives. Culture stewards foster sustainable team engagement by nurturing shared values and emotional connections, enhancing organizational cohesion and performance.
Experience Architect
Experience architects shape organizational culture by designing environments that prioritize employee engagement and innovation, contrasting with bosses who primarily focus on authority and task execution. By fostering collaboration and psychological safety, experience architects enable sustainable culture development that drives long-term business success.
Empowerment Facilitator
A Boss directs tasks and enforces rules, often limiting employee autonomy, whereas a Culture Steward acts as an Empowerment Facilitator by nurturing trust, encouraging collaboration, and enabling team members to take ownership of their work. This approach drives higher engagement, innovation, and sustainable organizational growth through a culture of empowerment and accountability.
Trust Catalyst
A Boss drives results primarily through authority and control, often limiting open communication and employee engagement, whereas a Culture Steward fosters a trusting environment that encourages collaboration and innovation by acting as a trust catalyst. Trust catalysts increase organizational transparency, promote psychological safety, and empower teams, leading to higher employee satisfaction and sustained performance.
Adaptive Leadership
Adaptive leadership demands that managers act as culture stewards rather than traditional bosses, guiding teams through change by fostering collaboration and learning. This approach emphasizes emotional intelligence, resilience, and the ability to navigate complex organizational dynamics to sustain a thriving corporate culture.
Vulnerability Modeling
A Culture Steward enhances organizational trust by modeling vulnerability, encouraging open communication and psychological safety among team members. Bosses who embrace vulnerability foster collaboration, innovation, and resilience, transforming workplace dynamics beyond traditional authority-based management.
Boss vs Culture Steward Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com