Bosses often rely on authority and control to direct teams, while servant leaders prioritize the growth and well-being of their employees. Servant leadership fosters trust, collaboration, and empowerment, resulting in higher employee engagement and productivity. Choosing servant leadership over a traditional boss approach cultivates a positive work environment that drives sustainable success.
Table of Comparison
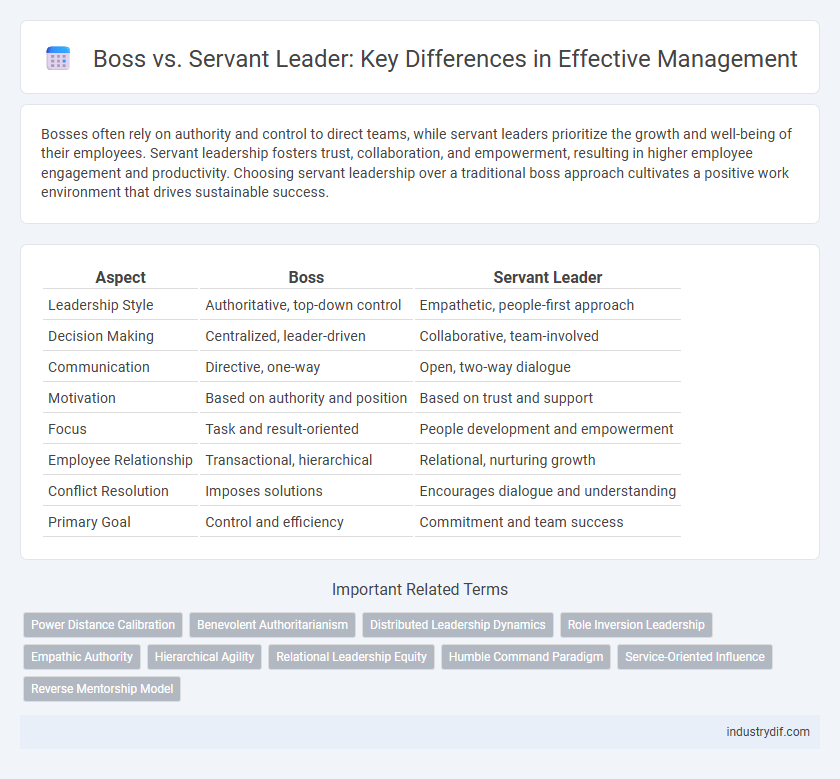
| Aspect | Boss | Servant Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Leadership Style | Authoritative, top-down control | Empathetic, people-first approach |
| Decision Making | Centralized, leader-driven | Collaborative, team-involved |
| Communication | Directive, one-way | Open, two-way dialogue |
| Motivation | Based on authority and position | Based on trust and support |
| Focus | Task and result-oriented | People development and empowerment |
| Employee Relationship | Transactional, hierarchical | Relational, nurturing growth |
| Conflict Resolution | Imposes solutions | Encourages dialogue and understanding |
| Primary Goal | Control and efficiency | Commitment and team success |
Defining Boss vs Servant Leader
A boss typically exercises authority through control and directs employees to achieve organizational goals, emphasizing hierarchy and task completion. A servant leader prioritizes the well-being and development of team members, fostering collaboration and empowering individuals to contribute meaningfully. The distinction lies in the approach to leadership: one focuses on command and control, while the other emphasizes support and service.
Key Characteristics of Bosses
Bosses often exercise authoritative control, emphasizing hierarchy and direct commands to maintain order and achieve goals efficiently. They prioritize task completion and expect obedience, frequently relying on positional power rather than personal influence. Bosses may focus on short-term results, using punishment or rewards to motivate employees rather than fostering collaboration or empowerment.
Core Traits of Servant Leaders
Servant leaders prioritize empathy, listening, and stewardship, fostering a collaborative and supportive work environment that drives team empowerment and growth. They exhibit strong commitment to the personal and professional development of their employees, promoting trust and open communication. Core traits such as humility, self-awareness, and a focus on serving others distinguish servant leadership from traditional authoritative management styles.
Communication Styles Compared
Bosses often rely on directive communication, issuing commands and expecting compliance, which creates a top-down flow of information. Servant leaders emphasize active listening and open dialogue, fostering collaboration and trust within their teams. This shift toward empathetic communication enhances employee engagement and drives better organizational performance.
Decision-Making Approaches
Bosses typically adopt a top-down decision-making approach, emphasizing control and authority to direct team actions and ensure adherence to organizational goals. In contrast, servant leaders prioritize collaborative decision-making, encouraging input from team members to foster trust, empowerment, and shared ownership of outcomes. This participative style enhances innovation and employee engagement by valuing diverse perspectives within the decision process.
Impact on Team Performance
Boss leadership often results in decreased team morale and limited innovation due to authoritative decision-making and lack of empathy. Servant leadership enhances team performance by fostering trust, collaboration, and personal growth, leading to higher engagement and productivity. Studies show teams led by servant leaders experience up to 20% greater efficiency and employee satisfaction compared to those led by traditional bosses.
Influence on Workplace Culture
Bosses often rely on authority and control, which can create a hierarchical and rigid workplace culture marked by limited employee engagement. Servant leaders prioritize empathy, support, and development, fostering a collaborative and trust-based environment that enhances morale and productivity. This approach encourages innovation and loyalty, leading to sustained organizational growth and a positive workplace atmosphere.
Employee Empowerment & Engagement
Bosses typically exercise control through directives, limiting employee autonomy and often reducing engagement levels. In contrast, servant leaders prioritize employee empowerment by fostering trust, encouraging collaboration, and supporting professional growth, which significantly enhances motivation and commitment. Studies show organizations embracing servant leadership experience up to 50% higher employee engagement and improved retention rates.
Leadership Outcomes in Industry
Boss leadership often results in lower employee engagement, reduced innovation, and higher turnover rates, negatively impacting organizational performance. Servant leadership fosters a culture of trust, collaboration, and empowerment, leading to increased productivity and enhanced customer satisfaction. Industry studies reveal companies with servant leaders experience sustained growth and stronger competitive advantages.
Choosing the Right Leadership Model
Selecting the right leadership model significantly impacts organizational culture and employee engagement. Boss leadership often relies on authority and control, driving short-term compliance but potentially hindering innovation and morale. Servant leadership prioritizes empathy, collaboration, and employee development, fostering long-term trust and sustainable productivity.
Related Important Terms
Power Distance Calibration
Effective management requires calibrating power distance by balancing authoritative decision-making with servant leadership's emphasis on empathy and team empowerment. Bosses often maintain high power distance to assert control, whereas servant leaders minimize hierarchical gaps to foster collaboration and trust.
Benevolent Authoritarianism
Benevolent authoritarianism in management emphasizes a leadership style where the boss maintains strict control and authority while prioritizing employee welfare and organizational goals, blending decisiveness with empathy. This approach contrasts with servant leadership by upholding hierarchical power to guide and protect teams rather than relinquishing control to promote autonomy.
Distributed Leadership Dynamics
Distributed leadership dynamics emphasize collaboration and shared responsibility, contrasting with traditional boss-centered models that centralize decision-making authority. Servant leaders foster autonomy and empowerment within teams, driving innovation and collective accountability in organizational management.
Role Inversion Leadership
Role inversion leadership redefines traditional hierarchies by positioning leaders as supporters rather than commanders, emphasizing empowerment, active listening, and facilitation. This approach fosters trust and collaboration, contrasting sharply with the authoritative control typical of boss-centered management.
Empathic Authority
Empathic authority in servant leadership fosters trust and collaboration by prioritizing the emotional well-being and development of team members, contrasting with traditional boss leadership that often relies on positional power and control. This approach enhances employee engagement, innovation, and long-term organizational success through genuine understanding and support.
Hierarchical Agility
Hierarchical agility distinguishes boss leadership, which relies on rigid authority and top-down control, from servant leadership, which embraces flexibility and empowerment across organizational levels. Servant leaders promote adaptive decision-making and agile communication, enabling teams to respond swiftly to dynamic challenges and enhance overall performance.
Relational Leadership Equity
Bosses often exercise authority through hierarchical power, whereas servant leaders prioritize relational leadership equity by fostering trust, collaboration, and shared decision-making among team members. This approach enhances organizational commitment and drives sustainable performance by valuing employee empowerment and mutual respect.
Humble Command Paradigm
Humble command paradigm positions servant leadership as a powerful contrast to traditional boss-driven management by emphasizing empathy, active listening, and empowering team members to enhance collaboration and innovation. This approach fosters trust and accountability, driving sustainable organizational success through servant leaders' commitment to serving first rather than commanding from a hierarchical stance.
Service-Oriented Influence
Service-oriented leaders prioritize the growth and well-being of their team by empowering employees, fostering collaboration, and modeling humility, which contrasts with traditional bosses who exercise authority through control and directive commands. This approach enhances organizational performance, employee engagement, and trust by emphasizing support and inspiration rather than hierarchy and power.
Reverse Mentorship Model
The Reverse Mentorship Model in management shifts traditional dynamics by empowering junior employees to share insights and expertise with senior leaders, fostering innovation and inclusivity. This approach contrasts with the Boss mentality, promoting servant leadership that values collaboration, continuous learning, and mutual respect across hierarchical levels.
Boss vs Servant Leader Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com