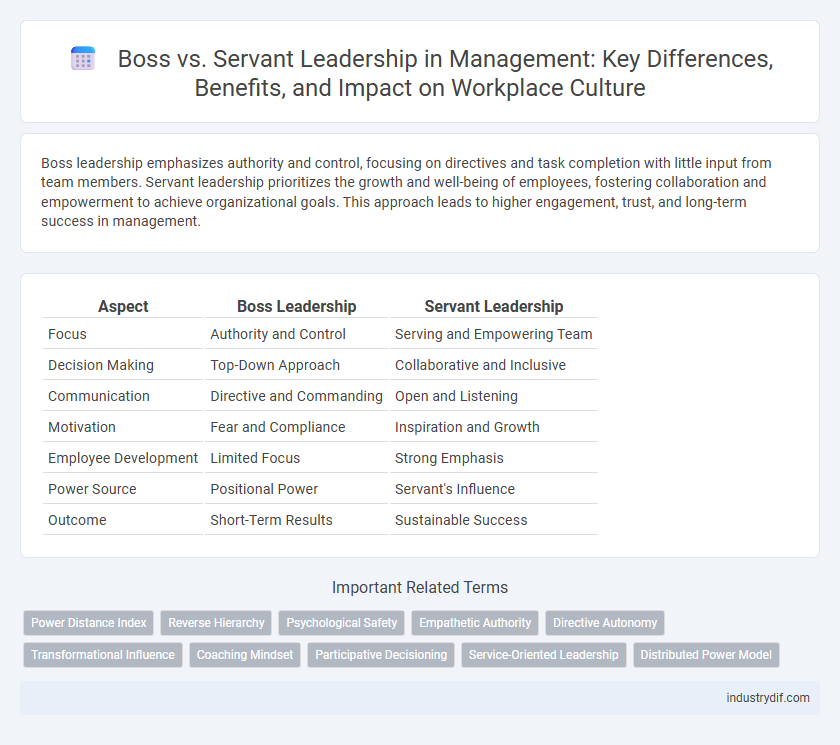
Boss leadership emphasizes authority and control, focusing on directives and task completion with little input from team members. Servant leadership prioritizes the growth and well-being of employees, fostering collaboration and empowerment to achieve organizational goals. This approach leads to higher engagement, trust, and long-term success in management.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Boss Leadership | Servant Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Authority and Control | Serving and Empowering Team |
| Decision Making | Top-Down Approach | Collaborative and Inclusive |
| Communication | Directive and Commanding | Open and Listening |
| Motivation | Fear and Compliance | Inspiration and Growth |
| Employee Development | Limited Focus | Strong Emphasis |
| Power Source | Positional Power | Servant's Influence |
| Outcome | Short-Term Results | Sustainable Success |
Defining Boss Leadership: Key Characteristics
Boss leadership is defined by authoritative decision-making, a top-down communication style, and strict control over subordinates' tasks and behaviors. This leadership approach often emphasizes compliance, clear directives, and performance metrics to enforce organizational goals. It prioritizes hierarchy and power, aiming for efficiency through command and control rather than collaboration.
Understanding Servant Leadership Principles
Servant Leadership emphasizes prioritizing the needs of employees and empowering them to achieve their full potential, fostering a collaborative and trust-based work environment. Key principles include empathy, active listening, stewardship, and commitment to the growth of people, which contrast sharply with traditional authoritative boss-centered approaches. This leadership style enhances organizational performance by promoting ethical behavior, employee engagement, and sustainable team development.
Decision-Making Styles: Top-Down vs Collaborative
Boss leadership typically employs a top-down decision-making style where directives flow from a central authority, emphasizing control and efficiency in management processes. Servant leadership prioritizes collaborative decision-making, engaging team members to contribute insights, fostering trust and shared ownership of outcomes. This collaborative approach often leads to increased innovation, employee satisfaction, and organizational agility.
Communication Approaches in Leadership Models
Boss leadership often relies on top-down, directive communication that emphasizes control and authority, leading to limited feedback and reduced team engagement. Servant leadership prioritizes open, empathetic dialogue, encouraging active listening and collaborative problem-solving to foster trust and empowerment among team members. Effective leadership communication models integrate transparency and responsiveness, enhancing organizational cohesion and performance.
Employee Engagement and Motivation Impact
Servant leadership significantly boosts employee engagement by fostering a supportive environment where team members feel valued and empowered, leading to higher motivation and productivity. In contrast, traditional boss leadership often relies on authority and control, which can diminish employee enthusiasm and reduce overall commitment. Studies indicate that organizations embracing servant leadership see increased retention rates and improved job satisfaction metrics compared to those with authoritarian management styles.
Productivity Outcomes: Comparing Leadership Styles
Boss leadership often emphasizes control and directive actions, leading to short-term productivity gains but potentially stifling creativity and employee engagement. Servant leadership fosters a supportive environment that enhances motivation, collaboration, and long-term performance improvements. Studies show organizations with servant leaders experience higher employee satisfaction and sustainable productivity growth compared to traditional boss-led workplaces.
Organizational Culture Shaped by Leadership
Servant leadership fosters a collaborative organizational culture by prioritizing employee empowerment, trust, and open communication, which boosts motivation and innovation. In contrast, boss leadership often cultivates a hierarchical culture characterized by rigid control, top-down decision-making, and limited employee autonomy. Organizational culture shaped by servant leaders typically exhibits higher levels of employee engagement, job satisfaction, and retention compared to cultures dominated by authoritarian leadership styles.
Navigating Change: Boss vs Servant Leader Responses
Boss leadership often relies on top-down directives and control during organizational change, potentially stifling innovation and employee engagement. In contrast, servant leaders prioritize empathy, active listening, and empowerment, fostering collaboration and adaptability that drive successful change adoption. Research indicates servant leadership enhances team resilience and trust, essential for navigating complex change environments effectively.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Leadership Style
Boss leadership often faces challenges such as resistance due to authoritative decision-making and limited employee engagement, which can result in low morale and decreased productivity. Servant leadership, while fostering trust and collaboration, may struggle with decisiveness and boundary-setting, potentially leading to delayed decisions and role ambiguity. Both styles are limited by their inherent focus--boss leadership emphasizes control, whereas servant leadership prioritizes support--requiring organizations to balance these approaches for effective management.
Adopting Effective Leadership in Modern Management
Effective leadership in modern management relies on embracing servant leadership principles, which prioritize employee empowerment, active listening, and fostering collaboration. Unlike traditional boss leadership that emphasizes authority and control, servant leadership enhances team performance by promoting trust and emotional intelligence. Organizations adopting this approach experience higher employee engagement and innovation, driving sustainable success in dynamic business environments.
Related Important Terms
Power Distance Index
Boss leadership often emphasizes hierarchical authority and clear power distance, creating a top-down management style where decisions flow from the leader to subordinates. In contrast, servant leadership reduces power distance by promoting collaboration, empathy, and shared decision-making, fostering a more inclusive and participative organizational culture.
Reverse Hierarchy
Reverse hierarchy in servant leadership empowers employees by placing the leader at the service of the team, fostering increased autonomy, innovation, and collaboration compared to traditional boss-centered management. This approach shifts decision-making closer to frontline workers, enhancing organizational agility and employee engagement.
Psychological Safety
Boss leadership often suppresses psychological safety by enforcing strict control and discouraging risk-taking, leading to reduced employee engagement and innovation. Servant leadership fosters psychological safety by prioritizing empathy and support, enabling team members to express ideas freely and collaborate effectively.
Empathetic Authority
Empathetic authority in leadership balances assertiveness with genuine understanding, enhancing team trust and motivation through active listening and emotional intelligence. Servant leadership prioritizes employee well-being and development, fostering collaboration, while traditional boss roles emphasize control and directive decision-making.
Directive Autonomy
Directive autonomy in boss leadership centers on top-down decision-making with limited employee input, emphasizing control and adherence to instructions. Servant leadership promotes autonomous decision-making by empowering employees, fostering collaboration, and enhancing engagement through supportive guidance.
Transformational Influence
Transformational influence in leadership emphasizes inspiring and motivating employees to exceed expectations through vision and personal development rather than relying on authority or control typical of boss-centered management. Servant leadership fosters a supportive environment where leaders prioritize employee growth and empowerment, driving innovation and organizational change by focusing on collaboration and shared goals.
Coaching Mindset
Boss leadership emphasizes authority and control, often directing teams with top-down decisions, whereas servant leadership prioritizes supporting and empowering team members through a coaching mindset that fosters growth and autonomy. This coaching approach cultivates trust, enhances collaboration, and drives higher engagement by focusing on employee development rather than merely task completion.
Participative Decisioning
Participative decision-making in servant leadership fosters collaboration by involving team members in the decision process, enhancing engagement and innovation, unlike traditional boss leadership which centralizes authority and limits input. This inclusive approach promotes trust, accountability, and improved organizational performance through shared responsibility.
Service-Oriented Leadership
Service-oriented leadership emphasizes empowering employees by prioritizing their needs, fostering trust, and enhancing collaboration, leading to higher engagement and productivity. Unlike traditional boss leadership, which relies on authority and control, servant leadership cultivates a positive organizational culture that drives sustainable success through empathy and support.
Distributed Power Model
The Distributed Power Model in leadership emphasizes decentralized decision-making, where both boss and servant leadership styles share authority across teams to enhance collaboration and innovation. By distributing power, organizations foster autonomy and accountability, enabling leaders to serve the needs of employees while maintaining strategic oversight.
Boss vs Servant Leadership Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com