Centralization in management pet fosters streamlined decision-making by concentrating authority at the top, enhancing consistency and control. Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) distributes decision power across members, promoting transparency, agility, and member empowerment through blockchain technology. Balancing centralization with DAO structures can optimize governance efficiency while encouraging innovation and responsiveness within the organization.
Table of Comparison
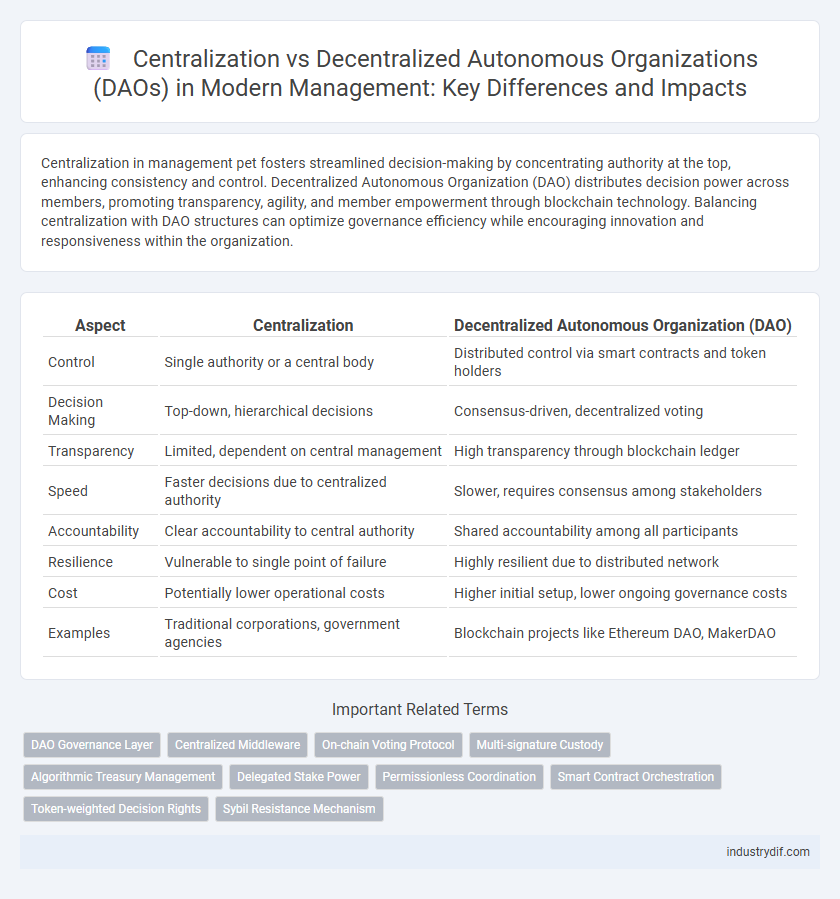
| Aspect | Centralization | Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Single authority or a central body | Distributed control via smart contracts and token holders |
| Decision Making | Top-down, hierarchical decisions | Consensus-driven, decentralized voting |
| Transparency | Limited, dependent on central management | High transparency through blockchain ledger |
| Speed | Faster decisions due to centralized authority | Slower, requires consensus among stakeholders |
| Accountability | Clear accountability to central authority | Shared accountability among all participants |
| Resilience | Vulnerable to single point of failure | Highly resilient due to distributed network |
| Cost | Potentially lower operational costs | Higher initial setup, lower ongoing governance costs |
| Examples | Traditional corporations, government agencies | Blockchain projects like Ethereum DAO, MakerDAO |
Definition of Centralization in Management
Centralization in management refers to the concentration of decision-making authority at the upper levels of an organizational hierarchy, where top executives hold the power to make key strategic decisions. This structure enables uniformity in policies, streamlined communication, and consistent implementation across all departments. Centralized management often leads to faster decision-making in crisis situations due to clear authority lines but may reduce flexibility and responsiveness at lower organizational levels.
Understanding Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) operate on blockchain technology, enabling transparent, trustless governance without centralized control. DAOs use smart contracts to automate decision-making processes, ensuring member participation and consensus through token-based voting systems. This structure enhances efficiency and democratizes authority, contrasting with traditional centralized management models.
Key Differences Between Centralization and DAOs
Centralization in management consolidates decision-making authority within a single leadership structure, enhancing control but often limiting agility and innovation. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) operate on blockchain technology, enabling distributed governance where stakeholders participate directly in decisions through smart contracts, promoting transparency and collective ownership. Key differences include the locus of control, with centralization favoring hierarchical power and DAOs emphasizing democratic participation enabled by automated protocols.
Governance Structures: Centralized vs DAO Models
Centralized governance structures concentrate decision-making authority within a top management layer, enabling streamlined control and uniform policies. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) distribute governance across members through blockchain-based voting mechanisms, promoting transparency and collective decision-making. The DAO model reduces hierarchical bottlenecks, enhancing adaptability but requiring robust consensus protocols to maintain cohesion.
Decision-Making Processes in Both Systems
Centralization consolidates decision-making authority at the top levels of management, enabling unified strategies and consistent policies across the organization. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) distribute decision-making power among members using blockchain technology and smart contracts, fostering transparency and democratic participation. While centralization offers streamlined control and swift execution, DAOs enhance flexibility and collective governance by leveraging decentralized consensus mechanisms.
Transparency and Accountability: A Comparative Analysis
Centralized management structures often limit transparency due to hierarchical information flow, whereas Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) leverage blockchain technology to enable real-time, immutable transaction records accessible to all members. This increased transparency enhances accountability by allowing stakeholders to audit decisions and resource allocations directly, reducing risks of mismanagement or fraud. Furthermore, DAOs' consensus-driven governance mechanisms distribute responsibility across participants, contrasting with centralized models where accountability rests primarily with top executives.
Scalability Challenges in Centralized and DAO Frameworks
Centralized management structures face scalability challenges due to bottlenecks in decision-making authority and limited flexibility in adapting to rapid organizational growth. In contrast, Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) leverage blockchain technology to distribute governance and operational roles, enhancing scalability through automated, transparent processes. However, DAOs encounter obstacles in aligning stakeholder incentives and maintaining cohesive coordination amid increased participant diversity.
Security and Risk Management Considerations
Centralization enhances security by providing a unified control system, simplifying risk management through consistent policy enforcement and streamlined incident response. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) distribute authority, increasing transparency and resilience but complicating security due to fragmented governance and potential smart contract vulnerabilities. Effective risk management in DAOs requires robust consensus mechanisms and continuous auditing of decentralized protocols to mitigate security threats.
Impact on Innovation and Organizational Agility
Centralization tends to streamline decision-making but may hinder innovation by limiting diverse input and slowing response times. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) empower distributed teams with greater autonomy, fostering a culture of innovation and rapid adaptation to market changes. This structural flexibility enhances organizational agility, enabling faster iteration and more dynamic responses to emerging opportunities.
Future Trends: Evolving Role of DAOs in Industry Management
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) are poised to transform industry management by promoting transparency, agility, and stakeholder participation beyond traditional centralized structures. Emerging blockchain technologies enable DAOs to automate governance and decision-making processes, reducing bureaucratic delays and fostering innovation at scale. The increasing adoption of DAOs in sectors such as finance, supply chain, and technology highlights a shift towards distributed leadership models that enhance efficiency and resilience in dynamic market environments.
Related Important Terms
DAO Governance Layer
The DAO Governance Layer fundamentally shifts decision-making power from centralized authorities to a distributed network of token holders, enhancing transparency and reducing single points of failure. By leveraging smart contracts, DAOs automate voting and proposal execution, fostering a more democratic and efficient management structure compared to traditional centralized frameworks.
Centralized Middleware
Centralized middleware enhances organizational control by providing a unified platform for data integration, security, and management, streamlining decision-making processes in centralized systems. This approach reduces latency and complexity in communication across departments, ensuring consistent policy enforcement and centralized data governance within a centralized management structure.
On-chain Voting Protocol
On-chain voting protocols within decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) leverage blockchain technology to enable transparent, tamper-proof decision-making, contrasting with centralized management where authority is concentrated. These protocols facilitate real-time stakeholder participation and consensus without intermediaries, enhancing governance efficiency and accountability in decentralized environments.
Multi-signature Custody
Multi-signature custody in decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) enhances security and accountability by requiring multiple approvals for transactions, reducing risks of single points of failure common in centralized management structures. This approach balances operational control and transparency, empowering distributed decision-making while maintaining robust asset protection.
Algorithmic Treasury Management
Algorithmic Treasury Management leverages automated smart contracts and real-time data analysis to optimize liquidity and asset allocation, outperforming traditional centralized control by reducing human error and increasing transparency. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) democratize decision-making through token-weighted governance, enabling dynamic treasury adjustments aligned with collective stakeholder interests, contrasting with rigid, hierarchical centralization.
Delegated Stake Power
Delegated stake power in decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) enables members to allocate voting authority proportionally, fostering distributed decision-making compared to centralized management where authority is concentrated at the top. This mechanism enhances transparency and accountability by empowering stakeholders to influence governance based on their vested interest, contrasting the rigid hierarchy typical of centralized structures.
Permissionless Coordination
Permissionless coordination in decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) enables stakeholders to participate in decision-making processes without hierarchical approval, fostering transparency and inclusivity. Centralized management models rely on controlled access and top-down authority, limiting agility and innovation compared to the open, trustless environment facilitated by DAOs.
Smart Contract Orchestration
Centralization in management concentrates decision-making authority at the top levels, enabling streamlined governance but potentially reducing flexibility and innovation. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) leverage smart contract orchestration to automate and distribute control across stakeholders, enhancing transparency, reducing operational bottlenecks, and enabling adaptive organizational dynamics.
Token-weighted Decision Rights
Token-weighted decision rights in decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) allocate voting power based on the quantity of tokens held, promoting shareholder influence proportional to investment and fostering distributed governance. In contrast, centralized management concentrates decision-making authority within a core leadership team, limiting broader stakeholder participation and potentially reducing transparency in strategic directions.
Sybil Resistance Mechanism
Centralization in management ensures streamlined decision-making but faces risks from Sybil attacks due to single points of failure, whereas decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) utilize Sybil resistance mechanisms such as token-weighted voting and identity verification to enhance security and democratic governance. Implementing robust Sybil resistance in DAOs mitigates fraudulent influence by ensuring unique, verifiable participant identities, fostering trust and resilience in decentralized management structures.
Centralization vs Decentralized Autonomous Organization Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com