Fixed roles provide structure and clarity in a management pet environment, ensuring consistent responsibilities and expectations. Job crafting allows employees to tailor their tasks and interactions, increasing engagement and adaptability. Balancing fixed roles with job crafting fosters a dynamic workplace that maximizes both stability and innovation.
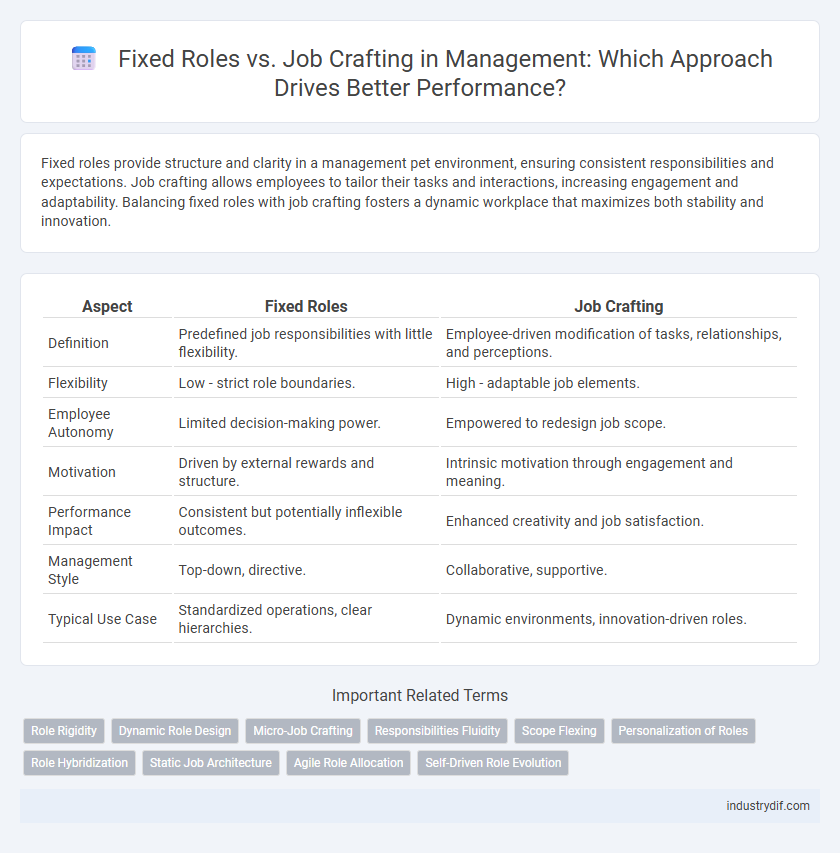
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fixed Roles | Job Crafting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Predefined job responsibilities with little flexibility. | Employee-driven modification of tasks, relationships, and perceptions. |
| Flexibility | Low - strict role boundaries. | High - adaptable job elements. |
| Employee Autonomy | Limited decision-making power. | Empowered to redesign job scope. |
| Motivation | Driven by external rewards and structure. | Intrinsic motivation through engagement and meaning. |
| Performance Impact | Consistent but potentially inflexible outcomes. | Enhanced creativity and job satisfaction. |
| Management Style | Top-down, directive. | Collaborative, supportive. |
| Typical Use Case | Standardized operations, clear hierarchies. | Dynamic environments, innovation-driven roles. |
Understanding Fixed Roles in Organizational Structures
Fixed roles in organizational structures establish clear responsibilities and hierarchical authority, promoting consistency and efficiency across teams. These predefined roles help minimize ambiguity, streamline communication, and ensure accountability by aligning tasks with specific job descriptions. Understanding fixed roles is crucial for maintaining operational stability and supporting organizational goals through structured workflows.
Defining Job Crafting: A Modern Approach
Job crafting represents a modern approach to management by allowing employees to proactively reshape their tasks, relationships, and perceptions within fixed roles, thereby enhancing job satisfaction and performance. Unlike traditional fixed roles, job crafting empowers individuals to tailor their work experience to better align with personal strengths and motivations. This dynamic process fosters greater engagement, creativity, and organizational commitment by integrating employee autonomy with organizational goals.
Key Differences Between Fixed Roles and Job Crafting
Fixed roles are predefined job positions with specific responsibilities and limited flexibility, designed to maintain organizational structure and consistency. Job crafting involves employees proactively modifying their tasks, relationships, and perceptions to enhance engagement and job satisfaction. The key difference lies in rigidity versus adaptability: fixed roles emphasize stability, while job crafting encourages personalized role development aligned with individual strengths and motivations.
Advantages of Fixed Roles in Management
Fixed roles in management provide clear accountability, streamlined decision-making, and consistent performance standards, which enhance operational efficiency. Defined responsibilities minimize role ambiguity, enabling managers to focus on specific objectives and optimize team productivity. This structure ensures stability and predictability, crucial for achieving organizational goals and maintaining hierarchical control.
Benefits of Job Crafting for Employee Engagement
Job crafting enhances employee engagement by allowing individuals to tailor their roles to better align with personal strengths and interests, leading to increased motivation and job satisfaction. This proactive approach fosters a sense of autonomy and purpose, which boosts productivity and reduces turnover rates. Studies show that organizations encouraging job crafting experience higher levels of employee commitment and overall performance.
Challenges of Implementing Fixed Roles
Implementing fixed roles often faces challenges such as reduced employee motivation and limited flexibility, which can hinder adaptability in dynamic business environments. Rigid role definitions may lead to skill stagnation and decreased innovation as employees are confined to specific tasks without opportunities for personal growth. Resistance to change and misalignment with evolving organizational needs further complicate the enforcement of fixed roles in management structures.
Barriers to Successful Job Crafting
Barriers to successful job crafting include organizational rigidity, where fixed roles limit employees' autonomy to customize tasks, relationships, and perceptions. Lack of managerial support and unclear boundaries between formal responsibilities and personalized adjustments hinder effective job crafting. Furthermore, organizational culture that prioritizes standardization over innovation can suppress employee initiative to reshape their roles meaningfully.
Impact on Team Dynamics: Fixed Roles vs Job Crafting
Fixed roles provide clear responsibilities and reduce ambiguity, fostering stability and predictability within team dynamics. Job crafting encourages employees to customize tasks and interactions, enhancing engagement and promoting creativity that can lead to improved collaboration. Balancing fixed roles with job crafting can optimize team performance by combining structure with individual initiative.
Best Practices for Integrating Job Crafting in Traditional Structures
Integrating job crafting in traditional management structures requires aligning employee-driven task modifications with organizational goals to maintain productivity and coherence. Encouraging open communication channels fosters flexibility while preserving fixed roles, enabling employees to tailor their responsibilities without disrupting established workflows. Implementing regular feedback loops and training programs ensures that job crafting enhances skill development and job satisfaction within existing hierarchical frameworks.
Future Trends: Evolving Roles in Management
Future trends in management emphasize a shift from fixed roles to job crafting as organizations adopt more agile and flexible structures. Job crafting empowers employees to tailor their responsibilities, enhancing engagement and innovation while aligning with dynamic business needs. This evolution supports a culture of continuous learning and adaptability, critical for managing complex, rapidly changing markets.
Related Important Terms
Role Rigidity
Role rigidity in fixed roles constrains employee autonomy, limiting adaptability and reducing engagement by enforcing predefined responsibilities. Job crafting enhances flexibility by allowing individuals to modify tasks, relationships, and perceptions, thereby increasing motivation and performance within dynamic organizational environments.
Dynamic Role Design
Dynamic role design integrates fixed roles with job crafting principles to enhance adaptability and employee engagement. By allowing individuals to tailor responsibilities within structured frameworks, organizations foster innovation and responsiveness in management practices.
Micro-Job Crafting
Micro-job crafting emphasizes small, individual adjustments employees make to tasks, relationships, or perceptions to enhance job satisfaction and performance. Unlike fixed roles, it encourages continual personalization of work elements, fostering agility and intrinsic motivation within organizational structures.
Responsibilities Fluidity
Responsibilities fluidity in fixed roles limits employees to predefined tasks, reducing adaptability and innovation within teams. Job crafting enables individuals to reshape their responsibilities dynamically, fostering greater engagement and responsiveness to organizational changes.
Scope Flexing
Scope flexing in job crafting allows employees to expand or narrow their task boundaries, fostering adaptability and engagement beyond rigid fixed roles. This dynamic approach enhances job satisfaction and organizational performance by aligning individual strengths with evolving workplace demands.
Personalization of Roles
Fixed roles provide clear structure and defined responsibilities, ensuring consistency and efficiency in organizational workflows. Job crafting empowers employees to personalize their roles by aligning tasks with individual strengths and interests, enhancing engagement and intrinsic motivation.
Role Hybridization
Role hybridization integrates fixed roles with job crafting by allowing employees to blend formal responsibilities with personalized tasks, enhancing flexibility and innovation. This approach improves workforce adaptability, job satisfaction, and organizational agility by fostering a dynamic balance between structured roles and individual creativity.
Static Job Architecture
Static job architecture emphasizes fixed roles with predefined responsibilities and limited flexibility, ensuring organizational clarity and consistent performance standards. Fixed roles reduce ambiguity but may stifle employee initiative and adaptability compared to dynamic job crafting approaches that encourage role personalization.
Agile Role Allocation
Agile role allocation enhances team adaptability by balancing fixed roles with job crafting, allowing employees to tailor responsibilities based on their strengths and project needs. This dynamic approach increases engagement and productivity by empowering team members to evolve their roles within organizational objectives.
Self-Driven Role Evolution
Fixed roles provide structured responsibilities and clear expectations, often limiting employee autonomy and adaptability; job crafting empowers individuals to reshape tasks, relationships, and perceptions to align better with their strengths and motivations. Self-driven role evolution enhances engagement and performance by encouraging proactive adjustments within organizational boundaries, fostering continuous personal and professional growth.
Fixed Roles vs Job Crafting Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com