Managers typically rely on hierarchical authority and structured control to guide teams, emphasizing clear roles and performance metrics. Teal leaders foster autonomy and self-management, encouraging collaboration and purpose-driven work without strict supervision. This shift prioritizes trust and adaptability over command-and-control approaches in modern organizational management.
Table of Comparison
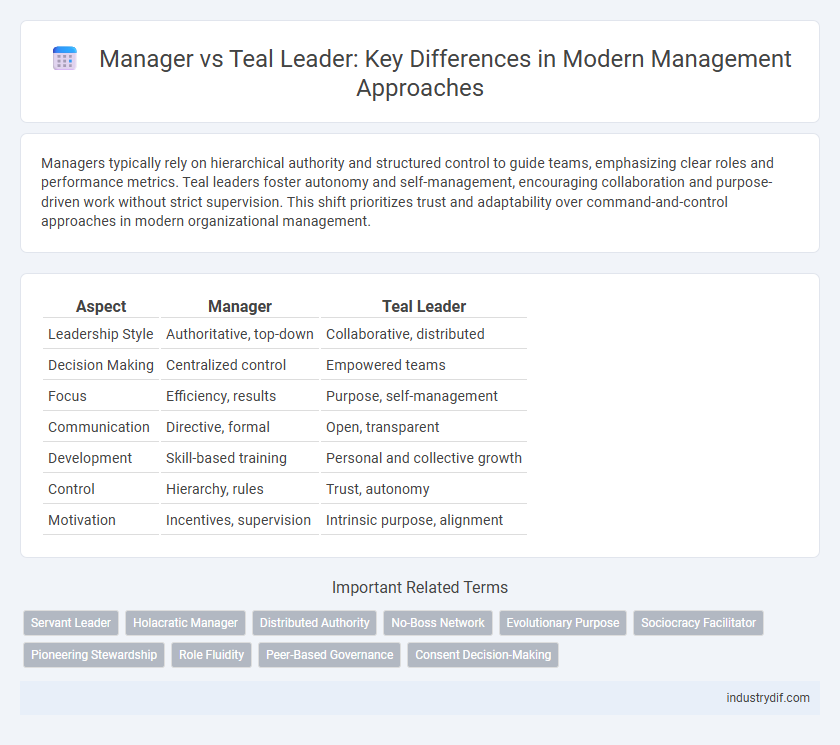
| Aspect | Manager | Teal Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Leadership Style | Authoritative, top-down | Collaborative, distributed |
| Decision Making | Centralized control | Empowered teams |
| Focus | Efficiency, results | Purpose, self-management |
| Communication | Directive, formal | Open, transparent |
| Development | Skill-based training | Personal and collective growth |
| Control | Hierarchy, rules | Trust, autonomy |
| Motivation | Incentives, supervision | Intrinsic purpose, alignment |
Understanding Management: Traditional Manager Defined
Traditional managers prioritize hierarchical control and task delegation, emphasizing clear authority and structured decision-making processes. Their role centers on maintaining order, efficiency, and accountability through defined roles and standardized procedures. This contrasts with teal leaders, who focus on self-management, autonomy, and fostering a collaborative culture driven by shared purpose and trust.
The Evolution of Leadership: Who Is a Teal Leader?
Teal leaders embody evolutionary leadership by fostering self-management, wholeness, and a deeper sense of purpose within organizations, contrasting with traditional managers who emphasize hierarchical control and performance metrics. This shift prioritizes autonomy, collaboration, and emotional intelligence, enabling teams to innovate and adapt in complex environments. Teal leadership integrates organizational purpose with individual growth, creating resilient cultures that thrive on trust and transparency.
Core Principles: Managerial Hierarchy vs. Teal Self-Management
Managers typically operate within a hierarchical structure, emphasizing control, clear roles, and top-down decision-making to ensure organizational efficiency. Teal leaders embrace self-management principles, fostering autonomy, distributed authority, and collective accountability among team members. This shift from managerial hierarchy to self-managed teams promotes adaptability, innovation, and intrinsic motivation in the workplace.
Decision-Making Authority: Top-Down vs. Distributed
Managers typically exercise top-down decision-making authority, centralizing control and directing tasks to ensure alignment with organizational goals. Teal leaders embrace distributed decision-making, empowering team members at all levels to contribute insights and share responsibility for outcomes. This shift enhances agility and innovation by fostering autonomy and collective ownership within the organization.
Role of Communication: Directive vs. Collaborative Approaches
Managers employ directive communication, providing clear instructions and expecting adherence to established processes, which ensures efficiency and control. Teal leaders adopt a collaborative communication style, encouraging open dialogue and shared decision-making to foster autonomy and innovation. This shift from top-down directives to inclusive conversations enhances team engagement and collective problem-solving.
Measuring Success: KPIs and Outcomes in Both Models
Managers primarily measure success through predefined Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that focus on efficiency, output, and adherence to organizational goals. Teal Leaders emphasize holistic outcomes, integrating qualitative metrics such as employee engagement, adaptability, and purpose-driven impact alongside quantitative KPIs. This approach fosters a balanced assessment combining financial results with human-centric value creation, promoting sustainable long-term success.
Employee Empowerment: Autonomy in Teal vs. Control in Management
Teal leaders prioritize employee empowerment by fostering autonomy, encouraging self-management, and trusting teams to make decisions aligned with organizational purpose. In contrast, traditional managers maintain control through hierarchical structures, emphasizing oversight and directive decision-making to ensure compliance and efficiency. This shift from control to autonomy enhances innovation, engagement, and adaptability within organizations following the Teal leadership model.
Adapting to Change: Flexibility of Teal Leadership
Teal leaders exhibit exceptional flexibility by fostering adaptive decision-making frameworks that respond swiftly to evolving organizational challenges, contrasting with traditional managers who often rely on hierarchical control and fixed protocols. Emphasizing self-management and decentralized authority, Teal leadership empowers teams to innovate and pivot in real-time, accelerating change adaptation. This dynamic approach enhances resilience and drives sustainable growth in complex, rapidly shifting business environments.
Organizational Culture: Impact of Managers vs. Teal Leaders
Managers typically enforce organizational culture through hierarchical control and adherence to established protocols, prioritizing efficiency and risk mitigation. Teal leaders foster a culture of self-management, trust, and purpose-driven collaboration, enabling greater employee autonomy and innovation. The shift from manager to teal leader significantly transforms workplace dynamics, promoting adaptability and emotional intelligence across teams.
Choosing the Right Approach: Industry Fit and Future Trends
Choosing the right leadership approach depends on industry dynamics and organizational culture, with traditional managerial styles excelling in highly regulated or hierarchical sectors, while Teal leadership thrives in innovative, agile environments prioritizing autonomy and purpose. Future trends indicate a shift towards Teal principles as digital transformation and workforce expectations evolve toward trust-based, self-managed teams. Evaluating industry fit and emerging work trends ensures leadership effectiveness aligns with long-term strategic goals and sustainable development.
Related Important Terms
Servant Leader
A Teal Leader embodies the servant leadership model by prioritizing team empowerment, autonomy, and emotional intelligence over traditional command-and-control management structures. This approach fosters collaboration, trust, and intrinsic motivation, driving sustainable organizational growth and innovation.
Holacratic Manager
A Holacratic Manager functions within a decentralized organizational structure where authority is distributed among self-organizing teams, contrasting traditional managers who rely on hierarchical control; this approach fosters autonomy, transparency, and adaptive decision-making. Teal leaders emphasize evolutionary purpose and wholeness, promoting environments where individuals contribute their full selves, aligning closely with Holacracy principles that dissolve rigid roles to empower collaborative governance.
Distributed Authority
Managers typically centralize decision-making authority, guiding teams through hierarchical structures that emphasize top-down control. Teal leaders embrace distributed authority by empowering individuals to self-manage, fostering collaboration and autonomy within decentralized organizational frameworks.
No-Boss Network
Managers typically rely on hierarchical authority to direct teams, whereas Teal Leaders foster a No-Boss Network by empowering self-management and shared decision-making, enhancing organizational agility and innovation. The No-Boss Network model eliminates traditional command structures, promoting transparency, autonomy, and collective accountability within teams.
Evolutionary Purpose
Managers typically drive organizational goals through hierarchical control and predefined strategies, emphasizing efficiency and predictable outcomes. Teal Leaders, however, foster an Evolutionary Purpose by encouraging self-management, adaptability, and collective intelligence to align the organization's direction with emerging opportunities and deeper meaning.
Sociocracy Facilitator
Sociocracy facilitators in teal leadership promote decentralized decision-making, fostering collaboration and shared responsibility, contrasting with traditional managers who often rely on hierarchical authority and top-down control. This approach enhances team autonomy and transparency, aligning with teal principles of self-management and purpose-driven work.
Pioneering Stewardship
Managers typically emphasize control and hierarchical decision-making to ensure organizational stability, while Teal Leaders prioritize pioneering stewardship by fostering autonomy, collaboration, and evolutionary purpose within teams. This approach encourages innovation and adaptive growth, aligning individual roles with the organization's long-term mission and sustainable success.
Role Fluidity
Managers typically maintain defined hierarchical roles with clear authority and task delegation, while Teal Leaders embrace role fluidity by adapting their responsibilities based on team needs and fostering collective decision-making. This dynamic flexibility enhances organizational responsiveness and empowers employees to contribute more effectively across various functions.
Peer-Based Governance
Managers typically rely on hierarchical authority and top-down decision-making structures, whereas Teal Leaders emphasize peer-based governance that fosters collective autonomy and distributed accountability. This approach in Teal organizations enhances collaboration, drives innovation, and aligns team members through shared purpose and trust rather than formal power dynamics.
Consent Decision-Making
Teal Leaders prioritize consent decision-making by involving all team members in discussions to reach agreements that do not harm the organization, fostering autonomy and collective responsibility. In contrast, traditional Managers often rely on hierarchical decisions, where authority dictates outcomes without requiring full team consent.
Manager vs Teal Leader Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com