Organizational hierarchy establishes clear lines of authority and responsibility, which enhances role clarity and decision-making efficiency in complex businesses. Flat organizations promote openness and faster communication by removing layers of management, encouraging employee empowerment and collaboration. Balancing these structures depends on company size, culture, and strategic goals to optimize productivity and innovation.
Table of Comparison
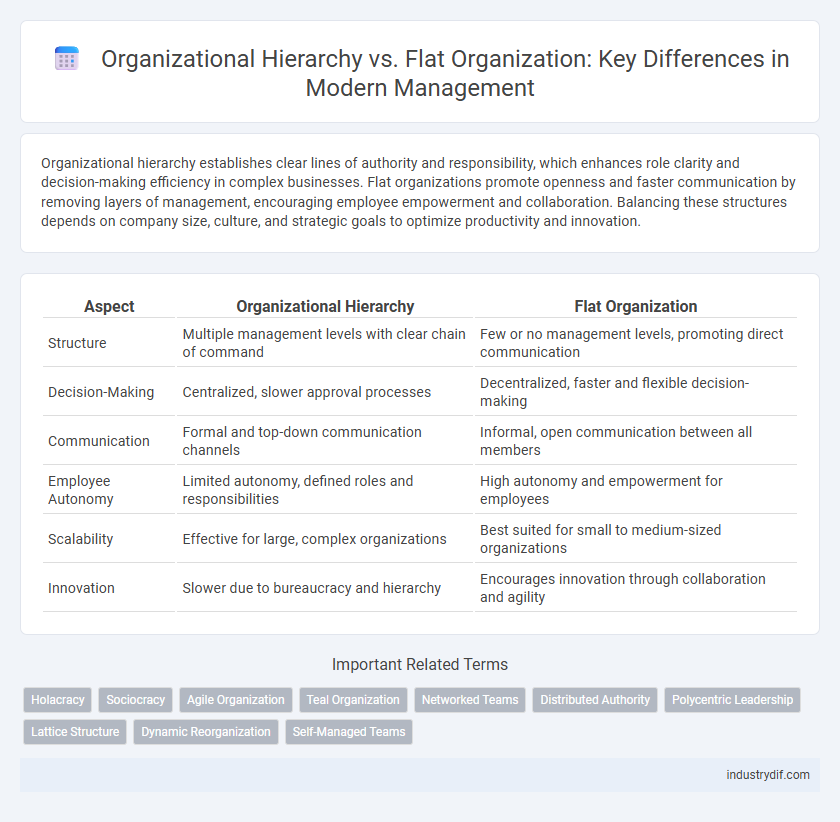
| Aspect | Organizational Hierarchy | Flat Organization |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Multiple management levels with clear chain of command | Few or no management levels, promoting direct communication |
| Decision-Making | Centralized, slower approval processes | Decentralized, faster and flexible decision-making |
| Communication | Formal and top-down communication channels | Informal, open communication between all members |
| Employee Autonomy | Limited autonomy, defined roles and responsibilities | High autonomy and empowerment for employees |
| Scalability | Effective for large, complex organizations | Best suited for small to medium-sized organizations |
| Innovation | Slower due to bureaucracy and hierarchy | Encourages innovation through collaboration and agility |
Introduction to Organizational Structures
Organizational hierarchy features multiple tiers of management, defining clear roles, responsibilities, and authority levels to streamline decision-making and accountability. Flat organizations minimize management layers, promoting open communication, faster decision processes, and increased employee empowerment. Understanding these structures aids in aligning management strategies with company culture and operational goals.
Defining Organizational Hierarchy
Organizational hierarchy refers to a structured system of authority where roles and responsibilities are clearly defined across multiple levels of management, facilitating effective decision-making and control. It establishes a chain of command, enabling clear communication channels and accountability within departments and teams. This traditional approach contrasts with flat organizations, which minimize layers to promote agility and employee autonomy.
Understanding Flat Organizations
Flat organizations eliminate multiple management layers, fostering direct communication and faster decision-making among employees. This structure enhances agility and innovation by empowering teams with greater autonomy and reducing bureaucratic delays. Employees in flat organizations often experience increased job satisfaction due to clearer responsibilities and closer collaboration with leadership.
Key Differences: Hierarchical vs Flat Models
Organizational hierarchy features multiple levels of management with distinct roles and a clear chain of command, promoting control and specialization, while flat organizations minimize management layers to foster open communication and faster decision-making. Hierarchical models often create rigid structures with defined responsibilities, whereas flat models emphasize employee autonomy and collaboration. The choice between these models impacts organizational agility, employee engagement, and operational efficiency.
Decision-Making Processes in Both Structures
Organizational hierarchy establishes clear decision-making authority through defined managerial levels, enabling structured and consistent choices but potentially slowing responsiveness due to multiple approval layers. Flat organizations promote faster decision-making by empowering employees with broader responsibilities and reducing bureaucratic barriers, fostering innovation and agility. The choice between hierarchical and flat structures significantly impacts communication flow, employee autonomy, and the speed at which strategic decisions are implemented.
Communication Flow and Information Sharing
Organizational hierarchy structures communication through multiple layers, which can slow information flow and create bottlenecks, but ensures clear authority and responsibility channels. Flat organizations promote open communication and faster information sharing by reducing management levels, fostering collaboration and quicker decision-making. Effective management balances these models to optimize transparency and responsiveness within the company.
Impact on Employee Engagement and Morale
Organizational hierarchy often leads to clearer roles and defined paths for career advancement, which can enhance employee engagement by providing structure and recognition. In contrast, flat organizations promote autonomy and open communication, fostering a sense of ownership and higher morale among employees. Balancing hierarchy and flatness is crucial for optimizing employee motivation and retention in diverse work environments.
Scalability and Growth Considerations
Organizational hierarchy provides clear reporting lines and defined roles, which can streamline decision-making and support scalability in large, complex companies. Flat organizations promote agility and faster communication, enhancing innovation but potentially challenging consistent growth due to unclear authority structures. Balancing hierarchy with flat elements can optimize scalability by fostering both control and flexibility during expansion phases.
Industry Examples of Hierarchical and Flat Organizations
Hierarchical organizations like General Electric and Procter & Gamble utilize structured layers of management to ensure clear roles and efficient decision-making, fostering control in complex operations. In contrast, flat organizations such as Valve Corporation and Zappos emphasize minimal management levels, promoting employee autonomy and faster communication to drive innovation. These industry examples illustrate how organizational hierarchy impacts operational agility and workforce engagement depending on business needs.
Choosing the Right Structure for Your Business
Choosing the right organizational structure hinges on the size, goals, and culture of your business, where a traditional organizational hierarchy offers clear authority lines and defined roles, fostering accountability in complex operations. In contrast, a flat organization promotes open communication and agility, suitable for smaller teams seeking rapid innovation and employee empowerment. Evaluating factors like decision-making speed, employee autonomy, and scalability ensures alignment with your strategic objectives for optimal performance.
Related Important Terms
Holacracy
Holacracy replaces traditional organizational hierarchy with a decentralized structure where authority is distributed across self-organizing teams, enhancing agility and employee empowerment. This flat organization model eliminates rigid managerial roles, promoting transparency and dynamic role definition to improve decision-making and adaptability.
Sociocracy
Sociocracy fosters a flat organization by promoting decentralized decision-making and equivalence among members, which contrasts traditional organizational hierarchy characterized by rigid top-down authority. This governance model enhances transparency, collaboration, and adaptability, enabling organizations to respond swiftly to change while maintaining clear roles and accountability.
Agile Organization
Agile organizations favor flat organizational structures to enhance flexibility, accelerate decision-making, and foster collaboration across cross-functional teams. In contrast, traditional hierarchical organizations often face slower response times and reduced adaptability due to rigid layers of management.
Teal Organization
Teal organizations emphasize self-management, evolving beyond traditional hierarchical structures by promoting decentralized decision-making and autonomy among employees. This model aligns with agile management principles, fostering adaptability and intrinsic motivation while minimizing rigid layers seen in conventional organizational hierarchies.
Networked Teams
Networked teams in flat organizations enhance agility and innovation by promoting decentralized decision-making and seamless communication across functional roles. Unlike traditional hierarchical structures, these teams utilize interconnected relationships that foster collaboration, knowledge sharing, and rapid problem-solving, driving organizational adaptability.
Distributed Authority
Distributed authority in organizational hierarchies centralizes decision-making within defined management levels, ensuring consistent control and clear responsibility. Flat organizations promote decentralized authority, enhancing flexibility and faster decision-making by empowering employees across teams to take ownership and act autonomously.
Polycentric Leadership
Polycentric leadership thrives in flat organizations by empowering local managers to make decisions, enhancing cultural sensitivity and responsiveness compared to traditional hierarchical structures. This approach fosters decentralized authority, promotes innovation, and improves employee engagement across diverse geographic locations.
Lattice Structure
The lattice structure in organizational management eliminates rigid hierarchies by promoting open communication and collaboration across all levels, enabling faster decision-making and innovation. This approach contrasts with traditional hierarchical models by fostering a flexible network of relationships that enhances employee empowerment and responsiveness to change.
Dynamic Reorganization
Dynamic reorganization in flat organizations accelerates decision-making by reducing hierarchical layers, fostering agility and rapid adaptation to market changes. In contrast, traditional organizational hierarchies often experience slower restructuring processes due to multiple management tiers, limiting responsiveness and innovation.
Self-Managed Teams
Self-managed teams thrive in flat organizations by promoting autonomy and faster decision-making, reducing layers of middle management that often slow communication in traditional hierarchical structures. These teams enhance collaboration and accountability, enabling organizations to adapt quickly to market changes and improve operational efficiency.
Organizational Hierarchy vs Flat Organization Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com