Middle management plays a crucial role in traditional hierarchical organizations by acting as a bridge between executive leadership and front-line employees, facilitating communication, decision-making, and operational control. Flat organizations minimize layers of management, promoting a more collaborative and agile work environment where employees have greater autonomy and faster decision-making processes. The choice between middle management and flat structures depends on company size, culture, and the need for flexibility versus control.
Table of Comparison
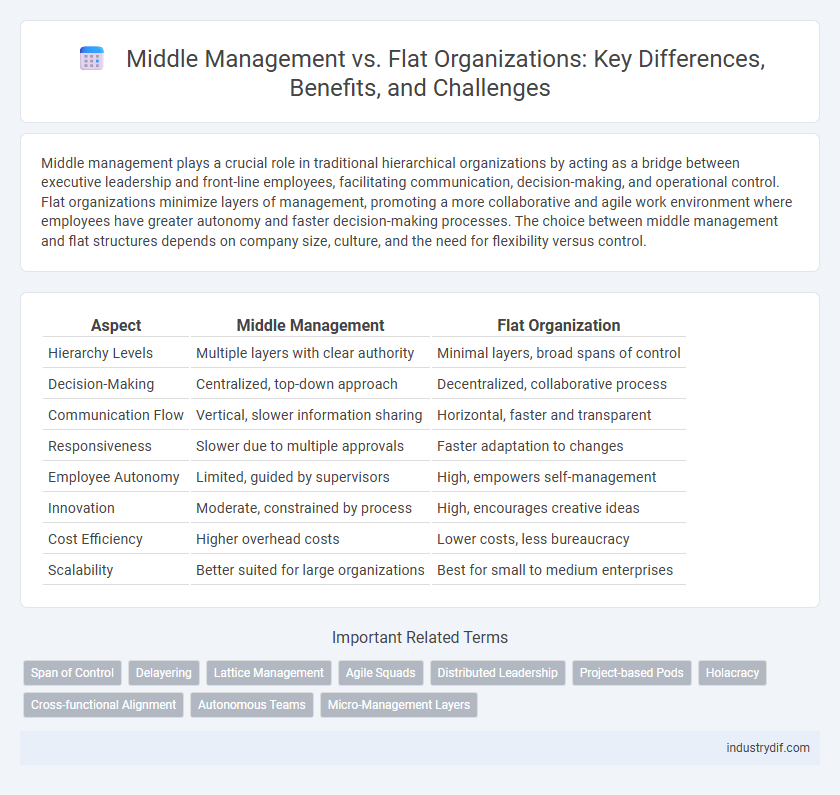
| Aspect | Middle Management | Flat Organization |
|---|---|---|
| Hierarchy Levels | Multiple layers with clear authority | Minimal layers, broad spans of control |
| Decision-Making | Centralized, top-down approach | Decentralized, collaborative process |
| Communication Flow | Vertical, slower information sharing | Horizontal, faster and transparent |
| Responsiveness | Slower due to multiple approvals | Faster adaptation to changes |
| Employee Autonomy | Limited, guided by supervisors | High, empowers self-management |
| Innovation | Moderate, constrained by process | High, encourages creative ideas |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher overhead costs | Lower costs, less bureaucracy |
| Scalability | Better suited for large organizations | Best for small to medium enterprises |
Definition of Middle Management
Middle management serves as an intermediary layer of managers who oversee operational teams and implement strategic directives from senior executives. This tier is responsible for coordinating departmental functions, facilitating communication between upper management and frontline employees, and driving productivity within defined units. In contrast, flat organizations minimize hierarchical levels, reducing or eliminating middle management roles to promote faster decision-making and greater employee autonomy.
Understanding Flat Organization Structures
Flat organization structures minimize hierarchical layers, empowering middle managers to adopt more collaborative and flexible roles. This structure enhances communication flow and accelerates decision-making by reducing bureaucracy traditionally associated with middle management. Understanding these dynamics helps organizations balance autonomy and control for optimal performance in flat environments.
Key Roles of Middle Managers
Middle managers play a critical role in bridging strategic goals and operational execution, ensuring effective communication between executive leadership and frontline employees. They facilitate resource allocation, performance monitoring, and team development, which maintains organizational stability and drives project success. In flat organizations, the reduced hierarchy places greater emphasis on middle managers to foster collaboration, agility, and employee empowerment.
Advantages of Flat Organizations
Flat organizations enhance communication speed and employee empowerment by reducing hierarchical layers, fostering a culture of collaboration and innovation. Decision-making processes become more agile, enabling quicker responses to market changes and customer needs. This structure often leads to increased job satisfaction and productivity, as employees have greater autonomy and visibility within the company.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Middle management typically involves hierarchical decision-making with multiple approval layers, which can slow response times but ensures thorough oversight and risk management. Flat organizations streamline decision-making by empowering employees at all levels to make choices directly, fostering rapid innovation and agility. This decentralized approach enhances communication efficiency but may require strong organizational culture to maintain alignment and accountability.
Communication Flow in Both Models
Middle management structures often create hierarchical communication channels that can slow decision-making and distort information as it passes through layers. Flat organizations promote open communication and direct interaction between employees and leadership, enhancing transparency and faster feedback loops. This streamlined communication flow in flat models boosts agility and responsiveness within teams compared to the traditional layered approach.
Employee Empowerment and Autonomy
Middle management structures often limit employee empowerment by enforcing hierarchical decision-making, whereas flat organizations promote autonomy by reducing layers of supervision and encouraging direct communication. Employees in flat organizations typically experience greater responsibility and freedom to innovate, fostering motivation and faster problem-solving. Empowering teams without rigid oversight aligns with contemporary management trends prioritizing agility and employee engagement.
Impact on Organizational Efficiency
Middle management provides clear hierarchical oversight that can improve organizational efficiency by streamlining decision-making processes and clarifying accountability. Flat organizations reduce layers of management, promoting faster communication and increased employee empowerment, which often leads to greater flexibility and innovation. However, the optimal structure depends on the company's size, complexity, and strategic goals for balancing control and agility.
Scalability and Growth Considerations
Middle management structures provide scalability by creating defined layers of oversight, enabling organizations to manage complexity and delegate tasks efficiently as they grow. Flat organizations promote rapid decision-making and agility but may face challenges in scaling due to limited hierarchy and potential role ambiguity. Balancing middle management and flat organizational elements can optimize growth strategies by leveraging structured control alongside flexible communication flows.
Choosing the Right Structure for Your Business
Choosing the right organizational structure hinges on your business goals and operational complexity; middle management offers clear hierarchies and defined roles, enhancing control and accountability in larger companies. Flat organizations foster agility and faster decision-making by reducing layers of management, ideal for startups and creative industries prioritizing innovation and collaboration. Evaluating factors such as company size, communication flow, and employee autonomy helps determine whether a traditional middle management tier or a flat structure better supports sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Related Important Terms
Span of Control
Middle management typically features a narrower span of control, allowing managers to closely supervise and support their teams, which can enhance specialization and accountability. In contrast, flat organizations have a wider span of control, promoting employee autonomy and faster decision-making by reducing hierarchical layers.
Delayering
Delayering reduces hierarchical levels in middle management, enhancing communication speed and decision-making efficiency by minimizing bureaucratic delays. Flat organizations emphasize this approach to empower employees, foster collaboration, and increase overall agility in dynamic business environments.
Lattice Management
Lattice Management emphasizes decentralized decision-making and peer collaboration, contrasting sharply with traditional middle management layers that often create hierarchical bottlenecks. Flat organizations adopting lattice structures enhance agility and innovation by fostering direct communication paths and shared leadership responsibilities.
Agile Squads
Agile squads thrive in flat organizations where decision-making is decentralized, enabling rapid iteration and cross-functional collaboration without the bottlenecks typical of middle management layers. Middle management often slows Agile adoption by enforcing rigid hierarchies, whereas flat structures empower squads with autonomy and accelerate innovation.
Distributed Leadership
Middle management facilitates distributed leadership by acting as a crucial link between executive strategy and frontline execution, ensuring efficient delegation and accountability throughout hierarchical layers. Flat organizations promote distributed leadership by minimizing hierarchical barriers, enabling team members to share decision-making responsibilities and foster collaboration across all levels.
Project-based Pods
Project-based pods in flat organizations empower middle managers by decentralizing decision-making, enhancing agility and collaboration across teams. This structure reduces hierarchical layers, enabling faster project execution and more direct communication compared to traditional middle management models.
Holacracy
Middle management structures often create hierarchical layers that can slow decision-making and obscure accountability, whereas flat organizations employing Holacracy distribute authority through self-managing teams, enhancing agility and transparency. Holacracy replaces traditional managerial roles with defined roles and governance processes, empowering employees to own responsibilities and drive innovation within a decentralized framework.
Cross-functional Alignment
Middle management facilitates seamless cross-functional alignment by acting as a communication bridge between departments, ensuring strategic objectives are consistently interpreted and executed. Flat organizations promote cross-functional collaboration by minimizing hierarchical barriers, enabling faster decision-making and greater adaptability to market changes.
Autonomous Teams
Autonomous teams in flat organizations empower middle management by reducing hierarchical layers and enhancing decision-making speed, fostering innovation and agility. Middle management shifts from directive roles to strategic facilitators, enabling teams to self-manage while ensuring alignment with organizational goals.
Micro-Management Layers
Middle management introduces multiple micro-management layers that can slow decision-making and reduce organizational agility, often leading to bottlenecks and communication gaps. In contrast, flat organizations minimize micro-management, promoting faster workflows and greater employee empowerment by reducing hierarchical barriers.
Middle Management vs Flat Organization Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com