Organizational charts provide a clear hierarchical structure that defines roles, responsibilities, and reporting lines, fostering accountability in management. Holacracy replaces traditional hierarchies with self-managing teams, empowering employees through distributed authority and dynamic role assignments. Choosing between these approaches depends on a company's need for control and flexibility in decision-making.
Table of Comparison
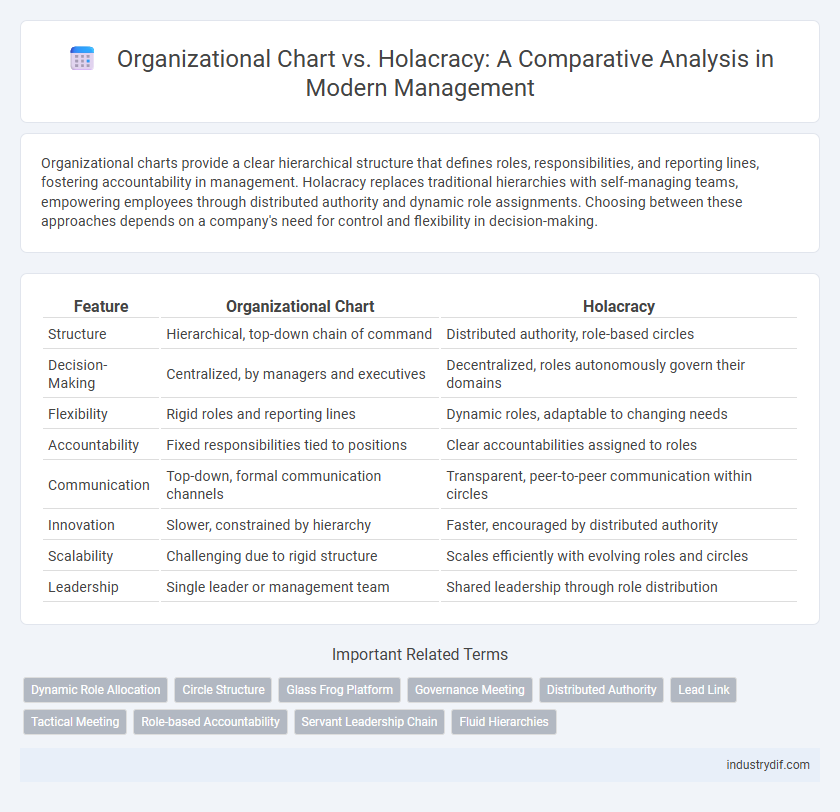
| Feature | Organizational Chart | Holacracy |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Hierarchical, top-down chain of command | Distributed authority, role-based circles |
| Decision-Making | Centralized, by managers and executives | Decentralized, roles autonomously govern their domains |
| Flexibility | Rigid roles and reporting lines | Dynamic roles, adaptable to changing needs |
| Accountability | Fixed responsibilities tied to positions | Clear accountabilities assigned to roles |
| Communication | Top-down, formal communication channels | Transparent, peer-to-peer communication within circles |
| Innovation | Slower, constrained by hierarchy | Faster, encouraged by distributed authority |
| Scalability | Challenging due to rigid structure | Scales efficiently with evolving roles and circles |
| Leadership | Single leader or management team | Shared leadership through role distribution |
Introduction to Organizational Structures
Organizational charts represent traditional hierarchical structures that clearly define roles, responsibilities, and reporting lines within a company. Holacracy replaces rigid hierarchies with decentralized governance, distributing authority across self-organizing teams called circles. Understanding these contrasting organizational structures is essential for adapting management practices to foster agility and employee empowerment.
Defining Traditional Organizational Charts
Traditional organizational charts depict a hierarchical structure dividing roles and responsibilities through clear lines of authority and reporting relationships. These charts emphasize top-down supervision, centralized decision-making, and functional departmentalization, promoting efficiency but often limiting flexibility and employee autonomy. Understanding this framework is essential for comparing it to alternative models like Holacracy, which decentralizes authority and embraces distributed governance.
Understanding Holacracy
Holacracy replaces traditional organizational charts by distributing authority through self-managing teams called circles, enhancing agility and employee autonomy. Unlike hierarchical structures, Holacracy emphasizes dynamic roles and transparent governance processes, enabling faster decision-making and adaptability. This system fosters accountability and innovation by aligning roles directly with organizational purpose rather than fixed job descriptions.
Key Differences: Hierarchy vs Distributed Authority
An organizational chart represents a traditional hierarchy with clear lines of authority and defined roles, facilitating centralized decision-making and top-down communication. In contrast, holacracy distributes authority across self-organizing teams, promoting decentralized decision-making and dynamic role assignments. This fundamental difference impacts organizational agility, with hierarchy emphasizing control and predictability, while holacracy fosters flexibility and employee empowerment.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Organizational charts define clear hierarchical decision-making processes where authority flows top-down from executives to employees, ensuring centralized control and accountability. Holacracy adopts a decentralized approach, distributing decision-making across self-managing teams called circles, empowering roles rather than individuals to make domain-specific decisions. This shift enhances agility and responsiveness by eliminating rigid chain-of-command structures and promoting collaborative governance.
Impact on Communication and Collaboration
An organizational chart establishes a clear hierarchy, defining roles and communication channels that streamline decision-making but may limit cross-departmental collaboration. Holacracy distributes authority across self-managing teams, enhancing transparency and promoting dynamic collaboration through fluid roles and open communication. This decentralized structure fosters innovation and quicker response times by breaking down traditional communication barriers inherent in hierarchical setups.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Each Model
Organizational charts provide a clear hierarchical structure that defines roles and responsibilities, promoting stability but limiting flexibility and adaptability in dynamic environments. Holacracy distributes authority through self-organizing teams, enhancing agility and rapid response to change by empowering employees to make decisions within their roles. This decentralized approach fosters continuous adaptation, making Holacracy more suited for organizations seeking innovation and responsiveness.
Organizational Scalability: Which Structure Wins?
Organizational scalability is often more effectively achieved through Holacracy, as its decentralized decision-making enables rapid adaptation and growth without the bottlenecks common in traditional hierarchical charts. Unlike rigid organizational charts that define fixed roles and reporting lines, Holacracy's dynamic role assignments and self-managing teams facilitate continuous evolution and responsiveness in complex environments. Companies embracing Holacracy report increased agility and innovation, critical factors for scaling in fast-changing markets.
Employee Roles and Responsibilities
Traditional organizational charts define clear hierarchical roles and responsibilities, ensuring structured communication and accountability within departments. Holacracy replaces fixed roles with dynamic, purpose-driven circles where employees assume multiple roles based on evolving needs, promoting autonomy and adaptability. This shift empowers individuals to take ownership of tasks, fostering innovation and streamlined decision-making.
Choosing the Right Structure for Your Business
Choosing the right organizational structure directly impacts business agility and decision-making efficiency. An organizational chart offers clear hierarchy and defined roles, promoting accountability, while holacracy emphasizes decentralized authority and self-management for innovation. Evaluating company size, culture, and strategic goals helps determine whether a traditional organizational chart or a holacracy best supports your business growth.
Related Important Terms
Dynamic Role Allocation
Organizational charts provide a fixed hierarchy with clearly defined roles, limiting flexibility in role allocation and adaptability to change. Holacracy employs dynamic role allocation, enabling teams to distribute responsibilities fluidly based on current needs, enhancing agility and employee empowerment within the management structure.
Circle Structure
The organizational chart represents a traditional hierarchical structure with clearly defined roles and reporting lines, whereas holacracy utilizes a circle structure that promotes decentralized authority and dynamic role assignment. Circle structures facilitate agility and collaboration by distributing decision-making power across self-organizing teams, improving transparency and responsiveness within the organization.
Glass Frog Platform
Glass Frog platform provides an innovative solution for implementing Holacracy by replacing traditional organizational charts with dynamic role-based structures that enhance transparency and accountability. Its interactive interface allows teams to self-manage governance and operational meetings, facilitating agile decision-making and continuous evolution within decentralized organizations.
Governance Meeting
Governance meetings in a traditional organizational chart focus on hierarchical decision-making and role clarity, whereas holacracy employs distributed authority with dynamic roles determined collaboratively through structured governance meetings. This method enhances agility and responsiveness by enabling team members to propose and adapt policies in real-time, fostering decentralized management and continuous organizational evolution.
Distributed Authority
Organizational charts visually represent hierarchical structures with centralized authority, while holacracy distributes authority across self-managing teams, enhancing agility and employee empowerment. Distributed authority in holacracy replaces traditional management roles with dynamic roles and circles, promoting faster decision-making and accountability at all organizational levels.
Lead Link
The Lead Link in Holacracy replaces traditional management roles by dynamically assigning accountabilities and linking circles, promoting agile decision-making and distributed authority. Unlike static organizational charts, this role shifts power to teams, enhancing transparency and adapting swiftly to changing business needs.
Tactical Meeting
An organizational chart provides a clear hierarchy and defined roles for decision-making, streamlining communication during tactical meetings with structured reporting lines. Holacracy replaces traditional hierarchy with distributed authority, enabling tactical meetings to focus on responsive governance and real-time role adjustments without relying on fixed positions.
Role-based Accountability
Organizational charts define clear hierarchical structures where role-based accountability is assigned through fixed positions and reporting lines, ensuring clarity in decision-making authority and responsibility. Holacracy replaces traditional hierarchies with distributed authority across dynamic roles, emphasizing flexibility in role-based accountability by allowing individuals to hold multiple roles with evolving responsibilities.
Servant Leadership Chain
Organizational charts define clear hierarchical structures with top-down authority, while Holacracy distributes decision-making through self-managed teams aligned by roles, emphasizing a Servant Leadership Chain that supports empowerment and accountability. This leadership approach prioritizes serving team needs and fostering collaboration, enhancing agility and innovation compared to traditional rigid hierarchies.
Fluid Hierarchies
Fluid hierarchies in organizational charts provide clear lines of authority and responsibility but often limit agility and employee autonomy. Holacracy replaces traditional hierarchies with dynamic roles and distributed decision-making, enhancing flexibility and responsiveness in complex management environments.
Organizational Chart vs Holacracy Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com