SWOT Analysis identifies an organization's internal strengths and weaknesses alongside external opportunities and threats, providing a comprehensive assessment of potential challenges and risks. SOAR Analysis emphasizes strengths, opportunities, aspirations, and results, focusing on leveraging positive attributes to drive strategic growth and innovation. Both frameworks guide management decisions but differ in approach, with SWOT offering a balanced risk perspective and SOAR fostering an optimistic, strength-based vision for future success.
Table of Comparison
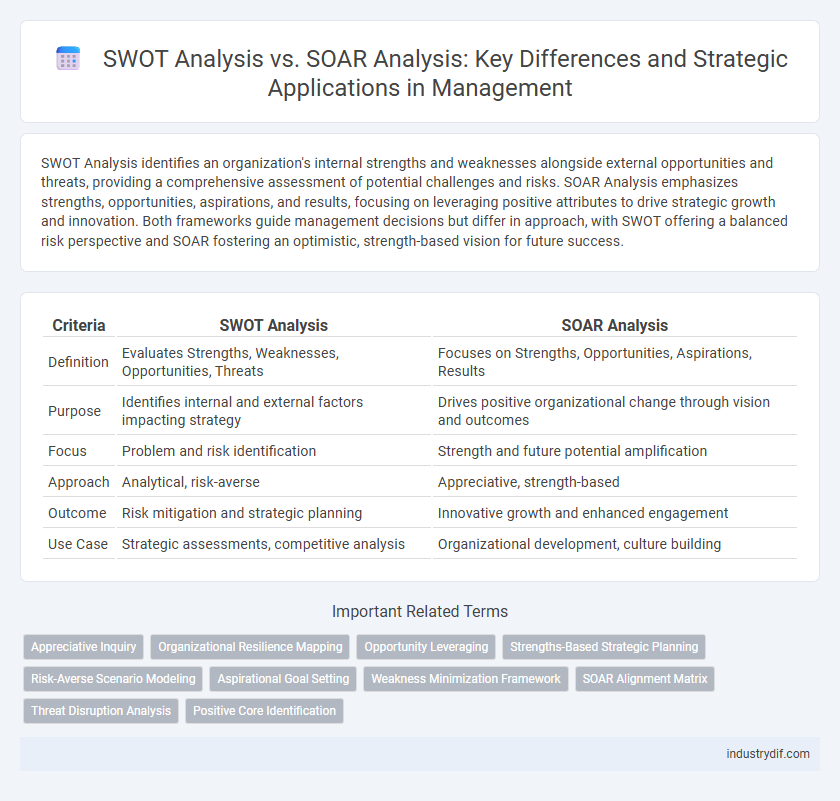
| Criteria | SWOT Analysis | SOAR Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluates Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats | Focuses on Strengths, Opportunities, Aspirations, Results |
| Purpose | Identifies internal and external factors impacting strategy | Drives positive organizational change through vision and outcomes |
| Focus | Problem and risk identification | Strength and future potential amplification |
| Approach | Analytical, risk-averse | Appreciative, strength-based |
| Outcome | Risk mitigation and strategic planning | Innovative growth and enhanced engagement |
| Use Case | Strategic assessments, competitive analysis | Organizational development, culture building |
Introduction to SWOT and SOAR Analysis
SWOT Analysis evaluates organizational Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats to provide a comprehensive view of internal and external factors influencing strategic decisions. SOAR Analysis focuses on Strengths, Opportunities, Aspirations, and Results to foster a positive, strengths-based approach for strategic planning and organizational growth. Both frameworks serve distinct roles in management by offering complementary insights for effective decision-making and performance improvement.
Defining SWOT Analysis in Management
SWOT Analysis in management is a strategic planning tool used to identify and assess an organization's internal Strengths and Weaknesses, along with external Opportunities and Threats. It provides a comprehensive snapshot of current performance factors, helping managers develop informed strategies that leverage core competencies while mitigating risks. This method fosters objective decision-making by balancing internal capabilities with market conditions.
Key Components of SOAR Analysis
SOAR Analysis focuses on Strengths, Opportunities, Aspirations, and Results, enabling organizations to build on what they do well and envision future goals. Unlike SWOT Analysis, which includes Weaknesses and Threats, SOAR emphasizes positive factors to foster collaborative strategic planning and innovation. Key components of SOAR drive goal-oriented discussions that align team aspirations with measurable outcomes.
Comparative Overview: SWOT vs SOAR
SWOT analysis identifies internal strengths and weaknesses alongside external opportunities and threats, providing a comprehensive risk and challenge assessment. SOAR analysis emphasizes strengths, opportunities, aspirations, and results, fostering a positive, strategic framework for growth and innovation. The comparative overview reveals SWOT's diagnostic approach versus SOAR's strategic, opportunity-driven mindset, making SOAR more suitable for forward-looking leadership and organizational development.
Strengths and Opportunities: A Dual Approach
SWOT Analysis highlights both internal Strengths and external Opportunities to identify strategic priorities, providing a balanced perspective on challenges and advantages. SOAR Analysis emphasizes leveraging Strengths and Opportunities to drive positive change, focusing on actionable insights and future growth. Combining these frameworks enables organizations to holistically assess assets while proactively exploring market potential for sustained competitive advantage.
Identifying Weaknesses vs Focusing on Aspirations
SWOT analysis emphasizes identifying weaknesses to address internal challenges and mitigate risks within an organization, enabling strategic problem-solving. In contrast, SOAR analysis concentrates on aspirations, fostering a positive outlook by leveraging strengths and opportunities to drive innovation and growth. This shift from problem-focused to possibility-driven approaches influences how management prioritizes development and sets future goals.
Application of SWOT Analysis in Strategic Planning
SWOT analysis identifies internal strengths and weaknesses alongside external opportunities and threats, providing a comprehensive framework for strategic planning in management. It helps organizations assess current performance and environmental factors to formulate actionable goals and allocate resources efficiently. The strategic insights gained from SWOT facilitate risk management and competitive advantage by aligning capabilities with market conditions.
Leveraging SOAR Analysis for Organizational Growth
SOAR Analysis leverages strengths, opportunities, aspirations, and results to foster organizational growth by aligning strategic initiatives with core capabilities and future goals. Unlike SWOT Analysis, which centers on identifying weaknesses and threats, SOAR emphasizes positive factors that drive innovation and employee engagement. By focusing on strengths and opportunities, SOAR Analysis enables management to create actionable growth strategies that enhance competitive advantage and long-term performance.
Choosing the Right Analysis for Your Business Needs
SWOT analysis identifies strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to provide a comprehensive view of a business's internal and external challenges. SOAR analysis focuses on strengths, opportunities, aspirations, and results, emphasizing positive growth and strategic vision alignment. Choosing between SWOT and SOAR depends on your business goals: use SWOT for risk management and competitive positioning, while SOAR suits organizations prioritizing innovation and stakeholder engagement.
Integrating SWOT and SOAR for Effective Management
Integrating SWOT and SOAR analysis enhances strategic management by combining SWOT's focus on identifying weaknesses and threats with SOAR's emphasis on strengths, opportunities, aspirations, and results, fostering a balanced perspective for decision-making. This fusion facilitates comprehensive organizational assessment, promotes positive dialogue, and drives actionable strategies aligned with both challenges and potential growth areas. Managers leveraging this integrated approach can optimize resource allocation, improve stakeholder engagement, and accelerate goal achievement within dynamic business environments.
Related Important Terms
Appreciative Inquiry
SWOT analysis identifies organizational strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, primarily focusing on problem-solving and risk mitigation. SOAR analysis, grounded in Appreciative Inquiry, emphasizes strengths, opportunities, aspirations, and results to foster positive strategic planning and enhance stakeholder engagement.
Organizational Resilience Mapping
SWOT analysis identifies internal strengths, weaknesses, external opportunities, and threats, providing a comprehensive framework for organizational resilience mapping by pinpointing vulnerabilities and potential growth areas. SOAR analysis emphasizes strengths, opportunities, aspirations, and results, fostering a positive, forward-looking approach that enhances resilience by aligning organizational capabilities with strategic objectives.
Opportunity Leveraging
SWOT Analysis identifies opportunities by examining external factors, highlighting potential risks alongside strengths and weaknesses, which may limit proactive opportunity leveraging. SOAR Analysis focuses on strengths and aspirations to actively co-create and capitalize on opportunities, fostering positive strategic and collaborative growth.
Strengths-Based Strategic Planning
SWOT analysis identifies organizational strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to provide a comprehensive risk assessment, while SOAR analysis focuses exclusively on strengths, opportunities, aspirations, and results to drive strengths-based strategic planning that maximizes existing capabilities and future potential. Strengths-based strategic planning through SOAR enhances employee engagement and innovation by leveraging core competencies and aligning organizational goals with positive aspirations.
Risk-Averse Scenario Modeling
SWOT analysis identifies internal weaknesses and external threats to mitigate risks in decision-making, while SOAR analysis emphasizes strengths, opportunities, aspirations, and results to foster positive strategic growth. In risk-averse scenario modeling, SWOT provides a comprehensive risk assessment framework, whereas SOAR enhances resilience by leveraging core capabilities and forward-looking opportunities.
Aspirational Goal Setting
SWOT analysis identifies strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to assess current organizational status, while SOAR analysis emphasizes strengths, opportunities, aspirations, and results to drive aspirational goal setting and positive strategic planning. Focusing on SOAR enables management to align team vision with actionable goals, fostering motivation and innovation through a strengths-based approach.
Weakness Minimization Framework
SWOT Analysis identifies internal weaknesses and external threats to develop strategies that mitigate risks, while SOAR Analysis emphasizes strengths, opportunities, and aspirations to drive positive change without directly addressing weaknesses. The Weakness Minimization Framework in SWOT enables organizations to allocate resources effectively by targeting specific areas for improvement and reducing vulnerabilities that could hinder performance.
SOAR Alignment Matrix
The SOAR Alignment Matrix enhances strategic planning by focusing on Strengths, Opportunities, Aspirations, and Results, fostering a positive, future-oriented mindset compared to the traditional SWOT Analysis's emphasis on weaknesses and threats. This matrix drives collaborative alignment and actionable outcomes, enabling organizations to leverage core competencies and stakeholder aspirations for sustainable growth.
Threat Disruption Analysis
SWOT analysis emphasizes identifying external threats that could disrupt business operations, providing a comprehensive risk assessment framework to mitigate potential challenges. SOAR analysis, however, focuses more on strengths and opportunities, offering limited insights into threat disruption, which may overlook critical risks impacting organizational resilience.
Positive Core Identification
SWOT analysis identifies strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, providing a balanced view including potential risks, while SOAR analysis focuses exclusively on positive core identification by emphasizing strengths, opportunities, aspirations, and results to drive strategic growth. Emphasizing positive core elements in SOAR fosters organizational alignment and engagement by leveraging what works well to inspire innovation and actionable outcomes.
SWOT Analysis vs SOAR Analysis Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com