Top-down management relies on hierarchical decision-making where authority flows from senior leaders to employees, often causing slower response times and reduced innovation. In contrast, Teal organizations promote self-management, decentralized control, and empowered teams that foster agility and employee engagement. Emphasizing purpose-driven collaboration, Teal structures enhance adaptability and sustain long-term organizational growth.
Table of Comparison
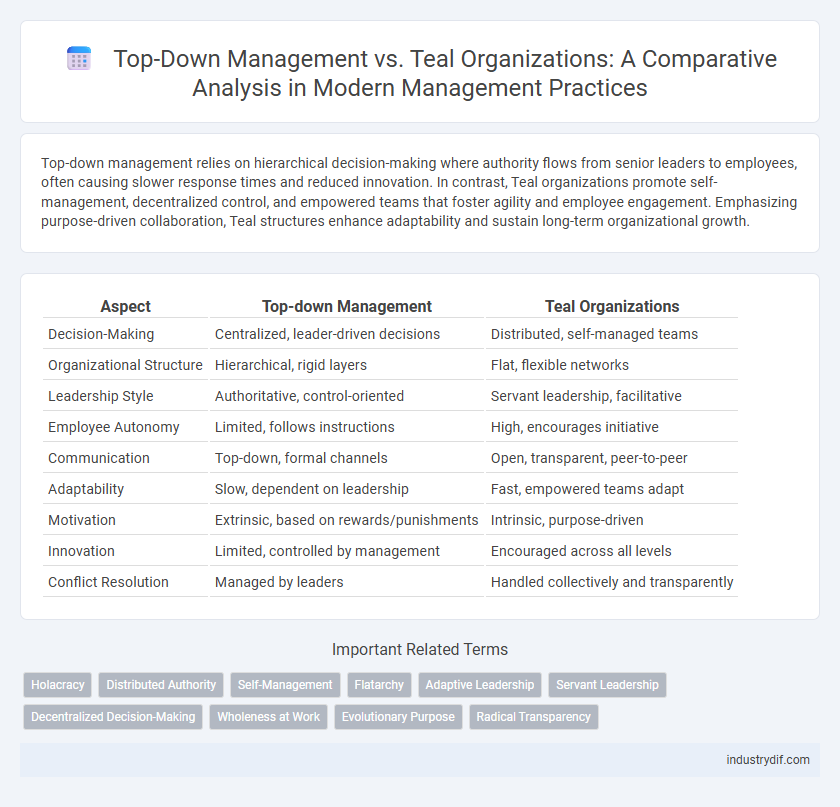
| Aspect | Top-down Management | Teal Organizations |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Centralized, leader-driven decisions | Distributed, self-managed teams |
| Organizational Structure | Hierarchical, rigid layers | Flat, flexible networks |
| Leadership Style | Authoritative, control-oriented | Servant leadership, facilitative |
| Employee Autonomy | Limited, follows instructions | High, encourages initiative |
| Communication | Top-down, formal channels | Open, transparent, peer-to-peer |
| Adaptability | Slow, dependent on leadership | Fast, empowered teams adapt |
| Motivation | Extrinsic, based on rewards/punishments | Intrinsic, purpose-driven |
| Innovation | Limited, controlled by management | Encouraged across all levels |
| Conflict Resolution | Managed by leaders | Handled collectively and transparently |
Introduction to Management Paradigms
Top-down management relies on hierarchical decision-making with clear authority lines, emphasizing control and efficiency in organizational operations. Teal organizations embrace self-management, decentralizing authority to empower teams and foster innovation through trust and autonomy. Understanding these paradigms reveals contrasting approaches to leadership, structure, and employee engagement in contemporary management.
Defining Top-down Management
Top-down management is a hierarchical approach where decision-making authority is concentrated at the upper levels of leadership, cascading directives downward through clear chains of command. This structure emphasizes control, consistency, and accountability by assigning specific roles and responsibilities within predefined layers. It contrasts with decentralized models by prioritizing centralized oversight to ensure alignment with organizational goals.
Understanding Teal Organizations
Teal organizations emphasize decentralized decision-making, self-management, and evolutionary purpose, contrasting sharply with the hierarchical structure of top-down management. These organizations prioritize employee autonomy, fostering intrinsic motivation and adaptability in complex environments. Understanding teal organizations involves recognizing their commitment to transparency, trust, and continuous learning as key drivers of organizational success.
Historical Evolution of Management Structures
Traditional top-down management structures originated during the Industrial Revolution, emphasizing rigid hierarchies and centralized decision-making to maximize efficiency and control. In contrast, teal organizations represent an evolutionary shift toward decentralized, self-managing teams that prioritize purpose, autonomy, and holistic employee development. This transition reflects broader historical trends in management theory, moving from command-and-control models to more adaptive, human-centric organizational designs.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Top-down management centralizes decision-making power within a hierarchical structure, where leaders set directives and employees follow predefined roles, often limiting flexibility and innovation. Teal organizations distribute decision-making across self-managing teams, empowering individuals to take initiative and adapt quickly to changing conditions. This decentralized model fosters greater employee engagement, faster problem-solving, and alignment with organizational purpose.
Leadership Roles and Authority
Top-down management centralizes leadership roles with clear hierarchical authority, where decision-making is concentrated at the top levels of the organization. Teal organizations distribute leadership through self-management principles, empowering employees to take initiative and make decisions collaboratively without rigid authority. This shift enhances adaptability, fostering a culture of trust and shared responsibility over traditional command-and-control structures.
Employee Engagement and Autonomy
Top-down management often limits employee engagement and autonomy by centralizing decision-making authority, which can reduce motivation and innovation. In contrast, Teal organizations emphasize self-management and distributed authority, fostering higher levels of employee empowerment and intrinsic motivation. Studies show that organizations adopting Teal principles experience increased job satisfaction, creativity, and organizational commitment among employees.
Organizational Communication Patterns
Top-down management relies on hierarchical communication where directives flow from leaders to employees, often limiting feedback and collaboration. Teal organizations embrace decentralized, self-managed teams that foster open, transparent communication and encourage collective decision-making. This shift enhances agility, employee engagement, and innovation by prioritizing multi-directional information exchange across all levels.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Each Approach
Top-down management ensures clear hierarchy and streamlined decision-making, which can enhance accountability but often stifles employee creativity and slows adaptability. Teal organizations promote self-management and decentralized control, fostering innovation and engagement while potentially leading to role ambiguity and coordination challenges. Both approaches offer distinct advantages: hierarchical structures provide order and predictability, whereas teal models encourage flexibility and empowerment in dynamic environments.
Choosing the Right Structure for Your Organization
Top-down management emphasizes hierarchical decision-making and clear authority lines, which can streamline accountability and ensure consistent direction in large or traditional organizations. Teal organizations prioritize self-management, decentralized control, and evolutionary purpose, fostering innovation and employee empowerment in dynamic or creative sectors. Selecting the right structure depends on organizational goals, culture, size, and industry demands to balance control with flexibility effectively.
Related Important Terms
Holacracy
Top-down management centralizes decision-making authority, often resulting in rigid hierarchies, whereas Teal organizations adopt decentralized structures emphasizing self-management, with Holacracy providing a framework that replaces traditional management roles by distributing authority through clear roles and circles. Holacracy enhances organizational agility and transparency by formalizing governance processes and enabling continuous evolution of roles aligned with purpose and accountabilities.
Distributed Authority
Top-down management centralizes decision-making authority within hierarchical leadership, limiting employee autonomy and slowing response times, whereas teal organizations distribute authority broadly across self-managing teams, fostering agility and innovation. Distributed authority in teal organizations empowers employees at all levels to make decisions aligned with organizational purpose, enhancing engagement and adaptive capacity.
Self-Management
Self-management in Teal organizations empowers employees with autonomy and decision-making authority, fostering innovation and accountability without hierarchical constraints. In contrast, top-down management relies on centralized control and directive leadership, often limiting adaptability and employee engagement.
Flatarchy
Top-down management relies on hierarchical decision-making, whereas teal organizations emphasize self-management and decentralized authority. Flatarchy combines elements of both by maintaining a flexible structure with minimal layers, promoting agility and cross-functional collaboration to enhance innovation and responsiveness.
Adaptive Leadership
Top-down management relies on hierarchical decision-making, often limiting adaptive leadership by concentrating authority at the top, whereas teal organizations promote decentralized control and self-management, fostering adaptive leadership through distributed intelligence and collaborative problem-solving. Emphasizing evolutionary purpose and trust, teal organizations enable leaders to respond flexibly to complex challenges, enhancing organizational resilience and innovation.
Servant Leadership
Servant leadership in teal organizations emphasizes empowering employees by fostering trust, collaboration, and autonomy, contrasting with top-down management's hierarchical control and directive decision-making. This approach enhances innovation and engagement by prioritizing team members' growth and aligning organizational goals with individual purpose.
Decentralized Decision-Making
Decentralized decision-making in teal organizations contrasts sharply with the top-down management approach by empowering employees at all levels to make decisions autonomously, fostering innovation and agility. This structure reduces bottlenecks common in hierarchical systems, enabling faster response times and enhanced organizational adaptability.
Wholeness at Work
Top-down management often limits wholeness at work by enforcing rigid hierarchies and compartmentalized roles, whereas Teal organizations foster wholeness through self-management, encouraging employees to bring their full authentic selves to the workplace. Emphasizing autonomy and trust, Teal models enhance engagement and innovation by integrating emotional, cognitive, and interpersonal dimensions within organizational cultures.
Evolutionary Purpose
Top-down management relies on hierarchical control with decisions flowing from executives to employees, often prioritizing short-term goals and control mechanisms. Teal organizations embrace an evolutionary purpose, allowing self-management and autonomous teams to adapt dynamically, fostering innovation and long-term organizational growth.
Radical Transparency
Radical transparency in teal organizations fosters open communication and trust by sharing information freely across all levels, contrasting with top-down management where decision-making remains hierarchical and information is often restricted to upper echelons. This approach enhances employee autonomy and accountability, driving innovation and alignment with organizational purpose.
Top-down Management vs Teal Organizations Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com