Traditional teams rely on fixed roles and hierarchical structures to manage tasks, which can limit flexibility and slow down decision-making processes. Swarm teams operate dynamically, with members collaborating fluidly based on real-time needs, enhancing adaptability and innovation. This approach fosters faster problem-solving and greater responsiveness to changing project demands.
Table of Comparison
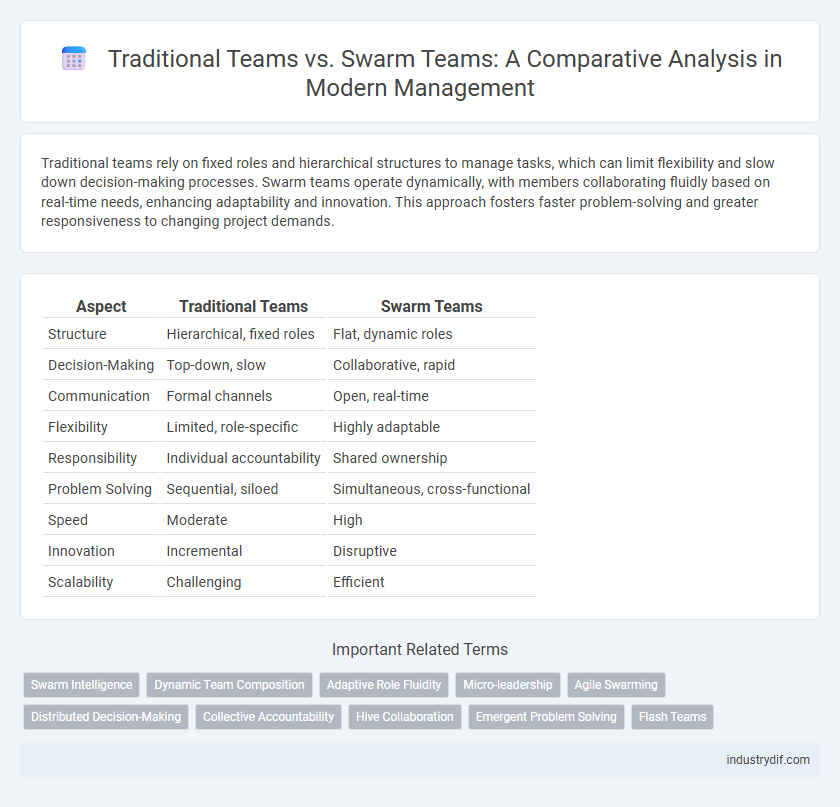
| Aspect | Traditional Teams | Swarm Teams |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Hierarchical, fixed roles | Flat, dynamic roles |
| Decision-Making | Top-down, slow | Collaborative, rapid |
| Communication | Formal channels | Open, real-time |
| Flexibility | Limited, role-specific | Highly adaptable |
| Responsibility | Individual accountability | Shared ownership |
| Problem Solving | Sequential, siloed | Simultaneous, cross-functional |
| Speed | Moderate | High |
| Innovation | Incremental | Disruptive |
| Scalability | Challenging | Efficient |
Defining Traditional Teams in Management
Traditional teams in management consist of fixed roles and hierarchical structures, where members have clearly defined responsibilities and decision-making authority is centralized. These teams operate within established workflows and communication channels, emphasizing stability and predictability in task execution. Leadership directs activities, and coordination occurs through formal processes, ensuring accountability and control over project outcomes.
Characteristics of Swarm Teams
Swarm teams exhibit high flexibility, rapid decision-making, and self-organization, distinguishing them from traditional teams with fixed roles and hierarchical structures. These teams prioritize real-time collaboration and collective problem-solving, enabling faster adaptation to dynamic project demands. The emphasis on distributed leadership and continuous feedback fosters innovation and increased responsiveness in complex environments.
Core Differences Between Traditional and Swarm Teams
Traditional teams operate with fixed roles and hierarchical decision-making, emphasizing specialization and linear task execution, whereas swarm teams utilize dynamic roles with decentralized authority, promoting rapid collaboration and adaptability. Swarm teams thrive on real-time communication and collective problem-solving, enabling faster innovation and responsiveness compared to the structured, process-driven approach of traditional teams. Core differences lie in flexibility, role fluidity, and decision autonomy, affecting productivity and efficiency in management practices.
Hierarchical Structures vs. Decentralized Approaches
Traditional teams rely on hierarchical structures where decision-making authority is concentrated at the top levels, promoting clear roles and accountability but often slowing responsiveness. Swarm teams employ decentralized approaches, enabling fluid collaboration and rapid adaptation through distributed leadership and collective problem-solving. This shift from rigid hierarchies to agile networks fosters innovation and enhances organizational resilience in dynamic environments.
Communication Styles and Collaboration Methods
Traditional teams often rely on hierarchical communication styles, with information flowing through defined channels and roles, creating structured but slower decision-making processes. Swarm teams embrace decentralized communication and dynamic collaboration, encouraging real-time feedback and adaptability through fluid roles and shared responsibilities. This shift enhances responsiveness and innovation by fostering continuous interaction and collective problem-solving.
Decision-Making Processes Compared
Traditional teams often rely on hierarchical decision-making where leaders or managers make key choices, potentially slowing response times and limiting input from all members. In contrast, swarm teams employ decentralized decision-making, enabling rapid, collaborative responses that leverage collective intelligence and adaptability. This approach enhances agility, fosters innovation, and improves problem-solving efficiency in dynamic environments.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Team Dynamics
Traditional teams often rely on fixed roles and hierarchical structures, which can limit their flexibility and slow response to change. Swarm teams embrace dynamic role allocation and real-time collaboration, enhancing adaptability and enabling rapid problem-solving in complex environments. This fluid team dynamic fosters innovation and resilience, critical for managing uncertainty and evolving project demands.
Impact on Innovation and Problem-Solving
Traditional teams often rely on hierarchical structures with defined roles, which can limit flexibility and slow the innovation process, while swarm teams leverage decentralized collaboration, enabling rapid idea generation and adaptive problem-solving. Swarm teams encourage diverse perspectives and real-time feedback, fostering a culture of continuous innovation and accelerating solution development compared to the linear decision-making typical in traditional teams. Organizations adopting swarm team models frequently experience enhanced creativity, faster response to complex challenges, and improved overall innovation outcomes.
Challenges of Transitioning from Traditional to Swarm Teams
Transitioning from traditional teams to swarm teams presents challenges such as resistance to change due to established hierarchical structures and unclear roles within self-organizing groups. Communication complexity increases as swarm teams rely on continuous collaboration and rapid information sharing, demanding advanced digital tools and trust among members. Organizations must address skill gaps and cultural shifts to foster agility, autonomy, and decentralized decision-making essential for effective swarm team performance.
Choosing the Right Team Model for Your Organization
Choosing the right team model for your organization depends on project complexity, speed requirements, and collaboration style. Traditional teams offer clear roles and stability suited for long-term, well-defined projects, while swarm teams emphasize cross-functional agility and rapid problem-solving ideal for dynamic environments. Evaluating organizational goals and workflow flexibility ensures alignment with strategic outcomes and maximizes productivity.
Related Important Terms
Swarm Intelligence
Swarm teams leverage swarm intelligence by enabling decentralized decision-making and dynamic collaboration, resulting in increased adaptability and rapid problem-solving compared to traditional hierarchical teams. This approach harnesses collective behavior to optimize resource allocation and innovation through real-time feedback and self-organization.
Dynamic Team Composition
Traditional teams operate with fixed roles and hierarchical structures, limiting adaptability in fast-changing environments. Swarm teams leverage dynamic team composition by rapidly assembling cross-functional experts to address specific challenges, enhancing flexibility and innovation.
Adaptive Role Fluidity
Traditional teams have fixed roles with clearly defined responsibilities, limiting flexibility and responsiveness to changing project requirements. Swarm teams exhibit adaptive role fluidity, enabling members to dynamically shift roles based on skills and workload, enhancing collaboration and accelerating problem-solving efficiency.
Micro-leadership
Traditional teams rely on centralized leadership and defined roles, whereas swarm teams emphasize micro-leadership, distributing decision-making power to empower individuals at every level. This shift fosters agility, rapid problem-solving, and enhanced collaboration by enabling team members to take initiative within their areas of expertise.
Agile Swarming
Agile swarming enhances team responsiveness by enabling cross-functional members to collaborate dynamically on high-priority tasks, contrasting with traditional teams' fixed roles and sequential workflows. This approach accelerates problem-solving and delivery, improving project adaptability and customer satisfaction in fast-paced environments.
Distributed Decision-Making
Traditional teams typically rely on centralized decision-making where authority is concentrated in leaders, slowing response times and reducing flexibility. Swarm teams embrace distributed decision-making, enabling members to collaborate dynamically and respond rapidly to challenges through shared authority and real-time information exchange.
Collective Accountability
Traditional teams often assign accountability to individual roles, which can lead to siloed responsibility and reduced collaboration, while swarm teams emphasize collective accountability, fostering shared ownership and accelerated problem-solving through real-time collaboration. This shift enhances team agility and innovation by distributing decision-making and encouraging mutual support in dynamic work environments.
Hive Collaboration
Traditional teams operate with hierarchical structures and defined roles, limiting real-time collaboration, while swarm teams leverage hive collaboration to dynamically pool expertise and rapidly adapt to challenges. Hive collaboration in swarm teams enhances collective intelligence by enabling fluid communication and decentralized decision-making, driving faster innovation and problem-solving.
Emergent Problem Solving
Traditional teams rely on predefined roles and hierarchical decision-making, which can slow down emergent problem solving due to rigid structures and limited real-time collaboration. Swarm teams leverage dynamic, self-organizing groups that rapidly adapt and share expertise, enabling faster identification and resolution of complex problems through collective intelligence.
Flash Teams
Flash teams, a form of swarm teams, rapidly assemble cross-functional experts to tackle specific projects with agility and minimal hierarchical constraints, enhancing innovation and speed. Unlike traditional teams, which rely on stable roles and prolonged collaboration, flash teams prioritize flexibility and real-time problem-solving in dynamic business environments.
Traditional Teams vs Swarm Teams Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com