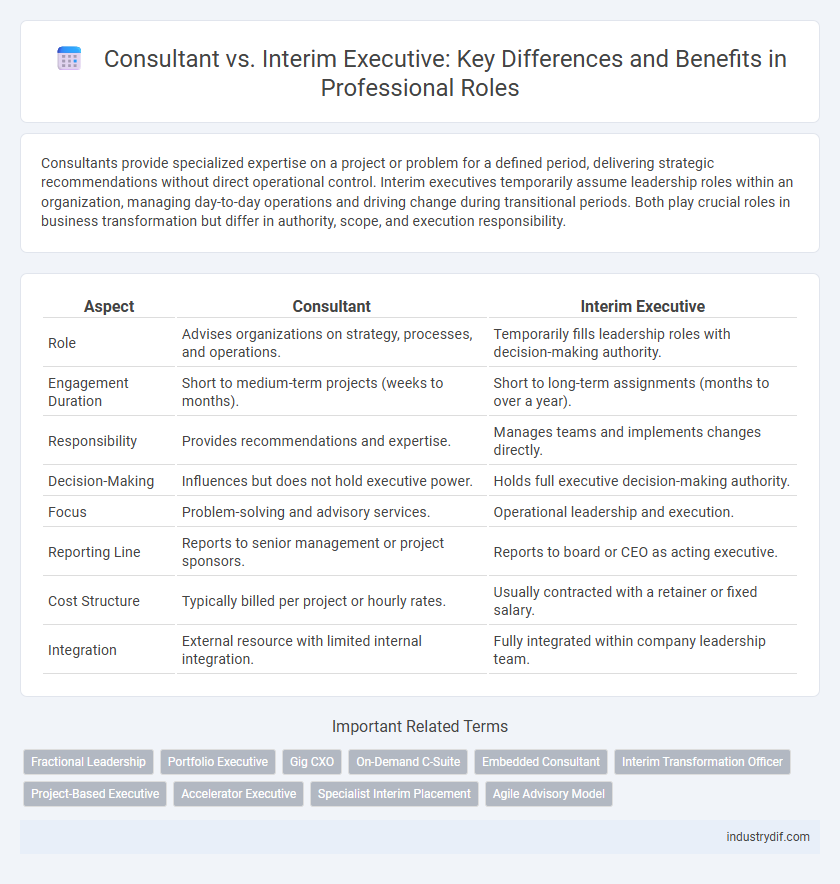
Consultants provide specialized expertise on a project or problem for a defined period, delivering strategic recommendations without direct operational control. Interim executives temporarily assume leadership roles within an organization, managing day-to-day operations and driving change during transitional periods. Both play crucial roles in business transformation but differ in authority, scope, and execution responsibility.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Consultant | Interim Executive |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Advises organizations on strategy, processes, and operations. | Temporarily fills leadership roles with decision-making authority. |
| Engagement Duration | Short to medium-term projects (weeks to months). | Short to long-term assignments (months to over a year). |
| Responsibility | Provides recommendations and expertise. | Manages teams and implements changes directly. |
| Decision-Making | Influences but does not hold executive power. | Holds full executive decision-making authority. |
| Focus | Problem-solving and advisory services. | Operational leadership and execution. |
| Reporting Line | Reports to senior management or project sponsors. | Reports to board or CEO as acting executive. |
| Cost Structure | Typically billed per project or hourly rates. | Usually contracted with a retainer or fixed salary. |
| Integration | External resource with limited internal integration. | Fully integrated within company leadership team. |
Defining Consultants and Interim Executives
Consultants provide expert advice and strategic recommendations to organizations on specific projects or challenges, leveraging specialized knowledge without being involved in daily operations. Interim Executives take on temporary leadership roles, managing teams and driving business results during transitional periods or executive vacancies. Both roles demand high-level expertise, but consultants focus on advisory services while interim executives deliver hands-on management and decision-making.
Key Differences in Roles and Responsibilities
Consultants provide expert advice and strategic recommendations to improve specific business functions or processes, often working on a project basis without direct management authority. Interim executives assume temporary leadership roles within an organization, taking full responsibility for decision-making and daily operations to maintain continuity during transitions or crises. While consultants influence change through guidance, interim executives implement and oversee changes as acting members of the leadership team.
Typical Engagement Scenarios
Consultants are typically engaged for project-based assignments requiring specialized expertise to address specific business challenges or implement strategic initiatives. Interim executives are often appointed during leadership transitions, crisis management, or organizational restructuring to provide hands-on management and maintain operational continuity. Both roles differ in scope and duration, with consultants focusing on advisory and analysis, while interim executives assume full managerial responsibilities temporarily.
Skill Sets and Qualifications
Consultants typically possess specialized expertise in areas like strategy, operations, or technology, offering tailored solutions based on deep analytical skills and industry knowledge. Interim executives combine strategic insight with hands-on leadership experience, often holding C-suite qualifications and a proven track record in managing organizational change during critical periods. Both roles demand strong communication and problem-solving abilities, but interim executives require robust operational management skills to drive execution alongside advisory capabilities.
Duration and Scope of Assignments
Consultants typically engage in short-term projects with a defined scope focused on delivering specialized expertise or recommendations. Interim executives operate in mid to long-term roles, assuming full leadership responsibilities to manage day-to-day operations and drive strategic initiatives during transitional periods. The duration and scope differences highlight consultants as advisors providing targeted solutions, while interim executives act as hands-on leaders embedded within the organization.
Impact on Organizational Change
Consultants provide expert analysis and strategic recommendations to drive organizational change without being embedded in day-to-day operations, enabling objective assessments and innovative solutions. Interim executives hold temporary leadership roles, directly managing teams and executing change initiatives to ensure immediate accountability and sustained progress. The tangible impact of interim executives often surpasses consultants by integrating change within the organizational structure and culture for lasting transformation.
Cost Structures and Compensation Models
Consultants typically operate on a project-based fee structure, charging hourly or fixed rates that cover advisory services without long-term employment costs. Interim executives often receive a higher total compensation package that includes a daily rate or retainer plus potential performance bonuses, reflecting their integration into company leadership roles. Understanding the distinct cost structures and compensation models helps organizations optimize budgeting while addressing short-term leadership needs versus specialized advisory expertise.
Integration with Existing Teams
Consultants provide specialized expertise and strategic recommendations without fully embedding in the company's day-to-day operations, allowing existing teams to maintain their workflow with minimal disruption. Interim Executives assume leadership roles within the organization, directly managing teams and driving change from within, which fosters closer integration and alignment with ongoing projects. Their hands-on involvement often accelerates decision-making and ensures that strategies are executed consistently across departments.
Advantages and Limitations
Consultants provide specialized expertise and objective analysis, often delivering strategic recommendations without long-term commitment, which allows companies to address specific challenges efficiently; however, they may lack in-depth operational involvement and authority to implement changes directly. Interim executives bring executive-level leadership and decision-making authority, enabling immediate operational control and cultural integration during transition periods, but their temporary presence can limit continuity and long-term strategic consistency. Both roles offer flexibility and expertise, yet organizations must weigh the trade-offs between external advisory roles and embedded leadership for effective problem-solving and transformation.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Selecting between a consultant and an interim executive depends on your business needs for expertise and leadership duration. Consultants provide specialized advice and strategic recommendations, ideal for project-based challenges or specific operational improvements. Interim executives deliver hands-on leadership and decision-making authority during transitions or crises, ensuring continuity and immediate impact within your organization.
Related Important Terms
Fractional Leadership
Fractional leadership uniquely combines the expertise of consultants with the active decision-making role of interim executives, providing organizations flexible, part-time strategic management without the full-time commitment. This hybrid approach enables companies to access high-level leadership tailored to specific projects or transitional phases, optimizing resource allocation and driving impactful business outcomes.
Portfolio Executive
A Portfolio Executive leverages deep industry expertise to drive strategic initiatives across multiple organizations, offering sustained leadership beyond the project-based scope typical of consultants. Unlike Interim Executives who temporarily fill leadership gaps, Portfolio Executives maintain ongoing oversight and influence in shaping long-term business outcomes within diverse client portfolios.
Gig CXO
Gig CXOs serve as interim executives providing strategic leadership during transitional phases, offering hands-on management and decision-making authority unlike consultants who primarily deliver analysis and recommendations. The gig economy's rise has increased demand for these flexible, experienced executives who integrate into organizations temporarily to drive performance and implement change.
On-Demand C-Suite
On-demand C-Suite services differentiate consultants and interim executives by scope and authority; consultants provide expert advice and strategic insights without direct decision-making power, while interim executives assume full operational control to drive immediate results during leadership gaps. Organizations leverage consultants for specialized project guidance and interim executives for hands-on leadership with accountability in transitional periods.
Embedded Consultant
An Embedded Consultant integrates deeply within an organization to provide tailored strategic guidance and hands-on support, enhancing internal capabilities while driving sustainable change. Unlike interim executives who temporarily fill leadership roles, Embedded Consultants maintain an advisory position that promotes long-term growth without direct operational control.
Interim Transformation Officer
An Interim Transformation Officer leads organizational change by implementing strategic initiatives and driving transformation projects within a defined timeframe, offering hands-on leadership compared to a consultant who primarily provides expert advice and recommendations. The interim executive's role centers on accountability and operational execution, ensuring seamless transition and sustainable business improvements during periods of significant change.
Project-Based Executive
Project-based executives deliver strategic leadership with full accountability for outcomes, embedding themselves within the organization to drive transformation and ensure sustainable results. Consultants provide expert advice and recommendations without long-term operational responsibility, often supporting decision-making rather than executing initiatives.
Accelerator Executive
An Accelerator Executive leverages deep industry expertise and strategic insight to drive rapid business growth, distinguishing their role from a Consultant who primarily offers advisory services and an Interim Executive who temporarily fills leadership gaps. Their focus on acceleration enables organizations to implement high-impact initiatives swiftly, fostering sustainable value creation and competitive advantage.
Specialist Interim Placement
Specialist interim placement offers organizations targeted expertise through interim executives who not only advise but also lead critical projects and operational changes, bridging gaps during transitions. Unlike consultants, interim executives assume full accountability for results, integrating seamlessly within leadership teams to drive performance and deliver measurable outcomes.
Agile Advisory Model
Consultants offer specialized Agile expertise to assess and recommend tailored strategies, while interim executives integrate into leadership roles to execute Agile transformations actively, ensuring sustained organizational change. The Agile Advisory Model leverages consultants for targeted insights and interim executives for hands-on leadership, maximizing adaptive capacity and business agility.
Consultant vs Interim Executive Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com