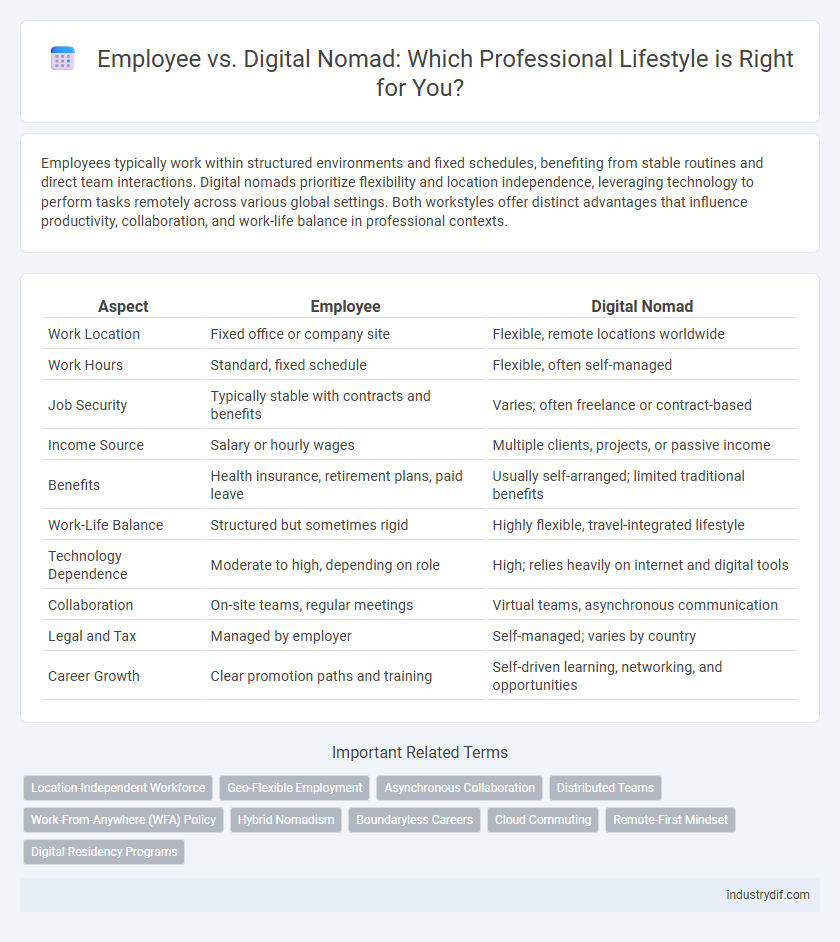
Employees typically work within structured environments and fixed schedules, benefiting from stable routines and direct team interactions. Digital nomads prioritize flexibility and location independence, leveraging technology to perform tasks remotely across various global settings. Both workstyles offer distinct advantages that influence productivity, collaboration, and work-life balance in professional contexts.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Employee | Digital Nomad |
|---|---|---|
| Work Location | Fixed office or company site | Flexible, remote locations worldwide |
| Work Hours | Standard, fixed schedule | Flexible, often self-managed |
| Job Security | Typically stable with contracts and benefits | Varies; often freelance or contract-based |
| Income Source | Salary or hourly wages | Multiple clients, projects, or passive income |
| Benefits | Health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave | Usually self-arranged; limited traditional benefits |
| Work-Life Balance | Structured but sometimes rigid | Highly flexible, travel-integrated lifestyle |
| Technology Dependence | Moderate to high, depending on role | High; relies heavily on internet and digital tools |
| Collaboration | On-site teams, regular meetings | Virtual teams, asynchronous communication |
| Legal and Tax | Managed by employer | Self-managed; varies by country |
| Career Growth | Clear promotion paths and training | Self-driven learning, networking, and opportunities |
Defining Employee and Digital Nomad Roles
Employees typically have fixed roles within an organization, working on-site or remotely with structured schedules, defined responsibilities, and direct supervision. Digital nomads, by contrast, leverage technology to perform their work from various global locations, enjoying flexibility in timing and workspace selection while managing freelance or contract-based projects. Both roles require distinct skill sets and adaptability, with employees emphasizing stability and team collaboration, and digital nomads prioritizing independence and self-management.
Work Environment: Office vs Remote Locations
Employees traditionally work in structured office environments that facilitate direct supervision, collaboration, and access to on-site resources essential for team-based projects. Digital nomads prefer remote locations, leveraging modern technology to maintain productivity while enjoying flexibility and diverse work settings. This shift highlights evolving workplace dynamics where connectivity and autonomy redefine how and where professional tasks are accomplished.
Flexibility in Work Schedules
Employee work schedules typically follow fixed hours determined by the employer, limiting personal flexibility but ensuring structured productivity. Digital nomads enjoy greater autonomy, crafting work hours around personal preferences and travel plans, which enhances work-life balance. This flexibility supports diverse lifestyles but requires strong self-discipline to meet deadlines and maintain performance.
Legal and Compliance Considerations
Employers must navigate complex legal frameworks governing employment contracts, tax obligations, and labor laws when managing both traditional employees and digital nomads. Digital nomads pose unique compliance challenges related to multi-jurisdictional work permits, data privacy regulations such as GDPR, and social security contributions across borders. Ensuring adherence to location-specific labor laws and maintaining robust employment agreements are critical for mitigating risks and maintaining operational integrity.
Benefits and Compensation Structures
Employees often benefit from structured compensation packages including fixed salaries, health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave, providing financial stability and predictable income. Digital nomads typically experience flexible income streams, often project-based or freelance, with potential tax advantages and travel benefits but less traditional job security or employer-provided benefits. Companies may tailor compensation structures to balance the stability valued by employees with the flexibility sought by digital nomads, leveraging technology to manage remote work and diverse payment methods.
Productivity Metrics and Measurement
Employee productivity metrics typically rely on fixed schedules, output quality, and task completion rates measured through time tracking software and performance reviews. Digital nomads use more flexible productivity metrics, emphasizing results-based outcomes, project milestones, and asynchronous communication effectiveness due to varying time zones and remote work environments. Both models benefit from data-driven analytics tools to enhance productivity measurement, but digital nomads require adaptive frameworks that prioritize deliverables over hours logged.
Collaboration and Team Dynamics
Employee collaboration thrives on structured environments and consistent communication channels, fostering stable team dynamics through defined roles and regular interactions. Digital nomads leverage flexible schedules and diverse cultural perspectives, enhancing creativity but challenging synchronous collaboration and immediate responsiveness. Optimizing team performance requires integrating digital tools that support both real-time engagement for employees and asynchronous collaboration suited for remote, nomadic workstyles.
Technology Requirements and Infrastructure
Professional employees typically rely on stable office-based technology infrastructures, including secure VPNs, high-speed internet, and centralized data management systems to ensure productivity and data protection. Digital nomads require flexible, portable technology solutions such as lightweight laptops, mobile hotspots, and cloud-based collaboration tools to maintain connectivity and workflow across diverse locations. Both roles depend on robust cybersecurity measures, but digital nomads face additional challenges in securing public networks and maintaining consistent access to organizational resources.
Career Development Opportunities
Employees benefit from structured career development programs, including mentorship, training workshops, and clear promotion pathways that foster long-term growth within established companies. Digital nomads often encounter limited access to formal career advancement resources but gain diverse skills through remote projects, global networking, and adaptability to various markets. The choice between stable career progression and flexible skill acquisition significantly influences professional trajectories in today's evolving work environment.
Future Trends in Workforce Models
Emerging workforce models reveal a growing preference for the digital nomad lifestyle driven by advancements in remote collaboration technologies and shifting corporate policies prioritizing flexibility. Traditional employees are increasingly adopting hybrid work arrangements, blending in-office presence with remote work to enhance productivity and work-life balance. Organizations investing in cloud-based platforms and cybersecurity frameworks are better positioned to support a decentralized workforce, signaling a transformational shift in talent management strategies.
Related Important Terms
Location-Independent Workforce
Employee roles often require fixed office locations and scheduled hours, limiting flexibility, whereas digital nomads leverage technology to work from any location, promoting a truly location-independent workforce. This shift enhances talent acquisition globally, reduces overhead costs, and increases employee satisfaction by supporting diverse work environments beyond traditional office settings.
Geo-Flexible Employment
Geo-flexible employment enables digital nomads to work seamlessly across global locations, leveraging remote collaboration tools and diverse time zones, while traditional employees often remain tethered to fixed office environments with limited mobility. Organizations adopting geo-flexible policies benefit from broader talent pools, increased employee satisfaction, and reduced overhead costs by supporting both digital nomads and conventional staff within hybrid work models.
Asynchronous Collaboration
Employees benefit from structured schedules and real-time collaboration within centralized teams, enhancing synchronous communication and immediate feedback. Digital nomads leverage asynchronous collaboration tools such as Slack, Trello, and GitHub, enabling flexible workflows across diverse time zones and fostering productivity independent of geographic constraints.
Distributed Teams
Distributed teams benefit from the stability and structured collaboration of traditional employees while leveraging the flexibility and global reach of digital nomads. Integrating remote work technologies enhances productivity, but balancing time zones and communication styles remains essential for effective team performance.
Work-From-Anywhere (WFA) Policy
Employee roles typically involve fixed work locations and structured schedules, limiting flexibility compared to digital nomads who leverage Work-From-Anywhere (WFA) policies to operate remotely across diverse geographic locations. Implementing a robust WFA policy enhances workforce agility, promotes global talent acquisition, and supports productivity by enabling employees to choose optimal work environments.
Hybrid Nomadism
Hybrid nomadism combines the stability of traditional employee roles with the flexibility of digital nomads, allowing professionals to maintain structured team collaboration while working remotely from diverse locations. This model enhances productivity and work-life balance by integrating scheduled in-office presence with extended periods of remote work, leveraging digital tools and adaptive organizational policies.
Boundaryless Careers
Employee roles typically follow structured career paths within organizational hierarchies, emphasizing stability and defined job descriptions, whereas digital nomads pursue boundaryless careers characterized by remote work flexibility, self-direction, and global mobility. This shift towards boundaryless careers reflects a growing trend in the professional landscape, driven by advancements in technology and evolving work preferences that prioritize autonomy, continuous learning, and diverse cultural experiences.
Cloud Commuting
Employee roles traditionally require fixed office locations with structured schedules, while digital nomads leverage cloud commuting to work remotely from any location using cloud-based collaboration tools and virtual desktops. Cloud commuting enhances flexibility and productivity by enabling seamless access to company resources, real-time communication, and secure data management across diverse geographic points.
Remote-First Mindset
Employees with a remote-first mindset prioritize structured communication and consistent productivity within established digital frameworks, fostering strong team cohesion despite physical distance. In contrast, digital nomads emphasize flexibility and adaptability, leveraging diverse environments to enhance creativity and autonomy while maintaining connectivity through cloud-based tools.
Digital Residency Programs
Digital residency programs offer remote workers, particularly digital nomads, the legal framework to live and work in foreign countries without traditional employment constraints, enhancing global mobility and tax optimization. Unlike conventional employees tied to a fixed location and employer, digital nomads leverage these programs to access diverse markets and optimize their work-life balance while maintaining compliance with international regulations.
Employee vs Digital Nomad Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com