Employees benefit from structured work environments, steady income, and defined roles that foster collaboration and skill development. Solopreneurs enjoy autonomy, flexible schedules, and direct control over business decisions but face greater financial risks and responsibility for all operational aspects. Understanding the distinct challenges and advantages of each path helps professionals make informed career choices aligned with their goals.
Table of Comparison
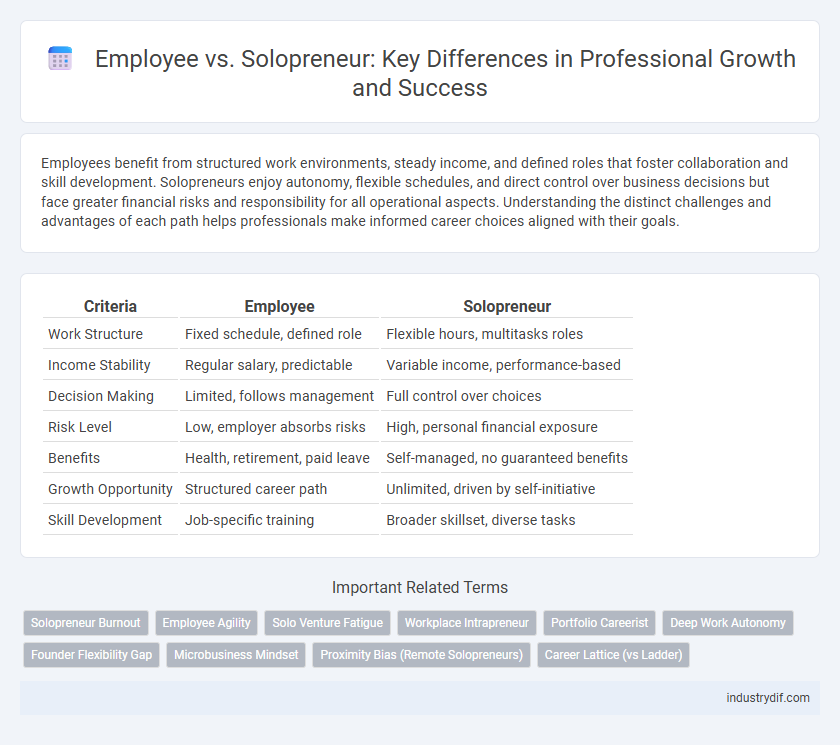
| Criteria | Employee | Solopreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Work Structure | Fixed schedule, defined role | Flexible hours, multitasks roles |
| Income Stability | Regular salary, predictable | Variable income, performance-based |
| Decision Making | Limited, follows management | Full control over choices |
| Risk Level | Low, employer absorbs risks | High, personal financial exposure |
| Benefits | Health, retirement, paid leave | Self-managed, no guaranteed benefits |
| Growth Opportunity | Structured career path | Unlimited, driven by self-initiative |
| Skill Development | Job-specific training | Broader skillset, diverse tasks |
Defining Employee and Solopreneur Roles
An employee typically operates within an organizational structure, adhering to defined roles, responsibilities, and schedules set by an employer, focusing on contributing to company goals. A solopreneur independently manages all aspects of their business, from product development to marketing and client relations, assuming full responsibility for success and risk. Understanding these distinctions clarifies career path decisions and aligns expectations with professional autonomy and accountability.
Key Differences in Work Structure
Employees operate within a defined organizational hierarchy, adhering to fixed roles, responsibilities, and schedules set by their employer. Solopreneurs independently manage all aspects of their business, including decision-making, project execution, and client relations, often exhibiting greater flexibility in work hours. The employee structure emphasizes stability and routine, while solopreneurs prioritize autonomy and adaptability in their workflow.
Financial Security: Payroll vs Profit
Employees benefit from consistent payroll that offers predictable income and financial stability backed by employer contributions to taxes and benefits. Solopreneurs rely on profit, which can vary widely due to business fluctuations, requiring careful cash flow management and financial planning. The trade-off involves employees having steady security, while solopreneurs face income volatility but retain control over earnings and business growth potential.
Autonomy and Decision-Making Power
Employees typically experience limited autonomy, as key decisions are often dictated by management structures and organizational policies. Solopreneurs exercise full decision-making power, allowing them to steer business strategies, operations, and resource allocation independently. This heightened autonomy enables solopreneurs to rapidly adapt to market changes and innovate without hierarchical constraints.
Risk Management in Both Careers
Employees face lower financial risk due to steady salaries and benefits, while solopreneurs manage higher risks from income variability and self-funded benefits. Effective risk management for employees involves career development and job security strategies, whereas solopreneurs prioritize diversification, insurance, and contingency planning. Both paths require proactive approaches to mitigate career uncertainties and financial instability.
Skill Development and Learning Opportunities
Employees benefit from structured skill development programs and access to ongoing training resources provided by their organizations, enhancing their expertise within specific roles. Solopreneurs engage in self-directed learning through diverse platforms and experiences, cultivating a broad skill set essential for business management and growth. Continuous upskilling for both requires adapting to industry trends and leveraging networking opportunities to stay competitive.
Work-Life Balance: Comparative Insights
Employees often experience more structured work hours and defined boundaries between professional and personal life, which can lead to a more predictable work-life balance. Solopreneurs face challenges in separating work from personal time due to flexible schedules and the constant need to manage all business aspects, impacting their ability to disconnect. Research indicates that effective time management and setting clear boundaries are critical strategies for solopreneurs to improve work-life balance compared to employees with fixed schedules.
Long-Term Career Growth Prospects
Employees benefit from structured career paths, including promotions, skill development programs, and retirement benefits that support long-term growth and financial stability. Solopreneurs, while enjoying autonomy and flexibility, often face unpredictable income streams and greater responsibility for business sustainability, which can complicate long-term planning. Strategic investment in continuous learning and networking is essential for both employees and solopreneurs to enhance career longevity and adaptability in evolving markets.
Social Connections and Networking
Employees benefit from structured social connections within organizations, gaining access to established networks that foster collaboration and career growth. Solopreneurs actively build diverse, cross-industry relationships to expand their opportunities and resource pool. Both rely on networking; employees capitalize on internal company networks, while solopreneurs leverage external connections for business development and support.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Professional Future
Employees benefit from structured environments, steady income, and defined career advancement within established organizations. Solopreneurs experience greater autonomy, direct control over business decisions, and the opportunity to build personal brand equity. Evaluating risk tolerance, desired work-life balance, and long-term financial goals is essential when choosing the right professional path.
Related Important Terms
Solopreneur Burnout
Solopreneurs face a higher risk of burnout due to long working hours, lack of support systems, and the continuous pressure of managing all aspects of their business independently. Unlike employees who benefit from structured schedules and team collaboration, solopreneurs often struggle with work-life balance and the mental strain of sole responsibility.
Employee Agility
Employee agility encompasses adaptability, continuous learning, and proactive problem-solving within organizational structures, enabling swift responses to market changes and technological advancements. This contrasts with solopreneurs who prioritize autonomy and personalized decision-making, but employees leverage collaborative resources and institutional support to enhance agility.
Solo Venture Fatigue
Solo venture fatigue often impacts solopreneurs who manage every aspect of their business independently, leading to increased stress and burnout compared to employees with structured roles and shared responsibilities. Employees benefit from established support systems and clearer work-life boundaries, reducing the risk of exhaustion prevalent in solo entrepreneurship.
Workplace Intrapreneur
Workplace intrapreneurs drive innovation from within established organizations by leveraging entrepreneurial skills to develop new products, services, or processes without the risks faced by solopreneurs. Unlike employees who follow set roles or solopreneurs who manage all business aspects independently, intrapreneurs blend creativity with organizational resources to accelerate growth and competitive advantage.
Portfolio Careerist
Portfolio Careerists blend elements of employee stability and solopreneur flexibility by managing multiple income streams and skill sets simultaneously. This strategic approach enhances career resilience and marketability in dynamic professional landscapes.
Deep Work Autonomy
Employees often face structured schedules and predefined tasks that limit their capacity for deep work autonomy, whereas solopreneurs can design their work environments and time blocks to maximize focused, uninterrupted productivity. This autonomy enables solopreneurs to engage in deep work more frequently, fostering innovation and complex problem-solving without external distractions or managerial oversight.
Founder Flexibility Gap
Employee roles typically offer structured schedules and limited autonomy, whereas solopreneurs experience greater founder flexibility, enabling them to tailor work hours and business strategies to personal preferences and market demands. This flexibility gap highlights the trade-off between predictable stability for employees and dynamic control that solopreneurs leverage for innovation and rapid decision-making.
Microbusiness Mindset
Employees prioritize stability and structured roles, often relying on established systems and predictable income streams, while solopreneurs embrace a microbusiness mindset characterized by agility, self-reliance, and innovative problem-solving to drive growth and adapt rapidly in dynamic markets. This mindset fosters entrepreneurial skills, risk tolerance, and autonomy essential for managing all aspects of a microenterprise efficiently.
Proximity Bias (Remote Solopreneurs)
Proximity bias often disadvantages remote solopreneurs by limiting visibility and opportunities compared to employees physically present in the office, affecting collaboration and career advancement. Companies should adopt inclusive evaluation metrics that prioritize output and engagement over physical presence to mitigate this bias.
Career Lattice (vs Ladder)
A career lattice offers employees diverse lateral and upward growth opportunities within an organization, promoting skill development and adaptability, whereas solopreneurs navigate a more fluid career path, leveraging multifaceted roles to drive business innovation and personal brand growth. Embracing a career lattice fosters collaboration and internal mobility for employees, contrasting with the solopreneur's autonomous decision-making and entrepreneurial risk management.
Employee vs Solopreneur Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com