A professional typically operates within established industries, leveraging specialized skills to deliver high-quality services or products, often aiming for long-term career growth and organizational advancement. In contrast, a micropreneur focuses on maintaining a small-scale business, prioritizing lifestyle flexibility and autonomy over rapid expansion or corporate hierarchy. Both roles require expertise and dedication, but their goals and operational scopes differ significantly, reflecting varying approaches to work and success.
Table of Comparison
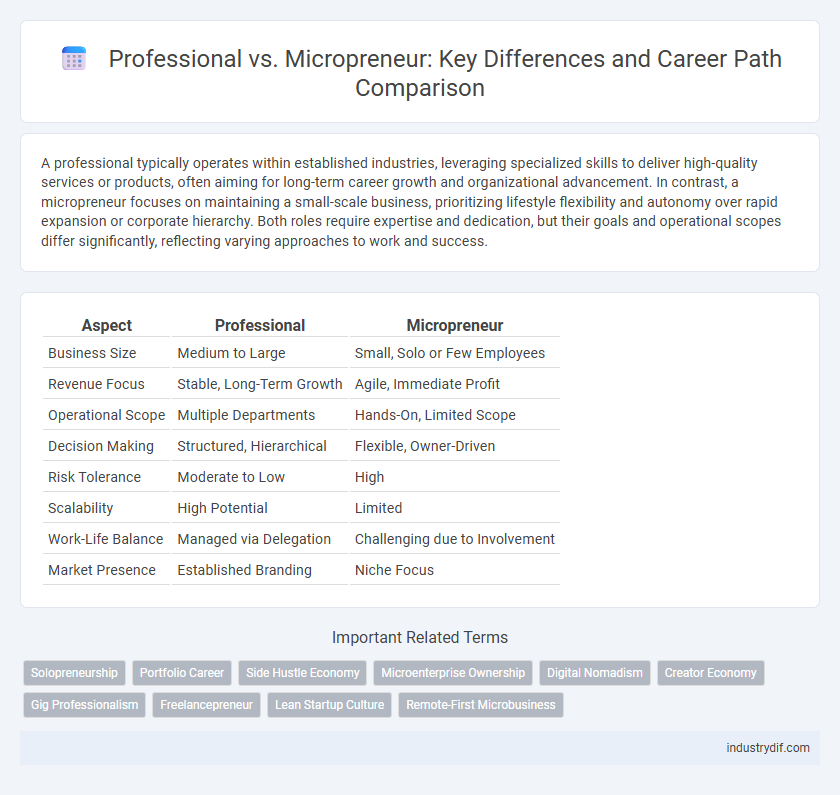
| Aspect | Professional | Micropreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Business Size | Medium to Large | Small, Solo or Few Employees |
| Revenue Focus | Stable, Long-Term Growth | Agile, Immediate Profit |
| Operational Scope | Multiple Departments | Hands-On, Limited Scope |
| Decision Making | Structured, Hierarchical | Flexible, Owner-Driven |
| Risk Tolerance | Moderate to Low | High |
| Scalability | High Potential | Limited |
| Work-Life Balance | Managed via Delegation | Challenging due to Involvement |
| Market Presence | Established Branding | Niche Focus |
Defining the Professional and Micropreneur
A professional typically holds specialized knowledge or skills acquired through formal education and certification, focusing on delivering high-quality services within established industry standards. A micropreneur operates a small-scale business emphasizing innovation, flexibility, and direct client engagement, often managing multiple roles to maintain personal control over growth and operations. Understanding these definitions highlights the contrast between structured expertise and entrepreneurial agility in the business landscape.
Core Characteristics: Professional vs Micropreneur
Professionals typically possess specialized expertise, formal education, and adherence to industry standards, emphasizing long-term career development and credential validation. Micropreneurs prioritize autonomy, lean operational structures, and rapid adaptability, often balancing multiple roles within their small-scale businesses. Core characteristics differentiate professionals' focus on mastery and compliance from micropreneurs' emphasis on flexibility and entrepreneurial agility.
Skill Sets: Specialized vs Diverse
Professionals typically develop specialized skill sets tailored to a specific industry or role, enabling deep expertise and high-quality output in their domain. Micropreneurs cultivate diverse skills across multiple areas such as marketing, sales, finance, and operations to manage and grow their small businesses independently. The contrast between specialized proficiency and broad adaptability defines the core difference in skill sets between professionals and micropreneurs.
Autonomy and Flexibility in Each Role
Professionals typically operate within structured environments, adhering to organizational guidelines that provide clear roles but limit autonomy and flexibility. Micropreneurs manage their own businesses, granting them greater control over decision-making and work schedules, enhancing their autonomy and flexibility. This independence allows micropreneurs to adapt quickly to market changes, while professionals may experience constraints due to hierarchical systems.
Risk and Reward: Contrasting Approaches
Professionals typically experience lower financial risk due to stable salaries and employer-backed benefits, whereas micropreneurs assume higher personal and financial risks by investing their capital and time. The reward structure for professionals usually involves incremental raises and promotions, while micropreneurs potentially gain substantial profits and business equity, but face uncertain income streams. This contrast highlights the trade-off between stability and entrepreneurial opportunity in career decision-making.
Work-Life Balance Differences
Professionals typically maintain a structured work schedule with clear boundaries between work and personal life, enabling a more predictable work-life balance. Micropreneurs often face blurred lines between work and personal time due to the demands of managing all aspects of their small business, leading to a more flexible but less consistent balance. Understanding these differences helps individuals choose the path that best aligns with their desired work-life integration and stress tolerance.
Income Streams and Financial Models
Professionals typically rely on singular income streams tied directly to their specialized skills or employment, often following a traditional salary or fee-for-service financial model. Micropreneurs diversify through multiple income streams by leveraging small business ventures, side projects, or digital products, embracing flexible, scalable financial models focused on recurring revenue and passive income. This strategic diversification in micropreneurship contrasts with the linear income approach common among professionals.
Growth Potential and Scalability
A professional typically offers specialized services with a steady client base, emphasizing consistent income but facing limitations in scalability due to time and resource constraints. In contrast, a micropreneur focuses on creating scalable business models by leveraging technology and outsourcing, enabling higher growth potential without being directly tied to daily operations. This scalability allows micropreneurs to expand market reach and increase revenue streams more rapidly than traditional professionals.
Networking and Collaboration Styles
Professionals typically engage in formal networking through structured industry events and established corporate channels, emphasizing long-term relationship building and hierarchical collaboration. Micropreneurs often adopt informal, flexible networking styles, leveraging digital platforms and peer-to-peer connections to foster rapid collaboration and innovation. These differing approaches influence how each group accesses resources, partnerships, and growth opportunities within their respective markets.
Choosing the Right Path: Key Considerations
Choosing between a Professional and a Micropreneur hinges on factors such as risk tolerance, business scale, and personal goals. Professionals often prioritize stability and expertise within established industries, while Micropreneurs embrace flexibility and innovation by managing small, agile ventures. Evaluating lifestyle preferences, financial objectives, and market opportunities helps determine the optimal path for career growth and fulfillment.
Related Important Terms
Solopreneurship
Solopreneurs balance the strategic mindset of professionals with the innovative agility of micropreneurs, leveraging streamlined operations to drive personalized, scalable business growth. Emphasizing self-reliance and niche expertise, solopreneurship optimizes resource allocation while maintaining high client value and adaptability in competitive markets.
Portfolio Career
A professional builds expertise within a singular field or role, often pursuing linear career growth, whereas a micropreneur operates multiple small-scale ventures simultaneously, fostering diverse income streams and agility. Embracing a portfolio career allows individuals to combine professional specialization with entrepreneurial ventures, enhancing skill diversification and financial resilience.
Side Hustle Economy
Professional entrepreneurs typically operate established businesses with scalable models and full-time commitments, while micropreneurs prioritize small-scale ventures often pursued as side hustles within the growing gig economy. The side hustle economy thrives on flexible, low-risk microbusinesses that supplement income and foster entrepreneurial skills without requiring the extensive resources of traditional professionals.
Microenterprise Ownership
Microenterprise ownership emphasizes managing smaller-scale businesses with limited employees and revenue, allowing for greater flexibility and hands-on control compared to traditional professional roles. This approach supports personalized customer relationships and agile decision-making, distinguishing micropreneurs from typical professionals who often operate within larger organizational structures.
Digital Nomadism
Professionals typically operate within structured organizations offering specialized expertise, whereas micropreneurs embrace entrepreneurship characterized by agility and minimal scale, often leveraging digital tools to sustain location-independent businesses. In digital nomadism, micropreneurs capitalize on remote work technologies and flexible business models to balance work-life integration across global environments, contrasting with professionals who may face traditional constraints on mobility and workspace.
Creator Economy
A professional typically operates within established industries, delivering specialized services or products, while a micropreneur in the creator economy builds small, independent ventures leveraging digital platforms to monetize creative content. The creator economy empowers micropreneurs to scale personal brands and diversify revenue streams through social media, subscriptions, and direct audience engagement.
Gig Professionalism
Professionalism in gig work demands consistent quality, reliable communication, and meeting deadlines, distinguishing gig professionals from micropreneurs who often juggle diverse ventures with less specialization. Gig professionals prioritize expertise in their niche, building reputation through client trust and demonstrated skill rather than broad entrepreneurial management.
Freelancepreneur
Freelancepreneurs balance the flexibility of micropreneurship with the strategic growth mindset of professional entrepreneurship, leveraging specialized skills to build scalable businesses. Unlike traditional professionals who may prioritize steady employment, freelancepreneurs optimize client relationships and digital platforms to expand their freelance ventures beyond sole proprietorships.
Lean Startup Culture
Professionals typically follow established industry standards and emphasize deep expertise, while micropreneurs adopt Lean Startup principles, focusing on rapid experimentation, customer feedback, and agile growth to minimize waste and maximize value. Embracing Lean Startup culture enables micropreneurs to pivot quickly and innovate efficiently in dynamic markets.
Remote-First Microbusiness
Remote-first microbusinesses prioritize agility and personalized client relationships, distinguishing themselves from professionals who often operate within larger organizational structures; micropreneurs leverage digital tools to manage small-scale, location-independent ventures that emphasize flexibility and direct customer engagement. This approach enables microbusiness owners to adapt rapidly to market changes while maintaining a lean operational model focused on specialized services or products.
Professional vs Micropreneur Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com