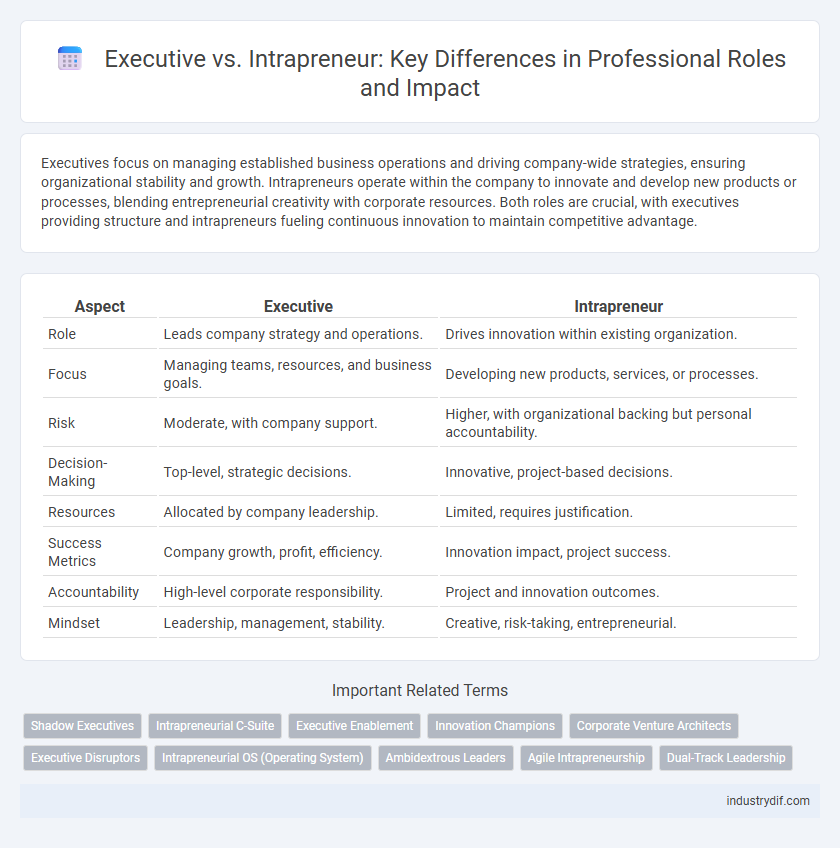
Executives focus on managing established business operations and driving company-wide strategies, ensuring organizational stability and growth. Intrapreneurs operate within the company to innovate and develop new products or processes, blending entrepreneurial creativity with corporate resources. Both roles are crucial, with executives providing structure and intrapreneurs fueling continuous innovation to maintain competitive advantage.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Executive | Intrapreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Leads company strategy and operations. | Drives innovation within existing organization. |
| Focus | Managing teams, resources, and business goals. | Developing new products, services, or processes. |
| Risk | Moderate, with company support. | Higher, with organizational backing but personal accountability. |
| Decision-Making | Top-level, strategic decisions. | Innovative, project-based decisions. |
| Resources | Allocated by company leadership. | Limited, requires justification. |
| Success Metrics | Company growth, profit, efficiency. | Innovation impact, project success. |
| Accountability | High-level corporate responsibility. | Project and innovation outcomes. |
| Mindset | Leadership, management, stability. | Creative, risk-taking, entrepreneurial. |
Executive vs Intrapreneur: Key Role Distinctions
Executives primarily focus on strategic decision-making, resource allocation, and organizational oversight to achieve company-wide objectives. Intrapreneurs drive innovation within the organization by identifying opportunities, leading projects, and taking calculated risks to develop new products or services. While executives manage existing structures and processes, intrapreneurs challenge the status quo to foster growth and competitive advantage.
Core Responsibilities of Executives and Intrapreneurs
Executives primarily focus on strategic decision-making, resource allocation, and overall organizational governance to drive long-term growth and stability. Intrapreneurs concentrate on innovation within the company, developing new products or processes while managing risks and championing entrepreneurial initiatives internally. Both roles require leadership, but executives emphasize broad operational oversight, whereas intrapreneurs prioritize creativity and agile project management.
Leadership Styles: Traditional vs Innovative Approaches
Executives typically employ traditional leadership styles centered on hierarchical decision-making and risk management to ensure organizational stability. In contrast, intrapreneurs adopt innovative approaches that encourage creativity, autonomy, and experimentation within the company to drive transformational change. Leadership frameworks like transformational and servant leadership align closely with intrapreneurship, fostering employee empowerment and agile problem-solving.
Decision-Making Powers: Authority and Autonomy
Executives typically possess formal authority granted by organizational hierarchy, enabling them to make high-level strategic decisions with substantial autonomy and accountability. Intrapreneurs operate within existing companies but exercise decision-making powers with significant independence to innovate and implement new ideas, often navigating organizational constraints. The distinction lies in the scope and source of their authority: executives derive power from positional legitimacy, whereas intrapreneurs rely on influence and creativity to drive change internally.
Risk Tolerance in Executives and Intrapreneurs
Executives typically exhibit moderate risk tolerance, balancing organizational stability with strategic growth opportunities to safeguard shareholder value. Intrapreneurs demonstrate higher risk tolerance by pursuing innovative projects within companies, often challenging existing processes to drive disruptive change. This distinction influences decision-making approaches, with executives prioritizing risk management and intrapreneurs embracing calculated risks to foster innovation.
Organizational Impact: Driving Change and Growth
Executives steer organizational strategy to maximize shareholder value, influencing large-scale change through formal authority and resource allocation. Intrapreneurs drive innovation from within, leveraging entrepreneurial mindset to initiate projects that foster growth and agility without formal authority. Both roles are critical for sustaining competitive advantage by balancing structured governance with creative problem-solving.
Career Paths: Advancement and Mobility
Executives typically follow a structured career path with clear hierarchical advancement within corporate organizations, often moving into senior management or C-suite roles by leveraging leadership experience and strategic decision-making. Intrapreneurs drive innovation within existing companies, gaining mobility by leading new projects or ventures that demonstrate value and influence, which can accelerate their rise or pivot into executive positions. Both paths offer opportunities for advancement, but executives usually advance through formal promotions, while intrapreneurs create unique roles that expand their career potential through entrepreneurial initiatives.
Performance Metrics and Success Criteria
Executives are typically evaluated using financial performance metrics such as revenue growth, profitability, and shareholder value, emphasizing strategic goal achievement and operational efficiency. Intrapreneurs, on the other hand, are assessed based on innovation outcomes, project milestones, and the successful implementation of new ideas within the organization. Success criteria for executives revolve around managing large-scale organizational performance, whereas intrapreneurs focus on driving transformative change and creating value through entrepreneurial initiatives inside the company.
Cultural Influence within the Corporate Structure
Executives shape corporate culture by setting strategic priorities and enforcing organizational values, often emphasizing top-down leadership and stability. Intrapreneurs drive cultural innovation from within, fostering creativity and adaptability by leveraging their deep understanding of internal processes and employee dynamics. Cultural influence in a corporate structure hinges on executives promoting a vision while intrapreneurs embed entrepreneurial spirit, enabling the organization to balance tradition with agility.
Future Trends for Executives and Intrapreneurs
Executives are increasingly adopting intrapreneurial skills to drive innovation and agility within established organizations, blending leadership with entrepreneurial thinking to stay competitive in rapidly evolving markets. Future trends highlight the rise of hybrid roles where executives foster intrapreneurship to accelerate digital transformation, harness emerging technologies, and cultivate a culture of continuous innovation. Data from Deloitte reveals that 79% of executives believe intrapreneurship is critical for sustainable growth, emphasizing the strategic value of merging executive decision-making with entrepreneurial agility.
Related Important Terms
Shadow Executives
Shadow Executives operate within organizations as intrapreneurs, leveraging internal resources to drive innovation while maintaining executive-level strategic influence without formal authority. Their unique position enables them to navigate corporate structures effectively, fostering change and growth by aligning entrepreneurial initiatives with executive goals.
Intrapreneurial C-Suite
Intrapreneurial C-suite leaders drive innovation within established organizations by integrating entrepreneurial agility with executive authority, fostering a culture of strategic risk-taking and cross-functional collaboration. Their ability to navigate corporate structures while championing disruptive initiatives distinguishes them from traditional executives focused primarily on operational efficiency and incremental growth.
Executive Enablement
Executive enablement enhances a leader's capacity to drive organizational growth by aligning strategic vision with operational execution, emphasizing decision-making, resource management, and stakeholder engagement. Unlike intrapreneurs who innovate within existing frameworks, executives require enablement tools that sharpen governance, influence, and long-term planning to sustain enterprise-wide impact.
Innovation Champions
Executives drive organizational growth through strategic oversight and resource allocation, while intrapreneurs act as innovation champions by cultivating creative solutions and spearheading transformative projects within established companies. Intrapreneurs leverage entrepreneurial thinking to accelerate product development and foster a culture of continuous innovation, bridging the gap between visionary ideas and practical execution.
Corporate Venture Architects
Corporate Venture Architects bridge the gap between executives and intrapreneurs by leveraging strategic leadership to foster innovation within established organizations. Their role combines executive decision-making with entrepreneurial agility, enabling the development of new ventures that align with corporate goals and drive sustainable growth.
Executive Disruptors
Executive disruptors drive innovation within established organizations by challenging traditional business models and fostering agile cultures that accelerate digital transformation. Their ability to leverage strategic vision and corporate resources positions them uniquely to integrate disruptive technologies and reshape market landscapes effectively.
Intrapreneurial OS (Operating System)
An intrapreneurial OS empowers employees to innovate within organizational frameworks by fostering autonomy, agility, and cross-functional collaboration, driving sustainable growth and competitive advantage. Unlike traditional executives who prioritize hierarchical control and risk mitigation, intrapreneurs leverage dynamic processes and entrepreneurial mindsets embedded in the operating system to accelerate internal innovation and business transformation.
Ambidextrous Leaders
Ambidextrous leaders uniquely balance the strategic vision of executives with the innovation-driven mindset of intrapreneurs, fostering both operational efficiency and entrepreneurial agility within organizations. This dual capability enables them to manage core business performance while simultaneously exploring new growth opportunities, driving sustainable competitive advantage.
Agile Intrapreneurship
Agile intrapreneurship empowers employees to innovate within established organizations by applying iterative development and adaptive planning, contrasting with executives who primarily focus on strategic decision-making and organizational leadership. This approach fosters a culture of continuous improvement and rapid problem-solving, leveraging cross-functional collaboration to drive business growth and competitive advantage.
Dual-Track Leadership
Dual-track leadership integrates executive management and intrapreneurship, enabling leaders to simultaneously drive organizational strategy while fostering innovation within internal ventures. This approach leverages the strategic decision-making of executives and the entrepreneurial agility of intrapreneurs, optimizing growth and adaptability in dynamic markets.
Executive vs Intrapreneur Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com