A portfolio showcases a curated collection of completed projects highlighting an individual's skills and style, while proof-of-work provides verifiable evidence of specific accomplishments or contributions. Portfolios emphasize breadth and creativity, making them essential for roles requiring diverse capabilities. Proof-of-work is crucial in technical fields where measurable results and documented achievements validate expertise.
Table of Comparison
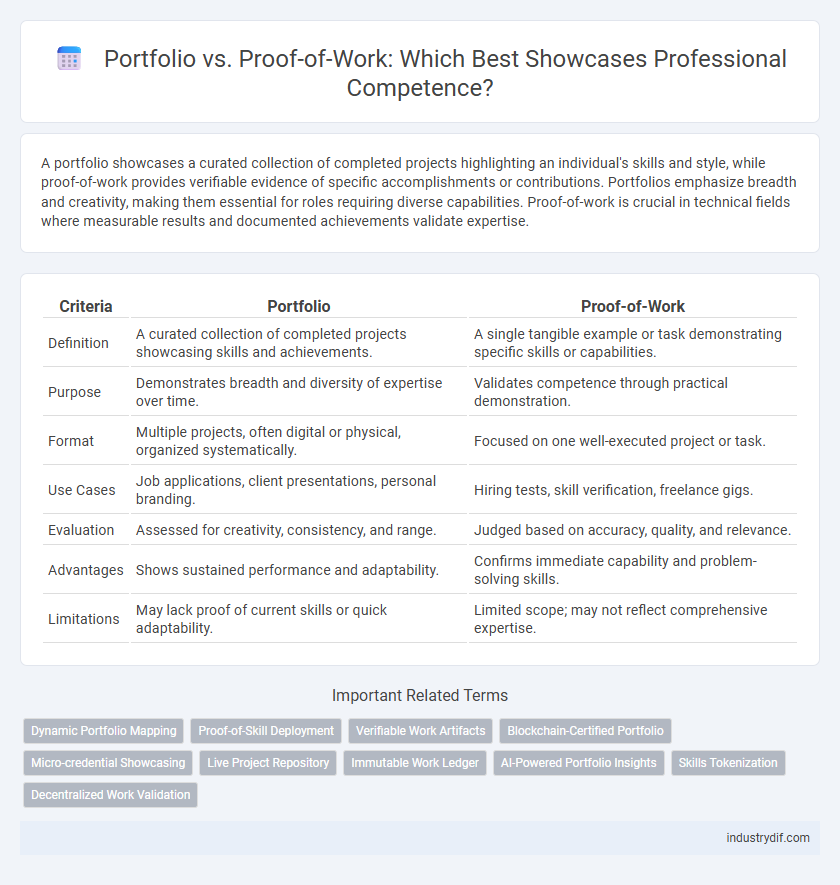
| Criteria | Portfolio | Proof-of-Work |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A curated collection of completed projects showcasing skills and achievements. | A single tangible example or task demonstrating specific skills or capabilities. |
| Purpose | Demonstrates breadth and diversity of expertise over time. | Validates competence through practical demonstration. |
| Format | Multiple projects, often digital or physical, organized systematically. | Focused on one well-executed project or task. |
| Use Cases | Job applications, client presentations, personal branding. | Hiring tests, skill verification, freelance gigs. |
| Evaluation | Assessed for creativity, consistency, and range. | Judged based on accuracy, quality, and relevance. |
| Advantages | Shows sustained performance and adaptability. | Confirms immediate capability and problem-solving skills. |
| Limitations | May lack proof of current skills or quick adaptability. | Limited scope; may not reflect comprehensive expertise. |
Defining Portfolio and Proof-of-Work
A portfolio is a curated collection of an individual's best work, showcasing skills, accomplishments, and projects relevant to their professional field. Proof-of-work refers to demonstrated evidence of task completion or problem-solving ability, often validated through tangible results or performance metrics. Both serve as critical indicators of expertise but differ in presentation, with portfolios emphasizing breadth and proof-of-work highlighting verifiable outcomes.
Key Differences Between Portfolio and Proof-of-Work
Portfolios showcase a curated collection of completed projects demonstrating a candidate's skills, creativity, and versatility, while Proof-of-Work specifically refers to tangible evidence or deliverables validating competency in a particular task or technology. Portfolios typically include diverse examples across different domains, highlighting problem-solving abilities and design choices, whereas Proof-of-Work centers on direct, verifiable outcomes such as code samples, completed assignments, or certifications. Understanding these distinctions aids employers in assessing both breadth of experience and depth of expertise during candidate evaluation.
Portfolio: Structure and Essential Elements
A professional portfolio is a well-organized collection showcasing an individual's skills, achievements, and projects, reflecting expertise across relevant domains. Key elements include a clear introduction, a detailed resume or CV, samples of work or project summaries, client testimonials, and certifications to demonstrate credibility. The structured presentation enhances impact, making it easier for potential employers or clients to assess qualifications and professional growth.
Proof-of-Work: Methods and Best Practices
Proof-of-Work (PoW) methods involve verifiable tasks demonstrating skills through real projects, client feedback, and code repositories such as GitHub. Best practices include showcasing diverse project types, maintaining up-to-date documentation, and highlighting measurable outcomes to establish credibility. Effective PoW emphasizes transparency, consistency, and direct relevance to target roles or industries.
Purpose and Use Cases in Professional Industries
Portfolios showcase a curated collection of completed projects highlighting a professional's skills, creativity, and versatility, making them essential for roles in design, marketing, and consulting. Proof-of-work systems, often used in blockchain and cybersecurity industries, serve to verify computational effort and secure decentralized networks through consensus mechanisms. While portfolios aim to demonstrate competence and attract clients or employers, proof-of-work ensures trust and integrity in digital transactions and data validation.
Evaluating Skill and Experience: Portfolio vs Proof-of-Work
Evaluating skill and experience through a portfolio allows professionals to demonstrate a curated selection of completed projects, showcasing creativity, technical ability, and industry relevance. Proof-of-work offers tangible evidence of task completion under real-world conditions, emphasizing practical expertise and reliability in delivering results. Together, these methods provide a comprehensive assessment by balancing qualitative presentation with quantifiable performance.
Industry Preferences: When to Use Each Approach
Industry preferences highlight that portfolios are preferred for creative fields like design and marketing to showcase a broad range of skills and projects, while proof-of-work is favored in technical industries such as software development and engineering for demonstrating specific problem-solving capabilities and coding expertise. Portfolios provide a holistic view of an applicant's versatility, making them ideal for roles requiring diverse creativity. Proof-of-work offers concrete evidence of technical proficiency, which is crucial for positions demanding stringent performance verification and technical validation.
Digital Trends Impacting Portfolios and Proof-of-Work
Digital trends such as AI-driven analytics and blockchain verification are reshaping portfolios and proof-of-work systems by enhancing authenticity and traceability. Portfolios now integrate multimedia content and real-time data to showcase skills dynamically, while proof-of-work mechanisms leverage decentralized networks to secure digital credentials. These advancements increase transparency and trust in professional evaluations, aligning with evolving industry demands.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Method
A professional portfolio showcases a curated selection of projects and skills, providing a comprehensive overview of expertise and creativity, but may lack real-time demonstration of problem-solving abilities. Proof-of-work emphasizes hands-on experience and practical results by validating tasks or challenges completed, offering concrete evidence of competency, yet it may not capture the full scope of an individual's capabilities or creative range. Balancing both methods allows a thorough assessment of technical skills, project depth, and professional adaptability in various contexts.
Future Outlook: Evolving Standards in Professional Validation
The future outlook of professional validation increasingly favors dynamic portfolios that integrate real-time project updates, interactive elements, and measurable outcomes over static proof-of-work exhibits. Emerging industry standards emphasize continuous learning and adaptability, with portfolios showcasing a candidate's evolving skill set and versatility in response to changing market demands. Advanced digital tools and AI-driven analytics are set to redefine validation by enabling more comprehensive, data-backed assessments of professional capabilities.
Related Important Terms
Dynamic Portfolio Mapping
Dynamic Portfolio Mapping enhances portfolio management by continuously aligning investment assets with real-time market data and individual risk profiles, unlike static Proof-of-Work demonstrations that emphasize solely past achievements. This approach leverages advanced analytics and machine learning to optimize asset allocation, improving decision-making efficiency and adaptability in evolving financial landscapes.
Proof-of-Skill Deployment
Proof-of-Skill deployment emphasizes demonstrating specialized expertise through practical applications and real-world problem-solving, offering measurable validation beyond traditional portfolio presentations. Unlike portfolios that showcase curated past projects, Proof-of-Skill provides dynamic, task-based evidence of proficiency aligned with industry standards and current professional demands.
Verifiable Work Artifacts
Verifiable work artifacts in a portfolio demonstrate tangible evidence of skills through completed projects, code repositories, and client feedback, providing concrete proof of competency. Proof-of-work emphasizes validated task completion and performance metrics, ensuring authenticity and measurable contributions within a professional context.
Blockchain-Certified Portfolio
Blockchain-certified portfolios leverage immutable ledger technology to verify the authenticity and provenance of professional achievements, offering greater trust compared to traditional portfolios or proof-of-work documents. This certification enhances credibility for skills, education, and project outcomes by providing transparent, tamper-proof evidence accessible to employers and clients worldwide.
Micro-credential Showcasing
Micro-credential showcasing effectively bridges the gap between portfolios and proof-of-work by providing verifiable, skill-specific endorsements that validate professional competencies in real-time. These digital badges or certificates enhance traditional portfolios by offering concrete evidence of capabilities, improving employability and professional credibility.
Live Project Repository
A live project repository offers real-time access to active codebases, showcasing practical skills and ongoing development beyond static portfolio samples. Unlike traditional portfolios, it provides dynamic proof-of-work that highlights adaptability, code quality, and collaboration within professional environments.
Immutable Work Ledger
An Immutable Work Ledger ensures the integrity and transparency of professional achievements by securely recording each project as verifiable proof-of-work, surpassing traditional portfolio limitations. This technology enhances accountability and trustworthiness by preventing alterations and enabling stakeholders to validate contributions in real-time.
AI-Powered Portfolio Insights
AI-powered portfolio insights leverage machine learning algorithms to analyze diverse asset performance, risk metrics, and market trends, enabling more accurate predictions and strategic adjustments. Unlike traditional proof-of-work validations, these insights focus on optimizing portfolio value through data-driven decision-making and continuous performance monitoring.
Skills Tokenization
Skills tokenization transforms individual competencies into verifiable digital assets, enabling dynamic portfolio management and streamlined proof-of-work validation. This approach enhances transparency and trust by securely linking skills to blockchain-based credentials, facilitating professional growth and talent acquisition.
Decentralized Work Validation
Portfolio-based evaluation compiles comprehensive records of skills, projects, and achievements, offering a holistic view of a professional's capabilities, while Proof-of-Work (PoW) in decentralized systems validates contributions through computational effort, ensuring security and consensus in blockchain networks. Decentralized work validation leverages PoW to authenticate transactions without centralized authorities, contrasting with portfolios that rely on curated self-reported evidence in traditional professional contexts.
Portfolio vs Proof-of-Work Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com