A generalist offers broad expertise across multiple areas, enabling flexible problem-solving and adaptability within various business functions. In contrast, a fractional specialist provides deep, targeted knowledge in a specific domain, delivering high-impact results on a part-time or project basis. Organizations benefit from generalists when seeking versatility and from fractional specialists when requiring expert-driven, focused interventions.
Table of Comparison
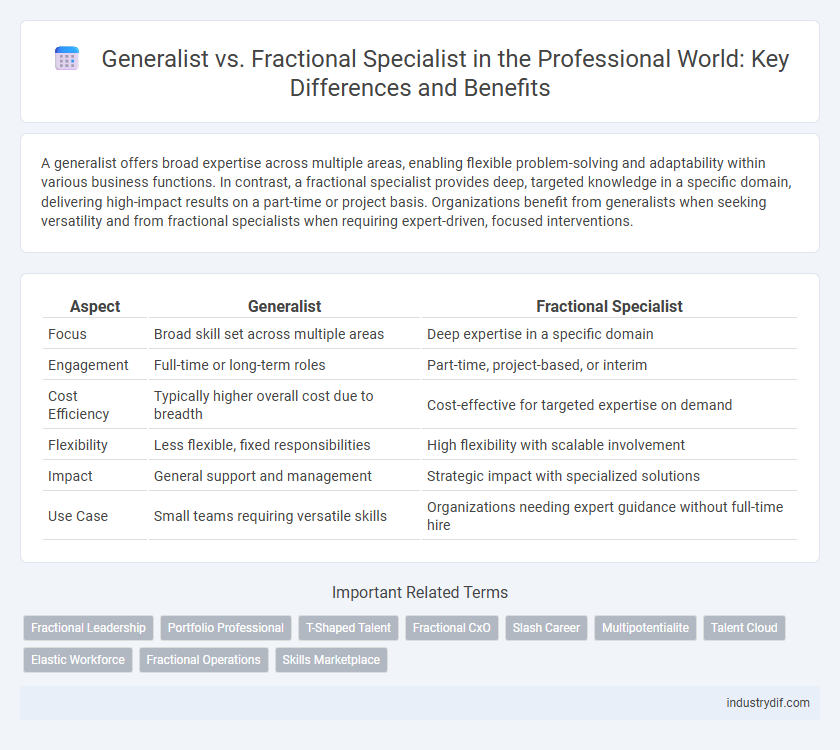
| Aspect | Generalist | Fractional Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Broad skill set across multiple areas | Deep expertise in a specific domain |
| Engagement | Full-time or long-term roles | Part-time, project-based, or interim |
| Cost Efficiency | Typically higher overall cost due to breadth | Cost-effective for targeted expertise on demand |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, fixed responsibilities | High flexibility with scalable involvement |
| Impact | General support and management | Strategic impact with specialized solutions |
| Use Case | Small teams requiring versatile skills | Organizations needing expert guidance without full-time hire |
Defining Generalists and Fractional Specialists
Generalists possess a broad skill set across multiple disciplines, enabling them to manage diverse tasks and adapt to various roles within an organization. Fractional specialists provide expert-level skills and strategic guidance in a specific domain on a part-time or contract basis, offering targeted solutions without full-time commitment. Organizations leverage generalists for versatility and flexibility, while fractional specialists address complex challenges requiring in-depth expertise.
Core Skills of Generalists
Generalists possess a versatile skill set that enables them to adapt across multiple domains, offering broad strategic insight and problem-solving abilities essential for dynamic business environments. Their core competencies include effective communication, critical thinking, project management, and cross-functional collaboration, which drive innovation and facilitate seamless team integration. This diverse expertise allows generalists to bridge gaps between specialized departments, enhancing overall organizational agility and decision-making.
Unique Strengths of Fractional Specialists
Fractional specialists offer unparalleled expertise by dedicating focused, part-time engagement to specific business areas, delivering high-impact results without the overhead of full-time employment. Their ability to tackle complex challenges with deep, specialized knowledge drives strategic growth and innovation within organizations. This targeted approach allows companies to access top-tier talent tailored to precise needs, maximizing efficiency and ROI.
Comparing Roles: Versatility vs Deep Expertise
Generalists provide versatility by managing diverse tasks across multiple functions, making them ideal for dynamic environments requiring adaptive problem-solving. Fractional specialists deliver deep expertise in specific domains, offering strategic insights and advanced skills on a part-time basis to maximize impact without full-time commitment. Organizations leverage generalists for broad operational efficiency while employing fractional specialists to address critical, complex challenges with precision.
Impact on Organizational Structure
Generalists provide versatile skills that streamline organizational structure by enabling flexible role assignments and reducing the need for multiple specialized positions. Fractional specialists introduce targeted expertise on a part-time basis, optimizing resource allocation while maintaining high-level strategic input without expanding full-time staff. This combination impacts organizational efficiency by balancing broad operational coverage with focused expert intervention.
Collaboration and Team Dynamics
Generalists provide broad expertise and adaptability, fostering seamless collaboration across diverse teams by bridging knowledge gaps and enhancing communication. Fractional specialists contribute deep, targeted skills on a part-time basis, driving focused innovation and addressing specific challenges within team dynamics. Balancing both roles optimizes team performance, blending agile problem-solving with expert insights to elevate collaborative outcomes.
Recruitment Considerations: Generalist or Fractional Specialist?
Recruitment considerations between a generalist and a fractional specialist hinge on organizational needs and budget constraints. Generalists offer versatility across multiple HR functions, supporting broader recruitment strategies, while fractional specialists provide deep expertise in niche areas, optimizing targeted talent acquisition. Evaluating whether ongoing, diverse HR support or specialized, project-based expertise aligns better with recruitment goals is essential for effective talent management.
Cost-Benefit Analysis in Hiring
Hiring a generalist often reduces costs by covering multiple roles but may sacrifice deep expertise, impacting specialized projects. A fractional specialist offers targeted skills for complex tasks, ensuring higher quality outcomes at a variable cost aligned with project needs. Evaluating the cost-benefit balance involves comparing the generalist's broader scope and lower salary against the specialist's focused impact and potential return on investment.
Career Pathways: Growth for Generalists and Fractional Specialists
Generalists typically experience steady career growth through broad skill development and adaptability across various functions, enabling progression into leadership roles or diverse industries. Fractional specialists grow by deepening niche expertise, often leveraging project-based roles or consultancy opportunities that offer higher compensation and flexibility. Both career pathways emphasize continuous learning, with generalists expanding their strategic impact and specialists enhancing technical mastery to meet evolving market demands.
Future Trends in Professional Specialization
Future trends in professional specialization indicate a growing demand for fractional specialists who offer deep expertise across multiple industries on a project basis, providing flexibility and cost-efficiency for organizations. Generalists maintain value through their adaptability and broad skill sets, enabling them to navigate complex, interdisciplinary challenges and lead strategic initiatives. Emerging technologies and rapid market changes are accelerating the convergence of specialized knowledge and generalist capabilities, fostering hybrid roles that combine strategic vision with technical precision.
Related Important Terms
Fractional Leadership
Fractional leadership offers companies access to specialized executive expertise on a part-time basis, maximizing strategic impact without the overhead of full-time salaries. This model enhances organizational agility by integrating expert guidance tailored to specific business needs, differentiating it from the broader skill set of generalist leaders.
Portfolio Professional
A portfolio professional leverages both generalist skills and fractional specialist expertise to adapt fluidly across diverse projects, maximizing value through versatile knowledge and targeted impact. This hybrid approach enhances organizational agility by combining broad strategic insight with deep, specialized contributions on a part-time basis.
T-Shaped Talent
T-Shaped talent combines broad generalist knowledge with deep expertise in a specific domain, enabling fractional specialists to deliver focused, high-impact contributions within a limited scope. This hybrid skill set allows businesses to leverage versatile professionals who adapt quickly while driving specialized outcomes.
Fractional CxO
Fractional CxOs deliver targeted executive expertise on a part-time basis, optimizing leadership costs while driving strategic growth in specialized areas such as finance, marketing, or technology. Their flexible engagement model suits startups and scaling companies needing high-level decision-making without full-time executive overhead.
Slash Career
A slash career combines roles as a generalist and fractional specialist, enabling professionals to leverage diverse skills across multiple industries simultaneously. This approach increases market adaptability and income streams by delivering specialized expertise on a part-time or project basis, while maintaining broad operational knowledge.
Multipotentialite
A multipotentialite thrives by integrating diverse skills from both generalist and fractional specialist roles, leveraging adaptability and deep expertise across multiple domains to drive innovation and efficiency in professional settings. Emphasizing versatile knowledge delivery, multipotentialites excel in dynamic environments where cross-functional collaboration and specialized insight are equally valued.
Talent Cloud
Talent Cloud offers both generalist and fractional specialist solutions, enabling businesses to access a diverse pool of expertise tailored to specific project needs. Generalists provide broad skill sets adaptable across functions, while fractional specialists deliver concentrated proficiency in niche areas, optimizing talent allocation and operational efficiency.
Elastic Workforce
An elastic workforce leverages the adaptability of generalists who manage diverse tasks effectively, while fractional specialists provide targeted expertise on a part-time basis to optimize project outcomes. Balancing generalists' broad skill sets with the precision of fractional specialists enhances organizational agility and operational efficiency.
Fractional Operations
Fractional Operations specialists deliver targeted expertise in process optimization and strategic execution on a part-time basis, enabling companies to scale efficiently without the overhead of full-time hires. Their focused skill set drives operational improvements, cost reduction, and agile problem-solving, making them essential for dynamic business environments.
Skills Marketplace
Generalists offer broad expertise across multiple domains, making them versatile in the skills marketplace, while fractional specialists provide deep, targeted knowledge on a part-time or project basis, catering to niche demands. Companies leverage generalists for adaptability and fractional specialists for specialized skill sets that optimize performance and cost-efficiency.
Generalist vs Fractional Specialist Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com