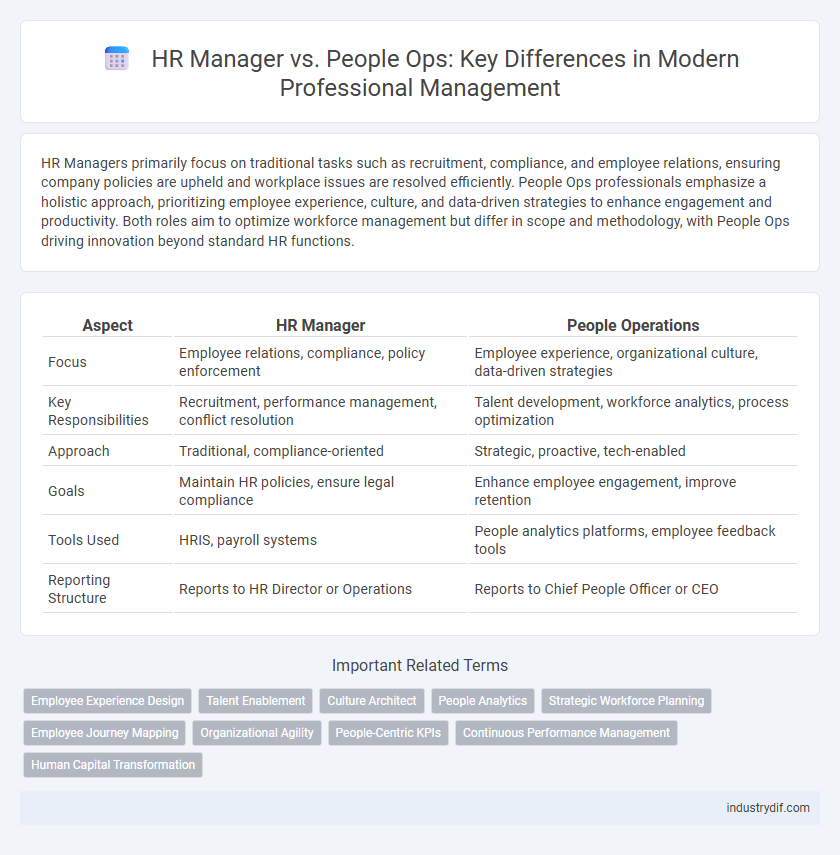
HR Managers primarily focus on traditional tasks such as recruitment, compliance, and employee relations, ensuring company policies are upheld and workplace issues are resolved efficiently. People Ops professionals emphasize a holistic approach, prioritizing employee experience, culture, and data-driven strategies to enhance engagement and productivity. Both roles aim to optimize workforce management but differ in scope and methodology, with People Ops driving innovation beyond standard HR functions.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | HR Manager | People Operations |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Employee relations, compliance, policy enforcement | Employee experience, organizational culture, data-driven strategies |
| Key Responsibilities | Recruitment, performance management, conflict resolution | Talent development, workforce analytics, process optimization |
| Approach | Traditional, compliance-oriented | Strategic, proactive, tech-enabled |
| Goals | Maintain HR policies, ensure legal compliance | Enhance employee engagement, improve retention |
| Tools Used | HRIS, payroll systems | People analytics platforms, employee feedback tools |
| Reporting Structure | Reports to HR Director or Operations | Reports to Chief People Officer or CEO |
Defining HR Management and People Operations
HR Management centers on administrative functions such as recruitment, compliance, payroll, and employee relations to maintain organizational structure. People Operations emphasizes a strategic approach to employee experience, engagement, and culture enhancement, driving productivity and retention. Both disciplines collaborate to align human capital with business objectives for sustainable growth.
Core Responsibilities: HR Manager vs People Ops
HR Managers primarily focus on recruitment, employee relations, compliance, and performance management to ensure organizational policies are upheld. People Operations extends beyond traditional HR functions by integrating data analytics, employee engagement strategies, and culture development to optimize workforce productivity. This evolution reflects a shift from administrative tasks to strategic roles centered on enhancing employee experience and organizational efficiency.
Organizational Structure and Reporting Lines
HR Managers typically oversee traditional functions such as recruitment, employee relations, and compliance within a defined organizational structure, reporting directly to the Director of Human Resources or Chief HR Officer. People Operations (People Ops) roles emphasize strategic initiatives around employee experience, culture, and data-driven decision-making, often reporting to the Chief People Officer or Chief Operating Officer. The reporting lines reflect organizational priorities, where HR Managers align with established frameworks, while People Ops positions integrate cross-functional collaboration and innovation within flatter hierarchies.
Approach to Employee Experience
HR Managers traditionally focus on compliance, policy enforcement, and administrative functions to maintain workforce stability. People Ops emphasizes a holistic employee experience by integrating data-driven insights, continuous feedback, and personalized development opportunities. This shift toward People Ops fosters engagement, innovation, and a culture aligned with organizational goals.
Recruitment and Talent Acquisition Strategies
HR Managers traditionally oversee recruitment processes focusing on compliance, job postings, and candidate screening to fulfill organizational staffing needs. People Operations emphasizes a strategic approach by integrating data-driven talent acquisition methods, employer branding, and candidate experience optimization to attract top-tier candidates. Both roles collaborate to align recruitment strategies with company culture, but People Ops prioritizes continuous improvement through analytics and innovative sourcing techniques.
Performance Management Differences
HR Managers primarily handle performance management by setting clear objectives, conducting evaluations, and implementing corrective actions to improve employee productivity. People Operations professionals emphasize continuous performance feedback, employee engagement, and leveraging data analytics to drive talent development and organizational growth. The shift reflects a move from traditional performance reviews to a more dynamic, employee-centered approach enhancing overall workforce effectiveness.
Technology Integration in HR vs People Ops
HR Managers traditionally handle technology integration by implementing HRIS systems for payroll, benefits, and compliance management, focusing on operational efficiency. People Ops professionals emphasize a broader technological landscape, incorporating employee experience platforms, data analytics, and AI-driven tools to foster engagement and development. Both roles leverage technology but differ in scope, with People Ops integrating cutting-edge innovations to align human capital strategy with organizational growth.
Change Management and Organizational Culture
HR Managers primarily focus on implementing change management strategies that align workforce capabilities with organizational goals, ensuring smooth transitions during restructuring or policy shifts. People Ops emphasizes fostering a proactive organizational culture by leveraging data-driven insights to enhance employee engagement, collaboration, and continuous improvement. Both roles are integral to cultivating adaptive work environments, but People Ops integrates a holistic approach combining technology and human-centric processes to sustain long-term cultural transformation.
Compliance and Risk Management
HR Managers primarily focus on compliance with labor laws and internal policies by establishing standardized processes to mitigate legal risks and ensure regulatory adherence. People Operations professionals adopt a proactive approach to risk management through data-driven strategies and continuous improvement of workplace practices that foster employee engagement and organizational resilience. Both roles collaborate to create a compliant, ethical environment, but People Ops emphasizes innovation in compliance solutions alongside traditional HR oversight.
Future Trends in HR and People Operations
The evolution of HR management towards People Operations reflects a strategic shift emphasizing data-driven decision-making, employee experience, and organizational agility. Future trends prioritize integration of AI and predictive analytics to enhance talent acquisition, retention, and personalized employee development. Embracing these innovations, People Ops teams drive continuous improvement in workforce engagement and operational efficiency, positioning companies for sustainable growth.
Related Important Terms
Employee Experience Design
HR Managers traditionally focus on administrative tasks and compliance, whereas People Ops prioritizes Employee Experience Design by using data-driven insights to enhance workplace culture and engagement. Emphasizing personalized career development and continuous feedback loops, People Ops drives strategic initiatives that improve employee satisfaction and retention.
Talent Enablement
HR Managers traditionally oversee employee relations, compliance, and administrative functions whereas People Ops professionals prioritize talent enablement through data-driven strategies, employee experience, and continuous development programs. Emphasizing talent enablement, People Ops drives organizational performance by fostering skills growth, engagement, and agile workforce planning aligned with business goals.
Culture Architect
HR Managers traditionally focus on administrative functions such as recruitment, compliance, and employee relations, while People Operations emphasizes a strategic approach to fostering a positive workplace culture and enhancing employee experience. As Culture Architects, People Ops leaders design and implement initiatives that align organizational values with employee engagement, driving innovation and long-term business success.
People Analytics
People Analytics in HR Management emphasizes data-driven decision-making to optimize workforce performance, while People Operations integrates these insights into broader employee experience and organizational strategy. HR Managers focus on traditional talent management metrics, whereas People Ops leverages advanced analytics to enhance engagement, retention, and productivity systematically.
Strategic Workforce Planning
HR Managers traditionally focus on administrative tasks and employee relations, while People Operations emphasizes data-driven strategic workforce planning to align talent acquisition, development, and retention with long-term business goals. People Ops leverages analytics and predictive modeling to optimize workforce capacity, enhance employee experience, and drive organizational agility in a rapidly changing market.
Employee Journey Mapping
HR Managers traditionally focus on administrative tasks and compliance, while People Operations professionals emphasize a holistic, data-driven approach to Employee Journey Mapping that enhances engagement and retention. By leveraging analytics and employee feedback, People Ops designs personalized experiences to optimize talent development throughout every stage of the employee lifecycle.
Organizational Agility
HR Managers traditionally oversee recruitment, compliance, and employee relations, ensuring organizational structure and policies support agility. People Ops focuses on leveraging data-driven insights and employee experience strategies to foster flexibility, innovation, and rapid response to market changes.
People-Centric KPIs
HR Managers traditionally focus on metrics such as employee turnover rate, time-to-fill positions, and compliance adherence, while People Operations emphasizes people-centric KPIs like employee engagement scores, internal mobility rates, and workforce well-being indices. Organizations adopting a People Ops approach prioritize data-driven insights that enhance employee experience and foster a culture of continuous feedback and development.
Continuous Performance Management
Continuous Performance Management in HR Manager roles emphasizes traditional performance reviews and compliance tracking, while People Ops integrates real-time feedback, employee development, and data-driven insights to foster ongoing growth and engagement. People Ops leverages advanced HR technology and analytics to optimize talent management, promoting a proactive and dynamic approach to workforce performance.
Human Capital Transformation
HR Managers traditionally focus on administrative functions such as recruitment, compliance, and employee relations, while People Ops emphasizes strategic human capital transformation by leveraging data analytics and technology to enhance employee experience and drive organizational performance. The shift to People Ops reflects a broader trend toward integrating continuous workforce development and agile talent management to support dynamic business goals.
HR Manager vs People Ops Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com