A manager typically oversees daily operations and ensures team productivity within a specific department, while a fractional leader provides strategic expertise and guidance across multiple areas on a part-time basis. Fractional leaders bring high-level experience to address complex challenges without the commitment of a full-time executive. This approach offers flexibility and cost-efficiency for organizations seeking specialized leadership without expanding their permanent management structure.
Table of Comparison
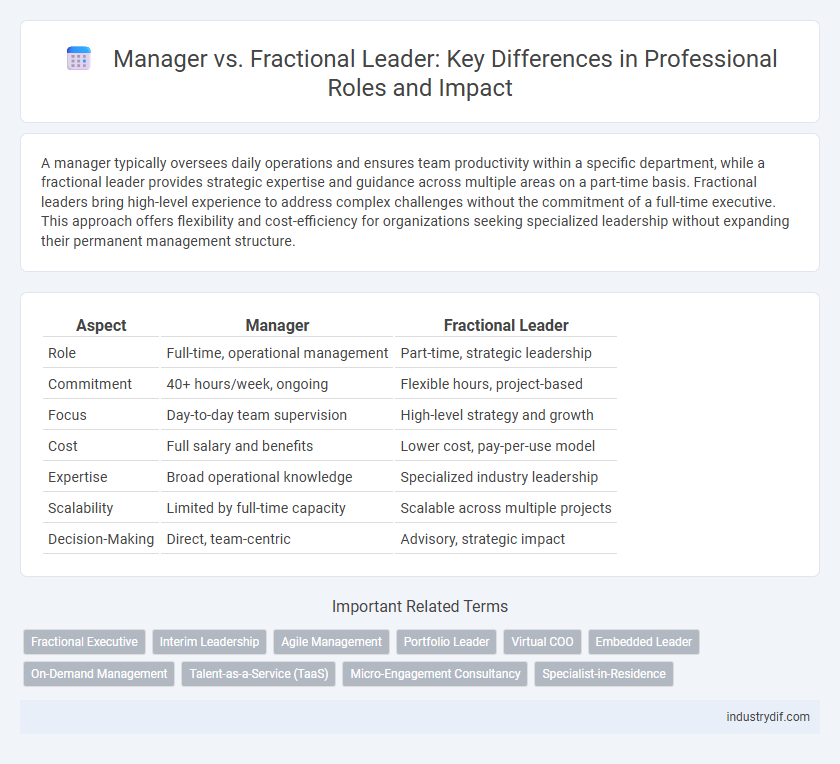
| Aspect | Manager | Fractional Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Full-time, operational management | Part-time, strategic leadership |
| Commitment | 40+ hours/week, ongoing | Flexible hours, project-based |
| Focus | Day-to-day team supervision | High-level strategy and growth |
| Cost | Full salary and benefits | Lower cost, pay-per-use model |
| Expertise | Broad operational knowledge | Specialized industry leadership |
| Scalability | Limited by full-time capacity | Scalable across multiple projects |
| Decision-Making | Direct, team-centric | Advisory, strategic impact |
Defining the Roles: Manager vs Fractional Leader
A manager oversees daily operations, team performance, and resource allocation within an organization, ensuring alignment with company goals. A fractional leader provides strategic leadership on a part-time or contract basis, often bringing specialized expertise to drive transformation or fill executive gaps. Both roles are crucial, but managers focus on execution while fractional leaders emphasize high-impact, flexible leadership solutions.
Core Responsibilities and Deliverables
Managers oversee daily operations, manage team performance, and ensure project completion within scope, time, and budget constraints. Fractional leaders provide strategic guidance, drive organizational change, and deliver high-level expertise on a part-time basis to support executive decision-making and long-term growth. While managers focus on execution and team management, fractional leaders concentrate on aligning business objectives with market opportunities and innovation.
Engagement Models and Commitment Levels
Manager roles typically involve full-time employment with a fixed commitment level, ensuring consistent oversight and team integration. Fractional leaders operate under flexible engagement models, providing strategic leadership on a part-time basis tailored to specific project needs or organizational goals. This approach allows companies to access high-level expertise without the ongoing obligations of a full-time hire, optimizing resource allocation and agility.
Strategic Impact on Organizational Growth
Managers typically focus on operational efficiency and team supervision within established frameworks, while fractional leaders drive strategic initiatives that accelerate organizational growth through high-level expertise. Fractional leaders bring cross-industry insights and innovative problem-solving skills, enabling businesses to navigate complex market dynamics and capitalize on new opportunities. Incorporating fractional leadership can result in more agile decision-making and a sharper competitive edge, directly influencing long-term success and scalability.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Leadership
Managers typically follow established protocols and focus on maintaining stability within a team, emphasizing consistency over change. Fractional leaders excel in flexibility and adaptability, stepping into diverse roles to address specific business challenges and drive strategic transformation. Their dynamic approach enables quick pivoting in response to market shifts, fostering innovation and resilience in leadership.
Cost and Resource Allocation Differences
Managers typically oversee full-time teams with fixed salaries and dedicated resources, leading to higher long-term personnel costs and less flexibility in scaling operations. Fractional leaders work on a part-time or project basis, offering expertise without the overhead of full-time employment, optimizing cost efficiency by aligning resource allocation precisely with business needs. This approach enables organizations to access strategic leadership while minimizing financial commitments and maximizing budget utilization.
Decision-Making Power and Authority
Managers typically have defined decision-making power within established guidelines and organizational hierarchies, ensuring consistent operational execution. Fractional leaders possess strategic authority often extending across multiple departments or projects, enabling high-impact decisions that shape broader business outcomes. This distinction in authority results in managers focusing on day-to-day management, while fractional leaders drive transformation and innovation at the executive level.
Talent Acquisition and Onboarding Processes
Managers oversee talent acquisition by coordinating recruitment teams and ensuring adherence to organizational hiring protocols, while fractional leaders strategically align talent acquisition with broader business goals on a part-time or project basis. Fractional leaders bring specialized expertise to optimize onboarding processes, driving faster integration and higher retention through tailored strategies that reflect company culture and operational priorities. Both roles play critical parts in enhancing hiring efficiency, but fractional leaders offer flexible leadership that adapts to evolving workforce needs.
Performance Metrics and Success Indicators
Managers typically focus on performance metrics such as team productivity, project completion rates, and budget adherence to ensure operational efficiency. Fractional leaders emphasize strategic success indicators including revenue growth, market expansion, and long-term sustainability to drive organizational transformation. Both roles utilize performance data but differ in scope, with managers overseeing day-to-day execution and fractional leaders steering high-impact initiatives.
Choosing the Right Leadership Model for Your Business
Selecting the ideal leadership model hinges on your business's scale, goals, and resource allocation. Managers typically provide consistent oversight within established frameworks, ensuring operational stability and team coordination. Fractional leaders bring specialized expertise and strategic insight on a part-time basis, ideal for businesses seeking flexible, high-impact leadership without the commitment of a full-time executive.
Related Important Terms
Fractional Executive
Fractional executives offer specialized leadership on a part-time basis, enabling organizations to access high-level expertise without the full cost of a permanent hire. Unlike traditional managers who oversee day-to-day operations, fractional leaders drive strategic initiatives and transformational growth with flexible, outcome-driven engagement.
Interim Leadership
Interim leadership bridges the gap between permanent management and fractional leadership by providing experienced professionals who step in temporarily to drive strategic initiatives and stabilize operations. Unlike fractional leaders who manage multiple organizations part-time, interim leaders dedicate their full expertise to a single company, ensuring focused decision-making and seamless transitions during critical periods.
Agile Management
Managers in Agile environments typically focus on task delegation and team coordination, ensuring processes align with organizational goals, while fractional leaders bring strategic agility by offering part-time, high-level expertise to drive transformation initiatives and foster adaptive leadership. The fractional leadership model enhances Agile management through flexible, outcome-driven guidance that accelerates innovation without the overhead of full-time executive roles.
Portfolio Leader
A Portfolio Leader operates as a Fractional Leader by overseeing multiple projects or business units simultaneously, driving strategic alignment and resource optimization without the full-time commitment of a traditional Manager. This role emphasizes high-impact decision-making and cross-functional leadership to maximize portfolio value and accelerate organizational growth.
Virtual COO
A Virtual COO acts as a fractional leader providing strategic oversight, operational efficiency, and executive decision-making without full-time commitment, unlike traditional managers who typically focus on day-to-day team supervision and task execution. This fractional leadership model enables businesses to access high-level COO expertise flexibly, optimizing growth and organizational scalability in virtual environments.
Embedded Leader
Embedded leaders integrate deeply within organizational teams, driving strategic initiatives and operational excellence without the traditional hierarchical constraints faced by managers, who often focus on direct supervision and daily task management. This approach enables embedded leaders to influence cross-functional collaboration and innovation more effectively than conventional managerial roles.
On-Demand Management
On-demand management by fractional leaders provides specialized expertise and strategic oversight without the full-time commitment required of traditional managers, enabling businesses to access high-level leadership tailored to specific projects or challenges. Fractional leaders deliver agile decision-making and resource optimization, maximizing efficiency and driving growth within fixed budgets and flexible timeframes.
Talent-as-a-Service (TaaS)
Managers typically oversee entire teams and operational functions full-time, while fractional leaders provide specialized expertise and strategic guidance on a part-time or project basis, optimizing Talent-as-a-Service (TaaS) models for scalable and cost-effective leadership. Leveraging fractional leadership in TaaS enables organizations to access high-level skills and agile decision-making without the commitment of permanent executive salaries.
Micro-Engagement Consultancy
In a Micro-Engagement Consultancy, a Manager typically oversees daily operations and team coordination, ensuring project milestones are met with efficiency and precision. A Fractional Leader provides strategic guidance and high-level expertise on a part-time basis, driving organizational growth and innovation without the cost of a full-time executive.
Specialist-in-Residence
A Specialist-in-Residence serves as a Fractional Leader by providing strategic expertise and high-impact guidance without full-time managerial responsibilities, enabling organizations to access specialized skills flexibly and cost-effectively. Unlike traditional managers who oversee daily operations and team management, Specialist-in-Residence roles concentrate on driving innovation and solving complex challenges within targeted areas of expertise.
Manager vs Fractional Leader Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com