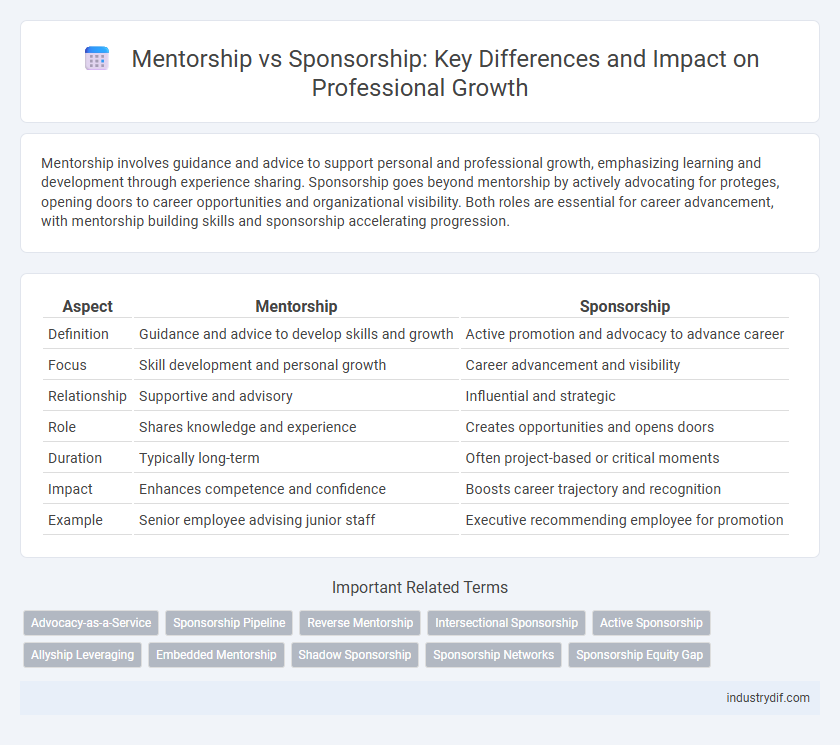
Mentorship involves guidance and advice to support personal and professional growth, emphasizing learning and development through experience sharing. Sponsorship goes beyond mentorship by actively advocating for proteges, opening doors to career opportunities and organizational visibility. Both roles are essential for career advancement, with mentorship building skills and sponsorship accelerating progression.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mentorship | Sponsorship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Guidance and advice to develop skills and growth | Active promotion and advocacy to advance career |
| Focus | Skill development and personal growth | Career advancement and visibility |
| Relationship | Supportive and advisory | Influential and strategic |
| Role | Shares knowledge and experience | Creates opportunities and opens doors |
| Duration | Typically long-term | Often project-based or critical moments |
| Impact | Enhances competence and confidence | Boosts career trajectory and recognition |
| Example | Senior employee advising junior staff | Executive recommending employee for promotion |
Understanding Mentorship and Sponsorship: Key Definitions
Mentorship is a developmental relationship where an experienced individual provides guidance, advice, and support to foster personal and professional growth. Sponsorship involves a senior leader actively advocating for and promoting the protege's career advancement within an organization. Understanding these key definitions highlights the distinct roles mentorship plays in skill-building versus sponsorship's focus on visibility and opportunity creation.
Core Differences Between Mentorship and Sponsorship
Mentorship involves a developmental relationship where an experienced professional provides guidance, advice, and support to foster skills and career growth, emphasizing knowledge transfer and personal development. Sponsorship goes beyond by actively advocating for the protege, leveraging influence and networks to create tangible career advancement opportunities such as promotions or high-visibility projects. The core difference lies in mentorship prioritizing learning and growth, whereas sponsorship centers on direct career acceleration through endorsement and strategic positioning.
The Role of Mentors in Career Development
Mentors provide personalized guidance, industry insights, and constructive feedback essential for professional growth and skill enhancement. They foster long-term relationships that support mentees in navigating challenges, setting career goals, and expanding their networks. Effective mentorship accelerates learning curves and builds confidence, directly influencing career advancement opportunities.
The Impact of Sponsors on Professional Advancement
Sponsors play a critical role in professional advancement by actively advocating for high-potential talent, opening doors to key opportunities and influential networks that mentors alone may not provide. Unlike mentors who offer guidance and advice, sponsors leverage their organizational power to champion proteges in promotions, high-visibility projects, and leadership roles. This direct intervention by sponsors significantly accelerates career growth and visibility within competitive industries.
Essential Qualities of Effective Mentors and Sponsors
Effective mentors demonstrate active listening, empathy, and a commitment to personal and professional growth, fostering trust and open communication with their mentees. Sponsors possess influence and authority, advocating for their proteges by providing visibility, opportunities, and strategic career advancement. Both roles require integrity, accountability, and a genuine investment in the mentee's success to maximize developmental impact.
How to Seek and Establish Mentorship Relationships
To seek and establish effective mentorship relationships, identify potential mentors with relevant expertise and a willingness to invest time in your growth. Approach them with clear, specific goals and demonstrate commitment to learning and professional development. Maintain regular communication, show appreciation for their guidance, and actively apply their advice to build a mutually beneficial connection.
Strategies for Gaining a Sponsor in the Workplace
Securing a sponsor in the workplace requires demonstrating high-impact performance and aligning with organizational goals to attract influential advocates. Building strategic relationships with senior leaders through visible projects and consistent value delivery enhances sponsor engagement. Proactive communication of career aspirations and seeking opportunities for exposure increase the likelihood of gaining a committed sponsor who advocates for key promotions and opportunities.
Organizational Benefits of Fostering Both Mentorship and Sponsorship
Fostering both mentorship and sponsorship within an organization enhances talent development and accelerates leadership readiness by providing comprehensive support and advocacy. Mentorship cultivates skill-building and knowledge transfer, while sponsorship actively promotes high-potential employees for critical opportunities and advancement. Organizations leveraging both strategies experience increased employee engagement, retention rates, and a more robust leadership pipeline that drives sustained business growth.
Overcoming Common Barriers in Mentorship and Sponsorship
Overcoming common barriers in mentorship and sponsorship requires addressing issues such as lack of access, misaligned expectations, and unconscious bias. Establishing clear communication channels and setting measurable goals can improve the effectiveness of these relationships. Leveraging organizational support and diversity initiatives enhances inclusivity and fosters meaningful career advancement opportunities.
Best Practices for Building a Holistic Career Support System
Effective mentorship involves providing guidance, knowledge sharing, and skill development opportunities, while sponsorship actively advocates for advancement by leveraging influence and networks. Combining both practices creates a robust career support system that balances personalized growth with strategic visibility and access. Organizations should establish structured programs fostering mentor-mentee alignment along with sponsor engagement to maximize talent development and promotion pathways.
Related Important Terms
Advocacy-as-a-Service
Mentorship provides guidance and skill development while sponsorship actively advocates for career advancement by leveraging influence and networks. Advocacy-as-a-Service amplifies sponsorship by systematically connecting professionals with champions who promote their opportunities within organizations.
Sponsorship Pipeline
Sponsorship pipeline development is critical for corporate leadership growth, as sponsors actively advocate for proteges by leveraging their influence to create high-visibility opportunities and accelerate career advancement. Organizations that cultivate robust sponsorship pipelines demonstrate higher retention rates and diverse executive representation by systematically connecting high-potential talent with senior leaders committed to mentorship and advocacy.
Reverse Mentorship
Reverse mentorship empowers senior leaders by pairing them with younger or less experienced employees who offer fresh perspectives on technology, diversity, and market trends, driving innovation and cultural agility. This approach differs from traditional sponsorship, which centers on advocating for career advancement, as reverse mentorship emphasizes learning and knowledge exchange across generational or hierarchical boundaries.
Intersectional Sponsorship
Intersectional sponsorship leverages the influence of sponsors to advocate for individuals from multiple marginalized identities, ensuring they receive access to critical opportunities and career advancement. This approach transcends traditional mentorship by actively promoting inclusivity and dismantling systemic barriers through strategic allyship and resource allocation.
Active Sponsorship
Active sponsorship directly accelerates career advancement by leveraging influential networks and advocating for high-visibility opportunities on behalf of proteges. Unlike mentorship, which primarily offers guidance and advice, active sponsors commit resources, open doors, and champion professional growth within organizational hierarchies.
Allyship Leveraging
Mentorship provides guidance and skill development, while sponsorship actively advocates for career advancement by leveraging networks and opportunities. Allyship in sponsorship involves using influence to remove barriers and create strategic visibility for underrepresented professionals within organizational structures.
Embedded Mentorship
Embedded mentorship integrates ongoing guidance within daily work environments, enhancing skill development and career growth through direct, context-specific support. Unlike traditional mentorship or sponsorship, embedded mentorship fosters continuous learning by embedding experienced professionals within teams to provide real-time feedback and strategic advice.
Shadow Sponsorship
Shadow sponsorship involves influential leaders advocating for talent behind the scenes, leveraging their networks to open opportunities without overt acknowledgment. Unlike traditional mentorship, shadow sponsors actively promote proteges' career advancement by discreetly influencing key decision-makers and organizational politics.
Sponsorship Networks
Sponsorship networks actively leverage influential advocates to provide high-visibility opportunities and career advancement for proteges, creating pathways to leadership roles through direct endorsement and resource allocation. Unlike mentorship, which centers on guidance and skill development, sponsorship networks drive tangible career growth by linking individuals to decision-makers and organizational power structures.
Sponsorship Equity Gap
Sponsorship plays a critical role in closing the equity gap by actively advocating for underrepresented professionals and providing them with access to high-visibility opportunities that mentorship alone often fails to secure. Organizations that implement structured sponsorship programs see improved career advancement rates and reduced disparities in leadership representation across diverse groups.
Mentorship vs Sponsorship Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com