Office workers often face rigid schedules and limited flexibility, which can impact their work-life balance and productivity. Digital nomads enjoy greater freedom to choose their work environments, leveraging technology to maintain efficiency while traveling or working remotely. Both lifestyles demand effective time management skills, but digital nomads prioritize adaptability and connectivity to thrive in diverse settings.
Table of Comparison
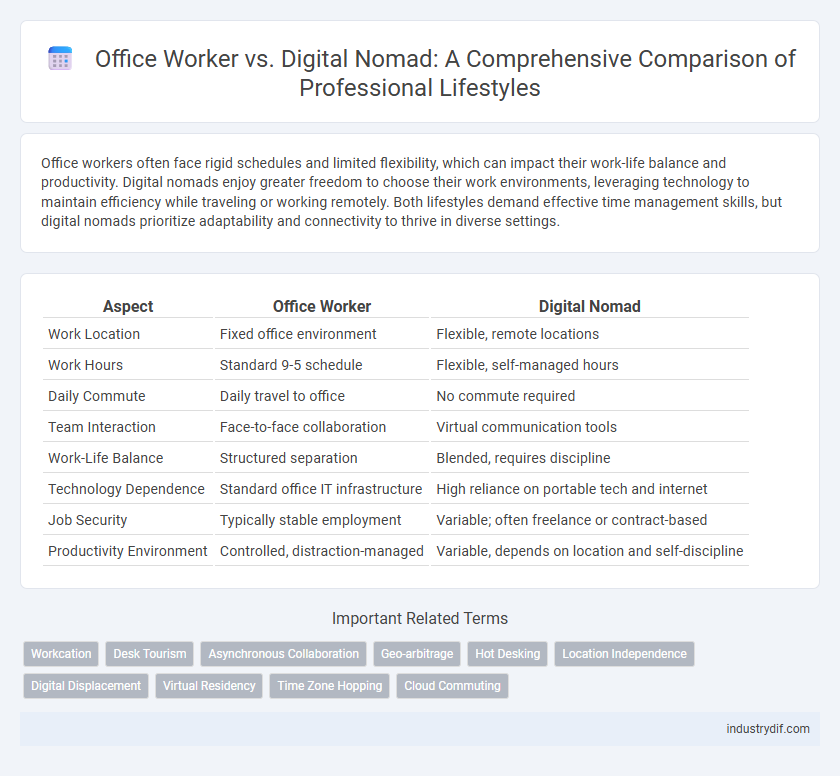
| Aspect | Office Worker | Digital Nomad |
|---|---|---|
| Work Location | Fixed office environment | Flexible, remote locations |
| Work Hours | Standard 9-5 schedule | Flexible, self-managed hours |
| Daily Commute | Daily travel to office | No commute required |
| Team Interaction | Face-to-face collaboration | Virtual communication tools |
| Work-Life Balance | Structured separation | Blended, requires discipline |
| Technology Dependence | Standard office IT infrastructure | High reliance on portable tech and internet |
| Job Security | Typically stable employment | Variable; often freelance or contract-based |
| Productivity Environment | Controlled, distraction-managed | Variable, depends on location and self-discipline |
Defining the Office Worker and the Digital Nomad
Office workers operate within traditional workplace settings, typically following fixed schedules and utilizing centralized office infrastructure. Digital nomads leverage technology to perform their tasks remotely, embracing mobility and flexible work hours across various global locations. The distinction centers on physical presence requirements and adaptability to location-independent work models.
Core Responsibilities and Daily Routines
Office workers typically adhere to structured schedules with clearly defined tasks such as attending meetings, managing emails, and collaborating in person, while digital nomads prioritize flexibility, balancing client communications, project management, and time zone coordination from remote locations. Core responsibilities for office workers often involve maintaining consistent work hours and following company protocols, whereas digital nomads rely on self-discipline and advanced digital tools to meet deadlines across diverse environments. Daily routines differ significantly, with office workers engaging in routine commutes and physical workspace interactions, contrasted by digital nomads who integrate travel, adapt to varying workspaces, and leverage cloud-based resources for seamless workflow continuity.
Workplace Flexibility and Autonomy
Office workers often experience structured schedules and limited workplace flexibility, confined to a specific physical location during standard business hours. Digital nomads leverage technology to work remotely from various locations worldwide, enabling greater autonomy and personalized work environments. This shift enhances productivity for those prioritizing work-life balance and self-management.
Technology and Digital Tools Utilized
Office workers primarily rely on established enterprise software such as Microsoft Office 365, Slack, and VPN technologies to ensure secure, efficient in-house collaboration and data management. Digital nomads utilize cloud-based platforms like Google Workspace, Trello, and VPNs to maintain seamless remote access and flexible communication across various geographical locations. Advanced digital tools such as virtual private networks, cloud storage solutions, and video conferencing software are pivotal in enabling both office professionals and digital nomads to optimize productivity in their respective environments.
Productivity Metrics and Performance Evaluation
Office workers often benefit from structured environments and direct supervision, which facilitate consistent tracking of productivity metrics such as task completion rates and time management efficiency. Digital nomads rely heavily on self-discipline and digital tools to monitor performance, using metrics like project milestones and output quality to evaluate effectiveness. Comparing these models reveals distinctive challenges in performance evaluation, with remote work necessitating adaptive measurement strategies to ensure accountability and sustained productivity.
Work-Life Balance and Employee Wellbeing
Office workers benefit from structured environments that provide predictable routines, enhancing mental stability and clear boundaries between work and personal life. Digital nomads face challenges in establishing work-life balance due to variable work locations and hours, which can impact employee wellbeing if not managed effectively. Implementing flexible schedules and wellness programs tailored for remote work can significantly improve productivity and reduce burnout in both office and nomadic settings.
Communication Styles and Collaboration Methods
Office workers typically rely on face-to-face communication and structured meetings, fostering immediate feedback and non-verbal cues that enhance collaboration. Digital nomads depend heavily on digital tools such as video conferencing, instant messaging, and cloud-based platforms to maintain communication across time zones and locations. Effective collaboration for office teams often involves co-located brainstorming sessions, whereas digital nomads prioritize asynchronous workflows and real-time digital collaboration to accommodate flexible schedules.
Career Advancement and Professional Development
Office workers benefit from structured environments that offer clear career progression paths, access to on-site mentorship, and regular professional development programs. Digital nomads gain diverse global experiences and adaptability skills but may face challenges securing consistent training and networking opportunities essential for long-term career advancement. Balancing flexibility with strategic skill-building is crucial for digital nomads aiming to match the professional growth of traditional office workers.
Challenges and Risk Management
Office workers face challenges such as rigid schedules, commuting stress, and limited flexibility, requiring effective time management and ergonomic risk mitigation to maintain productivity and health. Digital nomads encounter risks including unstable internet connections, data security vulnerabilities, and legal compliance across jurisdictions, demanding robust cybersecurity measures and adaptive risk management strategies. Both work styles necessitate tailored approaches to mitigate physical, technological, and regulatory risks to ensure sustained professional performance.
Future Trends in Workforce Mobility
The future of workforce mobility is increasingly shaped by the rise of digital nomads, driven by advancements in remote work technology and the demand for flexible work environments. Office workers may see hybrid models becoming standard, blending in-person collaboration with virtual connectivity to enhance productivity and work-life balance. Companies will prioritize secure, cloud-based solutions and global talent access to support this evolving dynamic between traditional office roles and location-independent work styles.
Related Important Terms
Workcation
Workcation offers office workers a flexible approach to productivity by blending remote work with travel, enabling professionals to maintain output while exploring new environments. Digital nomads leverage workcation to optimize work-life balance, using technology to stay connected across different locations without compromising professional responsibilities.
Desk Tourism
Office workers benefit from structured environments and consistent resources, enhancing productivity through familiarity and routine. Digital nomads engage in desk tourism by leveraging mobile work setups to explore diverse locations, fostering creativity and flexibility while maintaining professional output.
Asynchronous Collaboration
Office workers rely heavily on synchronous communication within physical spaces, whereas digital nomads maximize productivity through asynchronous collaboration tools such as Slack, Trello, and asynchronous video platforms. This shift allows digital nomads to overcome time zone barriers and maintain work continuity without the need for real-time interaction, enhancing flexibility and efficiency.
Geo-arbitrage
Office workers often face fixed costs tied to expensive urban centers, limiting their financial flexibility, while digital nomads leverage geo-arbitrage by living in lower-cost locations to maximize income and reduce living expenses. Geo-arbitrage enables digital nomads to enhance their purchasing power and savings potential, creating a significant economic advantage compared to traditional office-based employment.
Hot Desking
Hot desking offers office workers flexible workspace options within a traditional office, promoting collaboration and efficient use of resources. Digital nomads benefit from hot desking by accessing professional environments worldwide without fixed desks, enhancing mobility and productivity.
Location Independence
Office workers typically operate within fixed physical locations, limiting their flexibility and requiring daily commutes; digital nomads embrace location independence, leveraging technology to work remotely from anywhere in the world, enhancing work-life balance and productivity. This geographic flexibility enables digital nomads to adapt to diverse environments and optimize their work settings based on personal preferences and lifestyle needs.
Digital Displacement
Digital displacement increasingly shifts traditional office workers towards remote roles, redefining workplace dynamics and productivity models through cloud-based collaboration and communication technologies. This transition highlights the growing prevalence of digital nomads who leverage flexible digital infrastructure to operate independently of physical office locations.
Virtual Residency
Virtual residency offers digital nomads the flexibility to work from anywhere while maintaining compliance with local regulations, unlike traditional office workers who are tied to physical office locations and standard work hours. This evolving trend enables companies to attract global talent and reduce operational costs by leveraging remote workforce models supported through virtual residency programs.
Time Zone Hopping
Office workers typically adhere to fixed schedules aligned with a single time zone, ensuring consistent collaboration within local business hours. Digital nomads often manage multiple time zones simultaneously, optimizing productivity by leveraging asynchronous communication tools and flexible work hours.
Cloud Commuting
Cloud commuting transforms traditional Office Worker roles by enabling seamless remote access to corporate resources, increasing productivity and flexibility. Digital Nomads leverage cloud commuting to work from any location, utilizing virtual desktops and cloud-based collaboration tools to maintain continuous connectivity and secure data access.
Office Worker vs Digital Nomad Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com