Professional workers typically possess specialized expertise and often operate within structured organizational hierarchies, prioritizing long-term career development and stability. In contrast, portfolio workers manage multiple roles or projects across various fields, emphasizing flexibility, diverse skill sets, and continual adaptation to evolving market demands. Understanding these distinctions helps organizations tailor management approaches and individuals align career strategies with their work preferences.
Table of Comparison
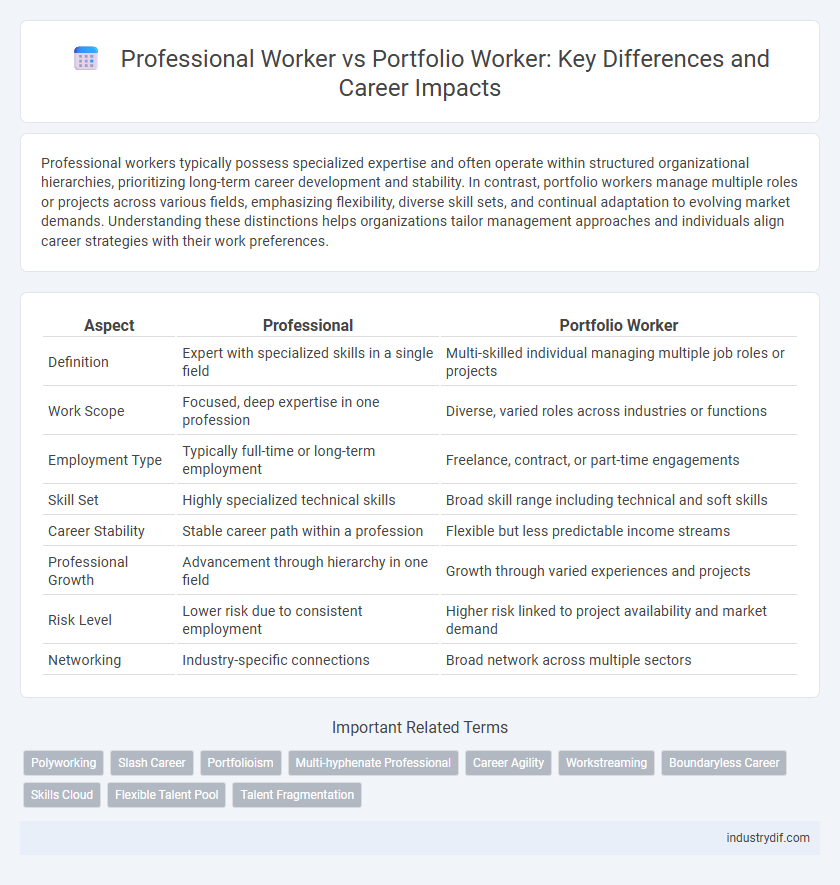
| Aspect | Professional | Portfolio Worker |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expert with specialized skills in a single field | Multi-skilled individual managing multiple job roles or projects |
| Work Scope | Focused, deep expertise in one profession | Diverse, varied roles across industries or functions |
| Employment Type | Typically full-time or long-term employment | Freelance, contract, or part-time engagements |
| Skill Set | Highly specialized technical skills | Broad skill range including technical and soft skills |
| Career Stability | Stable career path within a profession | Flexible but less predictable income streams |
| Professional Growth | Advancement through hierarchy in one field | Growth through varied experiences and projects |
| Risk Level | Lower risk due to consistent employment | Higher risk linked to project availability and market demand |
| Networking | Industry-specific connections | Broad network across multiple sectors |
Defining Professional and Portfolio Worker
A professional is an individual with specialized expertise, formal qualifications, and typically a consistent role within a single organization or industry, emphasizing deep knowledge and long-term career development. A portfolio worker, by contrast, manages multiple concurrent roles or projects across various fields, leveraging diverse skills to adapt to a fluctuating job market and autonomous work arrangements. Understanding the distinctions between professionals and portfolio workers is crucial for organizations navigating workforce planning and talent management strategies.
Key Differences Between Professional and Portfolio Worker
Professional workers typically specialize in a single field, offering deep expertise and stability within organizations, whereas portfolio workers manage multiple roles or projects across various industries to diversify skills and income streams. Professionals often pursue long-term career progression within one company or sector, while portfolio workers emphasize flexibility, adaptability, and continuous learning through varied engagements. The key distinctions lie in commitment style, work structure, and career development approaches that define each worker's value proposition in the labor market.
Skills Required for Professional Workers
Professional workers require specialized expertise, in-depth knowledge of industry standards, and continuous skill development to maintain competence in their field. Mastery of technical skills, critical thinking, and effective communication is essential for delivering high-quality results and solving complex problems. They also demonstrate adaptability and ethical judgment, ensuring compliance with professional regulations and fostering trust with clients and stakeholders.
Skills Required for Portfolio Workers
Portfolio workers require a diverse set of skills including adaptability, self-management, and strong networking abilities to successfully juggle multiple projects across different industries. They must excel in digital literacy, project management, and continuous learning to stay competitive in evolving markets. Effective communication and entrepreneurial mindset are essential for building client relationships and maintaining a versatile professional identity.
Benefits of Being a Professional Worker
Professional workers often enjoy greater job stability, access to comprehensive benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans, and clear career advancement pathways. They benefit from structured work environments with consistent income and employer-sponsored training programs that enhance skill development. These advantages lead to increased job security and long-term growth opportunities compared to portfolio workers.
Advantages of a Portfolio Career
A portfolio career offers significant advantages including diversified income sources, enhanced skill development, and increased job security by reducing dependence on a single employer. This approach allows professionals to leverage multiple roles or projects simultaneously, fostering adaptability and broader professional networks. Such flexibility also supports work-life balance and continuous personal growth within evolving industries.
Challenges Faced by Professionals
Professionals often encounter challenges such as maintaining up-to-date expertise amid rapidly evolving industries, managing rigid organizational structures, and navigating office politics that can impede career progression. Unlike portfolio workers who diversify skills across multiple projects, professionals face pressure to specialize deeply, which can limit flexibility and adaptability in dynamic job markets. The demand for continuous certifications and adherence to industry standards also contributes to stress and resource allocation challenges for professionals committed to long-term career development.
Challenges of the Portfolio Work Model
Portfolio workers face challenges such as inconsistent income streams, difficulty securing long-term contracts, and managing diverse skill sets across multiple industries. The lack of traditional employee benefits like healthcare and retirement plans creates financial vulnerability and stress. Balancing time management and client expectations requires advanced organizational skills to maintain productivity and professional reputation.
Industry Trends: Professional vs Portfolio Worker
Industry trends highlight a growing shift from traditional professionals, who typically specialize in a single field within established organizations, toward portfolio workers managing diverse roles across multiple sectors. Portfolio workers leverage a blend of skills, adapting to gig economy demands and prioritizing flexibility, often delivering higher innovation through varied experiences. Companies increasingly value this agile workforce model for its capacity to drive cross-functional collaboration and continuous learning in dynamic markets.
Choosing the Right Path: Professional or Portfolio Worker
Choosing the right career path depends on individual goals and work preferences; professionals often thrive in structured environments with clear roles, while portfolio workers leverage diverse skills across multiple projects for flexibility. Understanding market demands and personal strengths helps determine whether to pursue a traditional professional role or a dynamic portfolio worker approach. Evaluating long-term career growth, income stability, and job satisfaction is crucial in making an informed decision between these paths.
Related Important Terms
Polyworking
Polyworking integrates the flexibility of portfolio workers who manage multiple income streams with the specialized expertise of professionals focused on singular career paths. This hybrid approach enhances adaptability and skill diversification, meeting the evolving demands of dynamic job markets and delivering sustained professional growth.
Slash Career
A slash career involves professionals diversifying their expertise by simultaneously pursuing multiple roles, blending traditional professional identity with portfolio work. This approach enhances flexibility and marketability, allowing individuals to leverage varied skills across different industries while maintaining professional credentials.
Portfolioism
Portfolioism emphasizes a strategic approach where professionals actively manage multiple projects and skill sets to diversify income streams and enhance career resilience, contrasting with traditional single-employer work models. This model leverages continuous learning, networking, and personal branding to adapt rapidly in dynamic job markets and foster entrepreneurial opportunities.
Multi-hyphenate Professional
A multi-hyphenate professional seamlessly integrates diverse skill sets across multiple disciplines, distinguishing themselves from portfolio workers who typically manage varied, unrelated gigs. This hybrid expertise enhances adaptability and creates unique value propositions in dynamic professional landscapes.
Career Agility
Career agility distinguishes professionals, who typically specialize deeply within a single field, from portfolio workers, who leverage diverse skills across multiple projects or roles, fostering adaptability in dynamic job markets. Embracing career agility enables both to navigate uncertainties by continuously updating competencies and capitalizing on varied opportunities for growth and innovation.
Workstreaming
Professional workers excel in specialized tasks within defined roles, benefiting from structured workstreaming that enhances efficiency and expertise application. Portfolio workers manage multiple projects across diverse fields, leveraging flexible workstreaming techniques to optimize time allocation and cross-disciplinary innovation.
Boundaryless Career
Professional workers often follow structured career paths within specific organizations, emphasizing expertise and role stability, whereas portfolio workers embrace a boundaryless career by managing diverse projects and multiple clients across industries, prioritizing flexibility and continuous skill development. This boundaryless career model fosters adaptability, autonomy, and broad professional networks, essential for success in today's dynamic job market.
Skills Cloud
Skills Clouds enable professional workers to showcase specialized expertise through detailed skill mapping, while portfolio workers benefit from dynamic aggregation of diverse competencies across multiple projects. This technology enhances talent matching by highlighting skill proficiency and adaptability, streamlining recruitment and career development processes in dynamic job markets.
Flexible Talent Pool
A flexible talent pool leverages both professional and portfolio workers to address dynamic project demands by combining specialized expertise with diverse, multi-disciplinary skills. Professional workers provide deep, domain-specific knowledge, while portfolio workers bring adaptability and a broad skill set, enhancing organizational agility and innovation capacity.
Talent Fragmentation
Talent fragmentation intensifies between professional and portfolio workers as specialists focus on niche skills while portfolio workers diversify across multiple disciplines. This shift challenges organizations to adapt talent management strategies that balance deep expertise with versatile skill sets.
Professional vs Portfolio Worker Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com