Public budgeting typically involves decisions made by government officials allocating funds based on predetermined priorities, often lacking direct community input. Participatory budgeting invites citizens to actively engage in the decision-making process, fostering transparency and ensuring that public spending reflects the community's needs and preferences. This collaborative approach enhances accountability and empowers residents to influence how local resources are distributed.
Table of Comparison
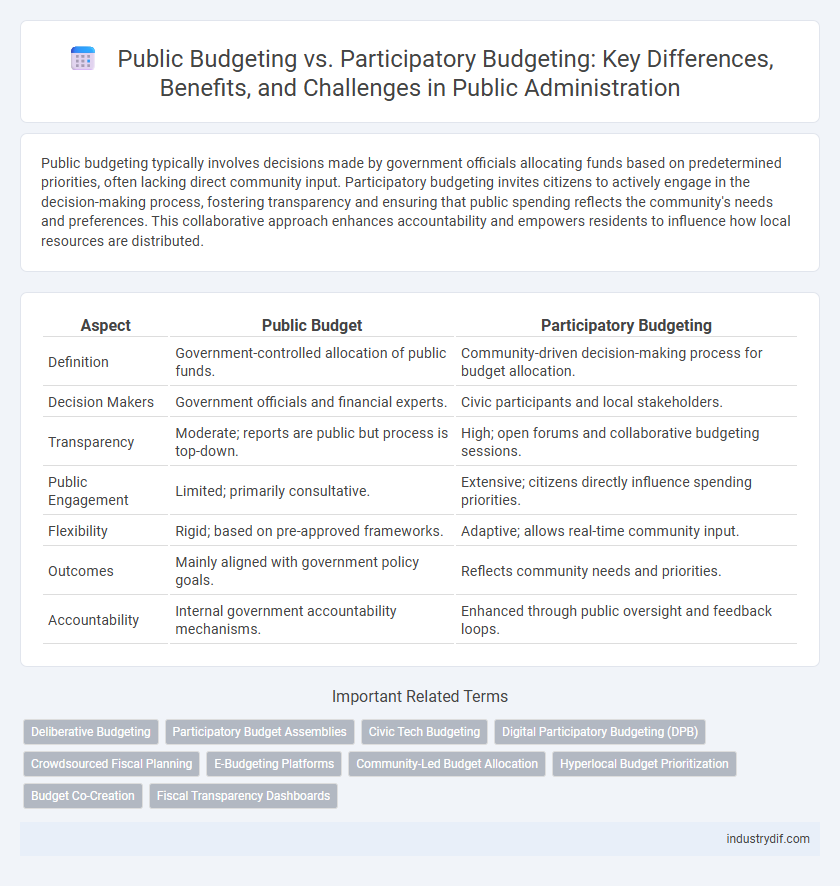
| Aspect | Public Budget | Participatory Budgeting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government-controlled allocation of public funds. | Community-driven decision-making process for budget allocation. |
| Decision Makers | Government officials and financial experts. | Civic participants and local stakeholders. |
| Transparency | Moderate; reports are public but process is top-down. | High; open forums and collaborative budgeting sessions. |
| Public Engagement | Limited; primarily consultative. | Extensive; citizens directly influence spending priorities. |
| Flexibility | Rigid; based on pre-approved frameworks. | Adaptive; allows real-time community input. |
| Outcomes | Mainly aligned with government policy goals. | Reflects community needs and priorities. |
| Accountability | Internal government accountability mechanisms. | Enhanced through public oversight and feedback loops. |
Understanding Public Budgeting: Core Concepts
Public budgeting involves the allocation of government resources based on revenue forecasting, expenditure planning, and fiscal policy to ensure efficient public service delivery. It emphasizes transparency, accountability, and legal compliance while prioritizing sectors like education, healthcare, and infrastructure. Participatory budgeting, by contrast, incorporates community input directly into decision-making, enhancing democratic engagement and aligning spending with local needs.
The Evolution of Participatory Budgeting
Participatory budgeting has evolved from a localized, community-driven initiative in Porto Alegre, Brazil, in 1989 to a global democratic innovation enhancing transparency and citizen engagement in public finance. This evolution reflects a shift from traditional public budgeting, which centralizes fiscal decisions within government authorities, to a collaborative process allowing residents to directly influence budget allocations. Modern participatory budgeting leverages digital platforms to expand inclusivity, enabling diverse populations to propose, discuss, and prioritize projects that address community-specific needs effectively.
Key Differences: Public vs. Participatory Budgeting
Public budgeting is a top-down financial planning process managed by government officials, emphasizing efficiency and compliance with legal frameworks. Participatory budgeting involves direct citizen engagement, allowing community members to propose and vote on spending priorities, thereby enhancing transparency and democratic involvement. The key difference lies in decision-making authority: public budgeting is expert-driven, while participatory budgeting democratizes fiscal decisions by incorporating public input.
Stakeholder Involvement in Budget Processes
Stakeholder involvement in public budgeting typically remains limited to government officials and elected representatives, whereas participatory budgeting actively engages community members and local organizations in decision-making. This inclusive approach facilitates transparency, accountability, and more equitable allocation of resources by incorporating diverse public input. Increased citizen participation in budget processes fosters trust and ensures that funding priorities better reflect community needs.
Transparency and Accountability in Budgeting
Public budgets often suffer from limited transparency, hindering citizens' understanding of resource allocation and diminishing accountability in government spending. Participatory budgeting enhances transparency by involving community members directly in decision-making processes, allowing for real-time insight into budget priorities and expenditures. This inclusive approach fosters greater accountability by enabling citizens to monitor and influence how public funds are allocated and spent, ultimately strengthening democratic governance.
Benefits of Participatory Budgeting for Communities
Participatory budgeting empowers communities by fostering transparency and direct involvement in allocating public funds, leading to more equitable and community-driven outcomes. This process enhances civic engagement, builds trust between citizens and local governments, and ensures that budget priorities reflect the actual needs of diverse populations. Studies show that participatory budgeting improves resource distribution efficiency and increases social cohesion among residents.
Challenges in Implementing Participatory Budgeting
Implementing participatory budgeting faces challenges such as limited public awareness, insufficient technical resources, and resistance from traditional bureaucratic structures. Ensuring equitable representation and overcoming voter apathy are critical hurdles in engaging diverse community members effectively. Lack of transparency and accountability mechanisms can further hinder the trust and long-term sustainability of participatory budgeting initiatives.
Impact on Resource Allocation and Prioritization
Public budgeting traditionally centralizes resource allocation decisions within government agencies, often limiting direct citizen influence on prioritization. Participatory budgeting empowers communities to actively engage in decision-making, resulting in resource distribution that closely aligns with local needs and preferences. Studies show that participatory budgeting enhances transparency, accountability, and equitable allocation, improving public trust and policy effectiveness.
Case Studies: Public vs. Participatory Budgeting in Practice
Case studies comparing public budgets and participatory budgeting reveal significant variations in transparency, citizen engagement, and allocation efficiency. In Porto Alegre, Brazil, participatory budgeting fostered increased public trust and prioritized community-driven projects, contrasting with traditional public budgets that often centralized decision-making and lacked grassroots input. Empirical evidence from multiple municipalities demonstrates participatory budgeting's capacity to enhance social equity by involving marginalized populations in fiscal decisions.
Future Trends in Democratic Financial Governance
Emerging trends in democratic financial governance emphasize the integration of public budget frameworks with participatory budgeting processes to enhance transparency and citizen engagement. Technological advancements such as blockchain and AI-driven analytics are increasingly deployed to optimize budget allocation and facilitate real-time public input. Data from recent studies indicate that participatory budgeting can improve resource allocation efficiency by up to 20% and strengthen trust in local governments.
Related Important Terms
Deliberative Budgeting
Deliberative budgeting enhances public budget processes by actively involving citizens in informed discussions and decision-making, ensuring greater transparency and accountability in resource allocation. This participatory approach fosters community engagement and aligns budget priorities with the public's needs, contrasting with traditional top-down public budgeting methods.
Participatory Budget Assemblies
Participatory Budget Assemblies empower citizens to directly influence the allocation of public funds by engaging in transparent decision-making processes that reflect community priorities. These assemblies enhance democratic governance, increase budget transparency, and foster greater public trust compared to traditional public budget approaches.
Civic Tech Budgeting
Public Budgeting traditionally allocates government funds through centralized decision-making processes, often lacking direct citizen input; in contrast, Participatory Budgeting leverages Civic Tech platforms to enable community members to propose, discuss, and vote on budget priorities, enhancing transparency and democratic engagement. Civic Tech Budgeting tools utilize digital interfaces and data analytics to facilitate real-time collaboration, increase accessibility, and improve accountability in public financial management.
Digital Participatory Budgeting (DPB)
Digital Participatory Budgeting (DPB) enhances transparency and citizen engagement by leveraging online platforms to facilitate community decision-making on public budget allocation, contrasting traditional public budgeting processes that often lack direct public input. By integrating digital tools, DPB enables real-time feedback, broader demographic participation, and efficient aggregation of preferences, driving more inclusive and accountable fiscal governance.
Crowdsourced Fiscal Planning
Public budgeting typically involves top-down allocation of resources by government officials, whereas participatory budgeting embraces crowdsourced fiscal planning to directly engage citizens in decision-making, increasing transparency and community investment. Crowdsourced fiscal planning leverages collective input and local knowledge, optimizing resource distribution to better reflect diverse public needs and priorities.
E-Budgeting Platforms
E-Budgeting platforms enhance transparency and citizen engagement by digitizing public budget processes, enabling real-time access and collaborative decision-making. Unlike traditional public budgeting, participatory budgeting integrated within these platforms empowers communities to directly influence fund allocation through interactive online tools.
Community-Led Budget Allocation
Public budget processes often centralize decision-making within government agencies, limiting direct community input in allocating resources. Participatory budgeting empowers citizens to co-create budget priorities, ensuring community-led budget allocation aligns spending with local needs and enhances transparency.
Hyperlocal Budget Prioritization
Hyperlocal budget prioritization enables communities to directly influence public budget allocation through participatory budgeting, ensuring that funds address specific neighborhood needs and improve local infrastructure. Public budgets traditionally allocate resources at broader administrative levels, often overlooking micro-level priorities that participatory budgeting actively captures for targeted impact.
Budget Co-Creation
Public budget planning traditionally involves top-down allocation of resources determined by government officials, whereas participatory budgeting emphasizes budget co-creation by engaging citizens directly in decision-making processes. This collaborative approach enhances transparency, promotes civic engagement, and ensures that budget priorities align with community needs and social equity goals.
Fiscal Transparency Dashboards
Fiscal transparency dashboards enhance public budget accountability by providing clear, real-time data on government expenditures and revenues, enabling citizens to monitor fiscal policies effectively. In participatory budgeting, these dashboards facilitate community engagement by visualizing project proposals, budget allocations, and spending outcomes, fostering transparent decision-making and increased public trust.
Public Budget vs Participatory Budgeting Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com