Public awareness campaigns increase knowledge about responsible pet ownership, but they often fail to change long-term behaviors without reinforcement. Behavioral nudging uses subtle prompts and environmental changes to encourage pet-friendly actions, such as providing waste bags in parks or designated pet zones. Combining awareness with nudging techniques leads to more consistent and positive outcomes for community pet management.
Table of Comparison
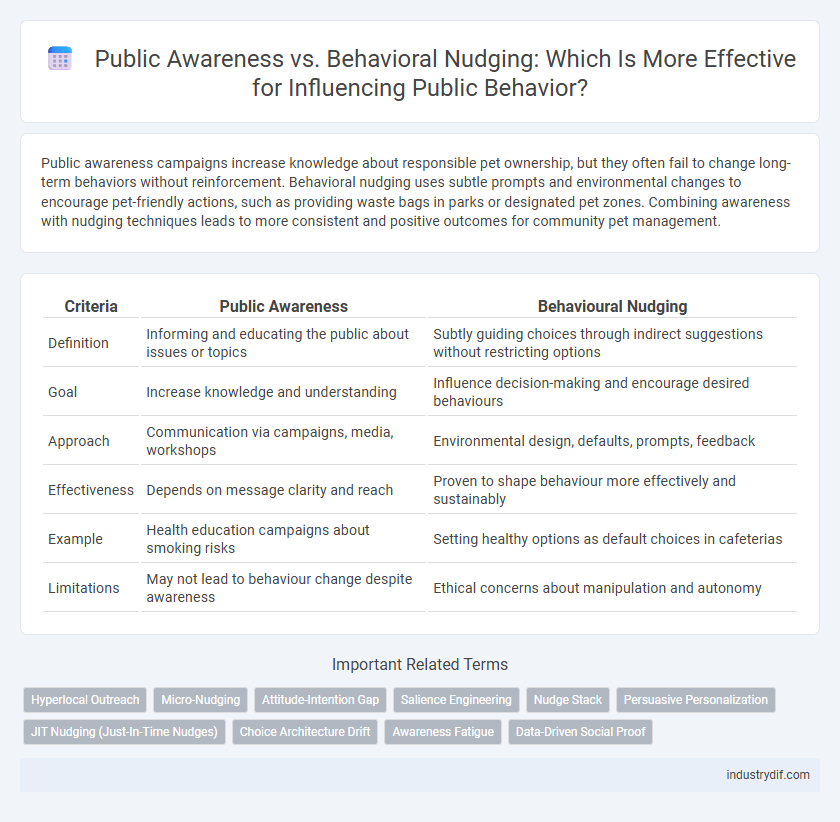
| Criteria | Public Awareness | Behavioural Nudging |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Informing and educating the public about issues or topics | Subtly guiding choices through indirect suggestions without restricting options |
| Goal | Increase knowledge and understanding | Influence decision-making and encourage desired behaviours |
| Approach | Communication via campaigns, media, workshops | Environmental design, defaults, prompts, feedback |
| Effectiveness | Depends on message clarity and reach | Proven to shape behaviour more effectively and sustainably |
| Example | Health education campaigns about smoking risks | Setting healthy options as default choices in cafeterias |
| Limitations | May not lead to behaviour change despite awareness | Ethical concerns about manipulation and autonomy |
Understanding Public Awareness: Definition and Importance
Public awareness refers to the collective knowledge and understanding that individuals have about specific issues, which shapes their perceptions and actions. It plays a crucial role in guiding community behavior by informing decision-making and fostering social responsibility. Enhancing public awareness is essential for effective behavioral nudging, as it creates the foundation for targeted interventions that encourage positive social change.
Behavioural Nudging: Concept and Applications
Behavioural nudging leverages subtle interventions to influence decision-making and promote positive behavioural changes without restricting choices. This approach uses psychological insights, such as heuristics and social norms, to encourage desired actions in areas like public health, environmental conservation, and financial planning. Applications include default options in organ donation registration, reminder messages for vaccination, and feedback systems that highlight energy consumption, effectively increasing participation and compliance rates.
Public Awareness vs Behavioural Nudging: Key Differences
Public awareness involves disseminating information to educate and inform individuals about important issues, aiming to influence attitudes and knowledge at a broad scale. Behavioural nudging uses subtle prompts and design changes in the environment to guide individuals towards desired behaviours without restricting choices. Key differences include the reliance on conscious decision-making in public awareness campaigns versus the automatic, often subconscious influence exerted by nudges in behavioural interventions.
Psychological Foundations Behind Behavioural Nudging
Behavioural nudging leverages psychological principles such as cognitive biases, heuristics, and social norms to influence decision-making without restricting choice. Techniques like framing effects and default options exploit automatic, System 1 thinking to encourage pro-social and health-promoting behaviours. Understanding constructs like loss aversion and reciprocity is crucial for designing effective nudges that align with human motivation and improve public compliance.
Communication Strategies for Enhancing Public Awareness
Effective communication strategies for enhancing public awareness leverage targeted messaging through multiple channels such as social media, community workshops, and public service announcements. Utilizing behavioral insights allows messages to be tailored, increasing relevance and emotional engagement, which significantly improves knowledge retention and motivates positive behavior change. Clear, consistent, and culturally sensitive communication fosters trust and encourages proactive participation in public health and safety initiatives.
Measuring the Impact of Public Awareness Campaigns
Measuring the impact of public awareness campaigns involves analyzing changes in knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors among targeted populations using surveys, behavioral data, and engagement metrics. Effective evaluation requires integrating qualitative feedback with quantitative indicators such as recall rates, participation levels, and behavioral shifts tracked over time. These measurement techniques help differentiate the influence of awareness efforts from behavioral nudging strategies, ensuring accurate assessment of campaign effectiveness.
Case Studies: Successful Behavioural Nudging Initiatives
Successful behavioural nudging initiatives have demonstrated significant improvements in public health and environmental conservation by subtly guiding individual decisions without restricting freedom of choice. Case studies such as the implementation of default organ donation enrollment in countries like Spain have led to dramatically increased consent rates, while energy conservation nudges using real-time feedback systems in households have reduced electricity consumption by up to 15%. These examples highlight how strategically designed nudges effectively transform awareness into measurable behavioural change across diverse populations.
Challenges in Driving Public Awareness and Behaviour Change
Challenges in driving public awareness and behavior change include overcoming deeply ingrained habits, misinformation, and cultural resistance. Effective communication strategies must address diverse audiences and leverage trusted messengers to enhance message credibility. Limited resources and measurement difficulties further complicate efforts to sustain long-term behavioral nudging campaigns.
Ethical Considerations in Behavioural Nudging
Ethical considerations in behavioural nudging emphasize transparency, respect for autonomy, and avoidance of manipulation when influencing public choices. Ensuring informed consent and protecting individual freedom to opt out are critical to maintaining trust and legitimacy in nudging strategies. Public awareness campaigns should complement nudges by fostering understanding rather than covertly steering behaviour.
Integrating Public Awareness with Behavioural Nudging for Greater Impact
Integrating public awareness campaigns with behavioural nudging techniques amplifies the effectiveness of social initiatives by combining knowledge dissemination with subtle cues that influence decision-making. Evidence shows that when citizens are informed through targeted messaging and simultaneously guided by nudges--such as default options or social norm feedback--there is a measurable increase in positive behaviours like energy conservation or health compliance. Leveraging data-driven insights to tailor both awareness content and nudging strategies leads to higher engagement rates and sustainable behavioural change.
Related Important Terms
Hyperlocal Outreach
Hyperlocal outreach enhances public awareness by tailoring messages to specific community needs, increasing relevance and engagement. Behavioral nudging complements this by subtly guiding individuals' decisions within these localized settings, resulting in more effective and sustained behavior change.
Micro-Nudging
Micro-nudging leverages subtle, context-specific cues to influence public behavior with minimal cognitive effort, enhancing the effectiveness of public awareness campaigns by directing choices without restricting freedom. This approach harnesses behavioral insights such as defaults, reminders, and social norms to promote positive actions in areas like health, environmental sustainability, and public safety.
Attitude-Intention Gap
Public awareness campaigns increase knowledge but often fail to close the attitude-intention gap, where positive attitudes do not consistently translate into behavioral changes. Behavioral nudging uses subtle environmental cues and incentives to bridge this gap by influencing decision-making processes without restricting choice.
Salience Engineering
Salience engineering leverages perceptual cues to enhance public awareness by making desired behaviors more prominent and easier to notice, effectively guiding decisions without restricting freedom of choice. Techniques like strategic placement, vivid visuals, and contextual framing increase the cognitive salience of target actions, resulting in higher compliance and improved behavioral outcomes.
Nudge Stack
Nudge Stack leverages layered behavioral interventions to enhance public awareness by subtly guiding decision-making without restricting choices, effectively bridging the gap between knowledge and action. Its strategic use of social norms, reminders, and default settings drives sustained behavioral changes, optimizing outcomes in public health, environmental conservation, and social welfare programs.
Persuasive Personalization
Persuasive personalization enhances public awareness by tailoring messages to individual values and preferences, increasing the effectiveness of behavioral nudging in promoting sustainable actions. This approach leverages data-driven insights to deliver targeted prompts, resulting in higher engagement and long-lasting behavior change.
JIT Nudging (Just-In-Time Nudges)
Just-In-Time (JIT) nudging leverages precise timing and contextual cues to influence public behavior effectively, enhancing decision-making at critical moments without overwhelming individuals with constant awareness messages. Evidence shows JIT nudges outperform general public awareness campaigns by delivering targeted prompts that trigger immediate action, optimizing behavioral change in areas like health, energy consumption, and public safety.
Choice Architecture Drift
Choice architecture drift refers to the gradual shift in how public awareness efforts influence individual decision-making environments, often reducing the effectiveness of behavioral nudging over time. Sustained behavioral impact requires continuously adapting choice architectures to maintain alignment with evolving public perceptions and contextual factors.
Awareness Fatigue
Public awareness campaigns often lead to awareness fatigue, where repeated exposure to health messages reduces their impact on behavior change; behavioural nudging, by subtly altering environments and choices, can sustain engagement without overwhelming the audience. Research shows nudges increase compliance with public health measures more effectively than traditional awareness efforts by minimizing cognitive overload and decision fatigue.
Data-Driven Social Proof
Data-driven social proof leverages real-time analytics and behavioral insights to enhance public awareness campaigns, promoting positive behavioral changes through evidence-based feedback loops. By showcasing aggregated community actions and outcomes, it strengthens trust and motivation, driving more effective nudging strategies across diverse populations.
Public Awareness vs Behavioural Nudging Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com