Public funding for pet-related initiatives often involves government grants and established institutions providing financial support, ensuring accountability and steady resources. Crowdfunding leverages the power of communities and social media, enabling pet projects to gain rapid funding through small contributions from many supporters. While public funding offers stability, crowdfunding fosters direct public engagement and awareness, making both methods valuable for advancing animal welfare.
Table of Comparison
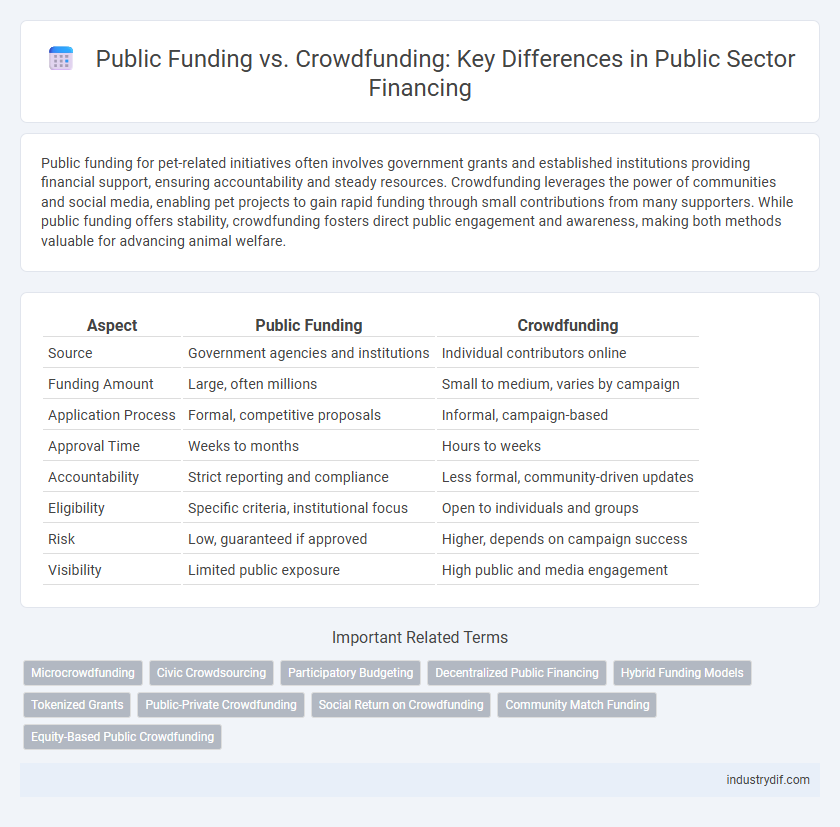
| Aspect | Public Funding | Crowdfunding |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Government agencies and institutions | Individual contributors online |
| Funding Amount | Large, often millions | Small to medium, varies by campaign |
| Application Process | Formal, competitive proposals | Informal, campaign-based |
| Approval Time | Weeks to months | Hours to weeks |
| Accountability | Strict reporting and compliance | Less formal, community-driven updates |
| Eligibility | Specific criteria, institutional focus | Open to individuals and groups |
| Risk | Low, guaranteed if approved | Higher, depends on campaign success |
| Visibility | Limited public exposure | High public and media engagement |
Understanding Public Funding: Definitions and Mechanisms
Public funding refers to financial support provided by government agencies or public institutions to projects or organizations, often through grants, subsidies, or loans. It involves a structured application process with eligibility criteria, regulatory oversight, and accountability mechanisms designed to ensure funds serve public interests. Crowdfunding, in contrast, leverages small contributions from a large number of individuals via online platforms, relying on community engagement rather than formal governmental processes.
What Is Crowdfunding? An Industry Overview
Crowdfunding is a method of raising capital through the collective effort of a large number of individuals, typically via online platforms, enabling entrepreneurs and creators to secure funds directly from the public. Unlike traditional public funding, which often involves government grants or institutional investments, crowdfunding leverages small contributions from a broad audience to finance projects, products, or causes. This industry has expanded rapidly, with platforms like Kickstarter and Indiegogo facilitating billions of dollars in funding across diverse sectors such as technology, arts, and social initiatives.
Key Differences Between Public Funding and Crowdfunding
Public funding is typically sourced from government budgets, grants, or taxpayer money aimed at supporting large-scale projects or public services, whereas crowdfunding relies on small contributions from a large number of individuals via online platforms. Public funding often involves stringent regulations, formal application processes, and accountability measures, while crowdfunding campaigns emphasize community engagement, marketing, and social proof to attract backers. The scale and purpose distinguish these methods, with public funding targeting infrastructure or research and crowdfunding supporting creative, entrepreneurial, or social initiatives.
Eligibility Criteria: Public Funding vs Crowdfunding Campaigns
Public funding typically requires organizations to meet specific eligibility criteria, including nonprofit status, detailed project proposals, and compliance with government regulations. Crowdfunding campaigns have more flexible eligibility, often open to individuals, startups, or nonprofits without formal documentation, relying instead on public interest and marketing strategy. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right funding method based on project scope and organizational structure.
Application Processes Compared: Traditional vs Digital Platforms
Public funding typically involves a structured, formal application process with strict eligibility criteria, requiring detailed proposals and governmental or institutional review boards. Crowdfunding platforms streamline this process through digital interfaces, allowing project creators to present ideas directly to potential donors, bypassing extensive bureaucratic evaluation. The ease of submission and real-time feedback on crowdfunding sites contrasts sharply with the often lengthy and competitive timelines characteristic of traditional public funding applications.
Funding Sources: Government Grants vs Crowd Contributors
Government grants provide substantial, structured funding from public agencies with stringent eligibility criteria and reporting requirements, ensuring project accountability. Crowd contributors offer flexible financial support through online platforms, leveraging widespread public engagement but often with unpredictable funding amounts and timelines. Choosing between these sources depends on project scope, funding stability needs, and stakeholder involvement goals.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Public funding involves strict compliance with government regulations, including detailed reporting, eligibility criteria, and auditing requirements to ensure transparency and accountability. Crowdfunding platforms operate under specific financial and consumer protection laws that vary by jurisdiction, often requiring adherence to securities regulations when offering investment opportunities. Navigating these regulatory frameworks is essential for both funding methods to mitigate legal risks and maintain public trust.
Advantages of Public Funding for Projects
Public funding offers significant advantages for projects, including stable and substantial financial support from government sources that often exceed what crowdfunding campaigns can achieve. It provides long-term investment opportunities with fewer risks and greater access to resources, such as expert guidance and infrastructure assistance, which enhance project success rates. Public funding also promotes transparency and accountability through stringent oversight, ensuring proper allocation and effective use of funds.
Crowdfunding Benefits and Potential Drawbacks
Crowdfunding offers accessible capital from diverse contributors, enabling startups and creative projects to bypass traditional financing constraints and validate market interest early. However, it requires significant marketing effort, risks intellectual property exposure, and success is not guaranteed, potentially leading to wasted resources or unmet funding goals. Public funding, while often more stable and substantial, typically involves stringent eligibility criteria and bureaucratic delays that can limit flexibility and speed.
Choosing the Right Funding Route for Public Initiatives
Public funding offers stable financial support from government sources, ensuring long-term project viability and compliance with regulatory standards. Crowdfunding attracts diverse individual contributors, generating community engagement and validating public interest in initiatives. Selecting the right funding route depends on project scale, urgency, and the desired level of public participation, optimizing resource allocation and outreach impact.
Related Important Terms
Microcrowdfunding
Microcrowdfunding represents a targeted form of crowdfunding that enables individuals or small groups to raise modest amounts of capital online, often bypassing traditional public funding channels such as government grants or institutional loans. This grassroots financing model harnesses the power of digital platforms to connect projects directly with niche supporters, facilitating faster access to funds and enabling innovative ideas to thrive without the bureaucratic hurdles typically associated with public funding.
Civic Crowdsourcing
Public funding relies on government allocations or institutional budgets to finance civic projects, ensuring accountability through regulatory frameworks. Civic crowdsourcing leverages community-driven contributions and collective intelligence, enhancing transparency and citizen engagement while diversifying resource acquisition beyond traditional public funds.
Participatory Budgeting
Participatory budgeting empowers citizens to allocate public funding through direct voting, enhancing transparency and community engagement in municipal projects, whereas crowdfunding sources funds from a broader public online but lacks formal democratic decision-making processes. This approach to public funding fosters equitable distribution of resources by involving diverse stakeholders in budgeting decisions, contrasting with crowdfunding's project-specific, often commercially driven financing.
Decentralized Public Financing
Decentralized public financing leverages blockchain technology to enable transparent, secure, and direct allocation of funds by the community, reducing reliance on traditional public funding channels prone to bureaucratic delays and opacity. Unlike conventional public funding, crowdfunding facilitates grassroots participation and democratic decision-making, empowering stakeholders to support projects aligned with their interests through decentralized platforms.
Hybrid Funding Models
Hybrid funding models combine public funding and crowdfunding to leverage the financial stability of government grants with the community engagement of online fundraising platforms, optimizing resource allocation for innovative projects. These models increase access to diverse capital sources, enhance transparency, and foster collaboration between public institutions and private contributors, accelerating project development and impact.
Tokenized Grants
Tokenized grants revolutionize public funding by leveraging blockchain technology to enhance transparency, traceability, and efficiency in resource allocation. Unlike traditional crowdfunding, tokenized grants enable precise tracking of fund usage and empower decentralized decision-making, accelerating innovation and accountability in public sector projects.
Public-Private Crowdfunding
Public-private crowdfunding combines government support with private investment to enhance project financing, leveraging public funds to reduce risks and attract diverse backers. This hybrid model accelerates innovation and community engagement by blending regulatory oversight with market-driven incentives.
Social Return on Crowdfunding
Crowdfunding generates higher social return by directly engaging communities and enabling projects with measurable social impact to gain financial support, unlike traditional public funding which often faces bureaucratic delays and limited community involvement. Social return on crowdfunding is amplified through transparency, stakeholder participation, and the ability to scale social innovation efficiently.
Community Match Funding
Community Match Funding leverages public funding by partnering with local organizations to double the contributions raised through crowdfunding campaigns, amplifying the financial impact for community projects. This approach incentivizes grassroots participation while ensuring accountability and transparency in the allocation of public resources.
Equity-Based Public Crowdfunding
Equity-based public crowdfunding enables startups to raise capital by offering shares to a broad range of public investors, providing greater access to funds compared to traditional public funding sources such as government grants or subsidies. This financing model leverages online platforms to democratize investment opportunities and fosters community engagement while allowing investors to potentially benefit from business growth through equity ownership.
public funding vs crowdfunding Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com