Public records offer centralized documentation maintained by government entities, ensuring legal validity but often vulnerable to tampering and inefficiency. Blockchain governance introduces a decentralized, transparent ledger system that enhances security, immutability, and real-time verification of records. This shift empowers public accountability and streamlines administrative processes by reducing dependence on traditional authorities.
Table of Comparison
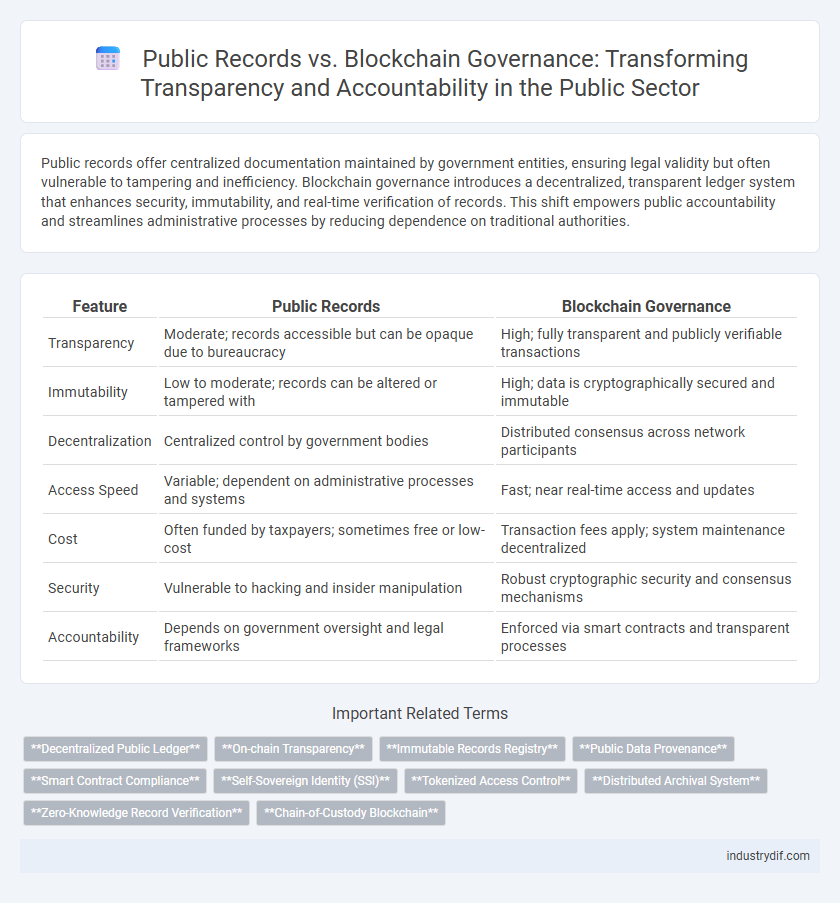
| Feature | Public Records | Blockchain Governance |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Moderate; records accessible but can be opaque due to bureaucracy | High; fully transparent and publicly verifiable transactions |
| Immutability | Low to moderate; records can be altered or tampered with | High; data is cryptographically secured and immutable |
| Decentralization | Centralized control by government bodies | Distributed consensus across network participants |
| Access Speed | Variable; dependent on administrative processes and systems | Fast; near real-time access and updates |
| Cost | Often funded by taxpayers; sometimes free or low-cost | Transaction fees apply; system maintenance decentralized |
| Security | Vulnerable to hacking and insider manipulation | Robust cryptographic security and consensus mechanisms |
| Accountability | Depends on government oversight and legal frameworks | Enforced via smart contracts and transparent processes |
Introduction to Public Records and Blockchain Governance
Public records are official documents or pieces of information created and maintained by government agencies, serving as authoritative evidence of activities, rights, and transactions accessible to the public for transparency and accountability. Blockchain governance involves decentralized protocols and consensus mechanisms that manage decision-making, security, and integrity of blockchain networks without centralized control. Comparing public records and blockchain governance highlights the shift from traditional centralized record-keeping to distributed ledger technology enabling enhanced transparency, immutability, and trust in data management.
Key Differences Between Public Records and Blockchain Systems
Public records are government-maintained documents that verify legal and historical facts, ensuring centralized authenticity and regulated access. Blockchain governance operates through decentralized ledgers that provide immutable, transparent transaction records secured by cryptographic consensus mechanisms. Unlike public records, blockchain systems enable trustless verification without a central authority, offering enhanced security but requiring consensus protocols for updates.
Transparency in Public Records vs. Blockchain
Public records offer legal transparency by providing verifiable documentation accessible through government databases, ensuring accountability and compliance with regulations. Blockchain governance enhances transparency via decentralized, immutable ledgers that record transactions in real-time, reducing the potential for data manipulation and increasing trust among stakeholders. The combination of traditional public records and blockchain technology creates a robust framework for transparency, fostering open access to accurate, tamper-proof information.
Data Security: Traditional Records vs. Distributed Ledgers
Public records stored in centralized databases are vulnerable to data breaches and unauthorized modifications due to single points of failure. Blockchain governance leverages distributed ledgers to enhance data security by ensuring immutability and transparency through cryptographic consensus mechanisms. This decentralized approach significantly reduces risks associated with tampering and unauthorized access compared to traditional record-keeping systems.
Access and Control: Who Governs the Data?
Public records are traditionally governed by government agencies, providing centralized access and control with legal oversight and established data privacy protocols. Blockchain governance, however, decentralizes access and control through distributed consensus mechanisms, enabling transparent and tamper-resistant data management without reliance on a single authority. This shift enhances public trust by offering more democratic data governance but requires robust mechanisms to balance transparency with privacy rights.
Auditability and Trust in Record-Keeping
Public records rely on centralized authorities for auditability, often leading to limited transparency and potential errors or tampering. Blockchain governance enhances trust in record-keeping by providing immutable, time-stamped entries verified through decentralized consensus mechanisms. This decentralized auditability ensures higher data integrity and real-time traceability, reducing fraud and increasing accountability.
Costs and Efficiency: Public Records vs. Blockchain Solutions
Public records systems often incur high administrative costs and processing delays due to centralized data management and manual verification processes. Blockchain governance offers enhanced efficiency by automating record verification through decentralized consensus mechanisms, significantly reducing operational expenses. The cost-effectiveness of blockchain solutions stems from minimized intermediaries and increased transparency, enabling faster, more secure public record maintenance.
Legal and Regulatory Implications
Public records operate under established legal frameworks ensuring transparency, admissibility, and regulatory compliance, while blockchain governance presents novel challenges in jurisdiction, data immutability, and cross-border regulation enforcement. Legal implications include the recognition of blockchain-stored data as evidence, privacy concerns under regulations like GDPR, and the need for updated laws to address decentralized authentication. Regulatory bodies must balance innovation with oversight by developing standards for blockchain governance that align with existing public record statutes and ensure accountability.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Public records management benefits from blockchain governance by enhancing transparency, immutability, and security in real-world applications such as land registries, voting systems, and identity verification. Case studies like Estonia's e-Residency program and Dubai's blockchain initiative demonstrate significant reductions in fraud and administrative costs while improving public trust. These decentralized solutions provide verifiable audit trails and streamline government services by leveraging smart contracts and distributed ledgers.
Future Trends in Record Management and Blockchain Governance
Future trends in record management emphasize the integration of blockchain technology to enhance transparency, immutability, and security of public records. Decentralized blockchain governance models are evolving to facilitate more efficient, tamper-proof record-keeping systems that reduce reliance on centralized authorities. Advances in smart contracts and consensus algorithms are expected to drive widespread adoption of blockchain-based public records, improving trust and accessibility in governmental and institutional data management.
Related Important Terms
Decentralized Public Ledger
A decentralized public ledger leverages blockchain technology to provide transparent, immutable records accessible by anyone, contrasting traditional public records managed by centralized authorities vulnerable to manipulation. This decentralized governance framework ensures data integrity and enhances trust through cryptographic consensus mechanisms, making it ideal for secure public record-keeping.
On-chain Transparency
On-chain transparency in blockchain governance enables immutable and real-time access to decision-making processes and transaction histories, ensuring accountability without reliance on centralized authorities. Public records, while accessible, often lack the instantaneous visibility and tamper-proof qualities inherent in blockchain systems, limiting their effectiveness in transparent governance.
Immutable Records Registry
Immutable records registry on blockchain governance ensures tamper-proof, permanent public records storage, enhancing transparency and trust compared to traditional public records systems vulnerable to alterations. This decentralized ledger technology records every transaction securely, providing an auditable, verifiable history unmatched by conventional, centralized public records databases.
Public Data Provenance
Public records serve as official archives ensuring transparency and accountability through verified data provenance, while blockchain governance enhances this by providing immutable, decentralized ledgers that guarantee tamper-proof public data provenance with real-time auditability. The integration of blockchain technology significantly improves the authenticity and traceability of public records, fostering trust in digital governance systems.
Smart Contract Compliance
Smart contract compliance in public records ensures automated, transparent verification and reduces human error in maintaining accurate legal documentation, while blockchain governance provides a decentralized framework that enforces these compliance rules through immutable, tamper-proof ledgers. The integration of smart contracts within blockchain governance enhances public record security by enabling real-time audits and automatic enforcement of regulatory standards.
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) leverages blockchain governance to empower individuals with full control over their public records, eliminating reliance on centralized authorities. This decentralized approach enhances privacy, security, and interoperability by enabling users to manage and verify their identities through cryptographic proofs stored on blockchain networks.
Tokenized Access Control
Tokenized access control in blockchain governance leverages cryptographic tokens to grant and manage permissions, enabling secure, transparent, and immutable public records management. Unlike traditional public records systems that rely on centralized authorities, tokenized access ensures decentralized verification and tamper-proof audit trails for all authorized users.
Distributed Archival System
Public records traditionally rely on centralized archival systems vulnerable to tampering and data loss, whereas blockchain governance implements a distributed archival system that ensures immutable, transparent, and decentralized record-keeping. This decentralized ledger technology enhances data integrity and public trust by distributing transaction copies across multiple nodes, eliminating single points of failure.
Zero-Knowledge Record Verification
Zero-knowledge record verification in blockchain governance allows public records to be validated without revealing underlying sensitive information, enhancing privacy and security. This cryptographic technique ensures transparent accountability while preserving data confidentiality, overcoming limitations found in traditional public record systems.
Chain-of-Custody Blockchain
Chain-of-Custody Blockchain provides an immutable, transparent ledger that enhances the integrity and auditability of public records by securely tracking the provenance and handling of digital assets. This decentralized approach ensures tamper-proof documentation, strengthening trust and accountability in public governance systems.
Public Records vs Blockchain Governance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com