Public funding allocates resources through centralized government decisions, often prioritizing large-scale pet care initiatives and infrastructure improvements. Participatory budgeting engages community members directly in deciding how funds are spent, fostering transparency and ensuring that pet-related projects address local needs. This inclusive approach enhances public trust and promotes equitable distribution of resources for pet welfare.
Table of Comparison
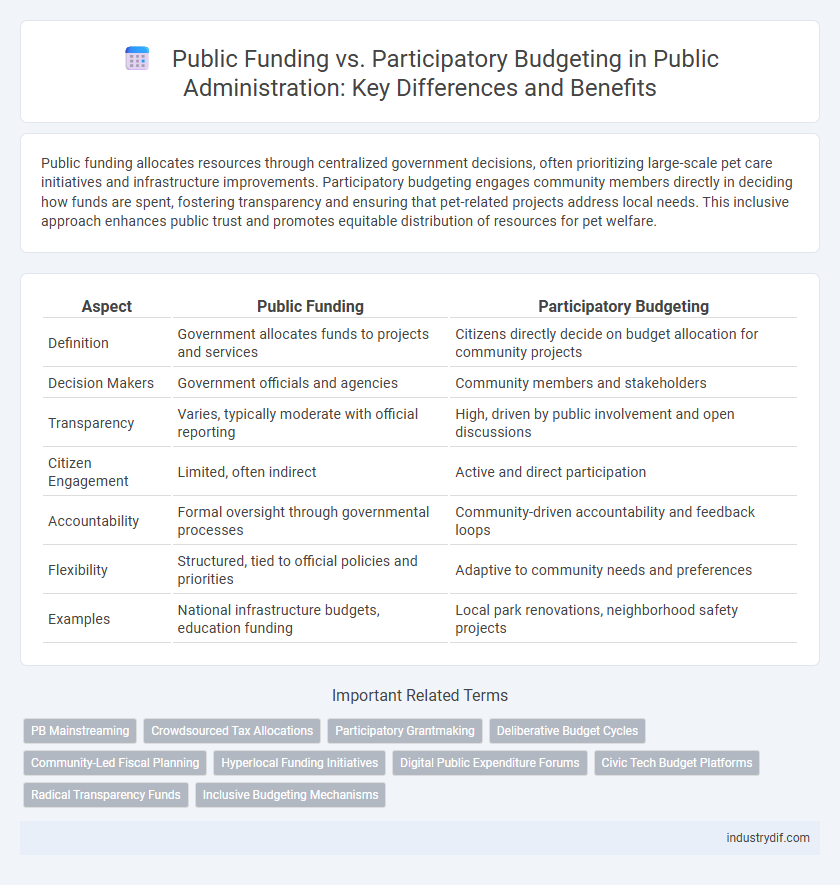
| Aspect | Public Funding | Participatory Budgeting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government allocates funds to projects and services | Citizens directly decide on budget allocation for community projects |
| Decision Makers | Government officials and agencies | Community members and stakeholders |
| Transparency | Varies, typically moderate with official reporting | High, driven by public involvement and open discussions |
| Citizen Engagement | Limited, often indirect | Active and direct participation |
| Accountability | Formal oversight through governmental processes | Community-driven accountability and feedback loops |
| Flexibility | Structured, tied to official policies and priorities | Adaptive to community needs and preferences |
| Examples | National infrastructure budgets, education funding | Local park renovations, neighborhood safety projects |
Understanding Public Funding in Government
Public funding in government refers to the allocation of financial resources sourced primarily from taxes, grants, and other state revenues to support public services and projects. It operates through established budgetary processes driven by elected officials and government agencies to ensure fiscal responsibility and alignment with policy priorities. Participatory budgeting, contrastingly, involves direct citizen engagement in decision-making on how public funds are allocated, promoting transparency, accountability, and community-driven priorities within the public funding framework.
What Is Participatory Budgeting?
Participatory budgeting is a democratic process in which community members directly decide how to allocate a portion of a public budget, promoting transparency and citizen engagement. Unlike traditional public funding, where government officials control financial decisions, participatory budgeting empowers residents to propose and vote on local projects and initiatives. This approach enhances public trust and ensures that budget allocations better reflect the community's priorities and needs.
Key Differences Between Public Funding and Participatory Budgeting
Public funding involves government allocation of resources through traditional budgetary processes, often led by elected officials or administrative bodies. Participatory budgeting empowers citizens to directly decide on the allocation of a portion of the public funds, fostering community engagement and transparency. Key differences include decision-making authority, with public funding centralized, while participatory budgeting decentralizes control and encourages local input.
Advantages of Traditional Public Funding
Traditional public funding ensures predictable and stable financial resources for large-scale infrastructure and essential public services, supporting long-term planning and sustainability. Centralized decision-making streamlines the allocation process, reducing administrative complexities and enabling efficient use of taxpayer funds. This method leverages expert assessments and established frameworks to prioritize projects aligned with broader policy goals and economic strategies.
Benefits of Participatory Budgeting for Communities
Participatory budgeting empowers communities to directly influence allocation of public funds, enhancing transparency and accountability in local governance. This inclusive process fosters stronger civic engagement, allowing residents to prioritize projects that address their specific needs, leading to more equitable resource distribution and improved public services. Studies show that participatory budgeting increases trust in government institutions and promotes social cohesion by involving diverse community voices in decision-making.
Challenges Facing Public Funding Models
Public funding models often struggle with inefficiency, lack of transparency, and limited citizen engagement, leading to misallocation of resources and reduced public trust. Challenges include bureaucratic delays, insufficient accountability mechanisms, and difficulty in addressing diverse community needs through top-down budget decisions. These issues highlight the need for more inclusive approaches like participatory budgeting that foster direct citizen involvement and improve resource allocation outcomes.
Limitations of Participatory Budgeting Processes
Participatory budgeting processes often face limitations such as restricted scalability, which confines citizen engagement to smaller communities or neighborhoods. Transparency issues arise due to the complexity of budget allocation, potentially leading to misunderstandings or mistrust among participants. Additionally, participatory budgeting may exclude marginalized groups lacking access to digital platforms or public meetings, limiting the inclusiveness of decision-making compared to traditional public funding mechanisms.
Impact on Social Equity: Public Funding vs Participatory Budgeting
Public funding often allocates resources based on top-down decisions that may overlook marginalized communities, potentially exacerbating social inequalities. Participatory budgeting empowers residents, especially underrepresented groups, to directly influence how funds are distributed, promoting transparency and equity. Studies show participatory budgeting increases social inclusion and addresses local needs more effectively than traditional public funding models.
Case Studies: Successful Participatory Budgeting Initiatives
Participatory budgeting initiatives in Porto Alegre, Brazil, and New York City have demonstrated significant improvements in local governance and resource allocation through citizen involvement. Porto Alegre's model redirected public funds to prioritize underserved communities, resulting in enhanced infrastructure and social services, while New York City's participatory budgeting engaged thousands of residents in decision-making, increasing transparency and public trust. These case studies highlight how public funding integrated with participatory budgeting fosters equitable development and strengthens democratic engagement.
The Future of Public Finance: Integrating Both Approaches
Public funding remains essential for large-scale infrastructure and social programs, offering stable, government-controlled resource allocation. Participatory budgeting empowers communities by involving citizens directly in financial decisions, enhancing transparency and local engagement. Integrating both approaches fosters a more inclusive, effective public finance system that balances centralized oversight with grassroots participation.
Related Important Terms
PB Mainstreaming
Participatory budgeting (PB) mainstreaming enhances public funding effectiveness by promoting transparent, community-driven allocation of resources that aligns with local priorities. Integrating PB into public funding frameworks increases accountability, fosters civic engagement, and ensures equitable distribution of funds based on collective decision-making processes.
Crowdsourced Tax Allocations
Crowdsourced tax allocations empower citizens to directly influence public funding decisions, increasing transparency and community engagement compared to traditional top-down public funding models. Participatory budgeting leverages collective input to allocate resources more equitably, fostering accountability and aligning expenditures with local priorities.
Participatory Grantmaking
Participatory grantmaking empowers communities by involving them directly in public funding decisions, enhancing transparency and accountability compared to traditional top-down public funding models. This approach leverages local knowledge and collective expertise to allocate resources more effectively, promoting equitable and inclusive development outcomes.
Deliberative Budget Cycles
Deliberative budget cycles enhance public funding effectiveness by integrating participatory budgeting processes, enabling citizens to collaboratively prioritize resource allocation based on community needs and transparency. This method fosters accountable governance, improves public trust, and aligns fiscal decisions with democratic engagement principles.
Community-Led Fiscal Planning
Community-led fiscal planning enhances public funding effectiveness by integrating participatory budgeting processes that empower local stakeholders to directly allocate resources based on collective priorities. This approach fosters transparency, accountability, and equitable distribution of public funds, driving sustainable community development through inclusive decision-making.
Hyperlocal Funding Initiatives
Hyperlocal funding initiatives leverage participatory budgeting to empower communities by allocating public funds directly to local projects, enhancing transparency and accountability in public spending. These approaches prioritize resident input and decision-making, leading to more tailored and effective resource distribution in specific neighborhoods or districts.
Digital Public Expenditure Forums
Digital Public Expenditure Forums enhance transparency and citizen engagement by allowing real-time tracking of public funding allocations, contrasting traditional top-down public funding methods with participatory budgeting's inclusive decision-making process. These digital platforms leverage data analytics and interactive tools to empower communities in prioritizing projects, thereby optimizing resource distribution and accountability in public financial management.
Civic Tech Budget Platforms
Civic Tech Budget Platforms enhance transparency and citizen engagement by enabling direct public participation in budget allocation, contrasting traditional public funding processes that are often top-down and less accessible. These platforms leverage digital tools to facilitate collaborative decision-making, increasing accountability and aligning budget priorities with community needs.
Radical Transparency Funds
Radical Transparency Funds enable public funding models where citizens directly allocate budgets through participatory budgeting, increasing accountability and reducing corruption. This approach fosters trust by publicly disclosing all financial decisions and spending in real-time, empowering communities to monitor and influence funding outcomes.
Inclusive Budgeting Mechanisms
Inclusive budgeting mechanisms elevate public funding by incorporating participatory budgeting processes that enable diverse community voices to directly influence allocation decisions, enhancing transparency and equity. This approach fosters social cohesion and accountability, ensuring resources address local priorities while expanding democratic engagement in public finance management.
public funding vs participatory budgeting Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com