Public infrastructure forms the backbone of urban development, providing essential services like transportation, utilities, and communication networks. Smart city solutions enhance this infrastructure by integrating digital technologies such as IoT, data analytics, and AI to optimize efficiency, reduce costs, and improve quality of life. These innovations enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and adaptive resource management, transforming traditional public infrastructure into intelligent systems.
Table of Comparison
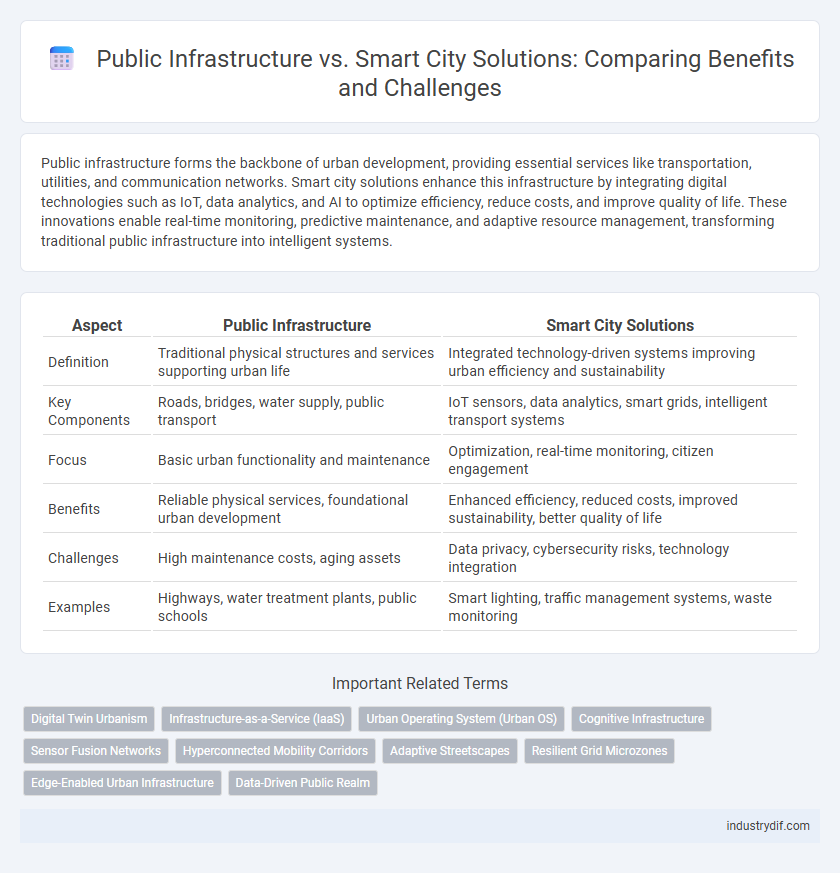
| Aspect | Public Infrastructure | Smart City Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional physical structures and services supporting urban life | Integrated technology-driven systems improving urban efficiency and sustainability |
| Key Components | Roads, bridges, water supply, public transport | IoT sensors, data analytics, smart grids, intelligent transport systems |
| Focus | Basic urban functionality and maintenance | Optimization, real-time monitoring, citizen engagement |
| Benefits | Reliable physical services, foundational urban development | Enhanced efficiency, reduced costs, improved sustainability, better quality of life |
| Challenges | High maintenance costs, aging assets | Data privacy, cybersecurity risks, technology integration |
| Examples | Highways, water treatment plants, public schools | Smart lighting, traffic management systems, waste monitoring |
Overview of Public Infrastructure
Public infrastructure encompasses essential physical systems such as transportation networks, water supply, energy grids, and communication facilities that support societal functions and economic activities. Investments in durable roads, bridges, public transit, and utilities ensure community connectivity, safety, and resilience. Efficient public infrastructure forms the foundation for urban development and serves as a critical baseline before integrating advanced smart city solutions.
Defining Smart City Solutions
Smart city solutions integrate advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and big data analytics to enhance urban infrastructure efficiency, sustainability, and citizen engagement. Unlike traditional public infrastructure that focuses on physical assets like roads and bridges, smart city solutions prioritize digital connectivity and real-time data management to optimize services such as traffic control, energy usage, and public safety. This transformation fosters smarter urban planning, reduces operational costs, and improves overall quality of life for residents.
Key Differences Between Traditional Infrastructure and Smart Solutions
Public infrastructure relies on static, physical systems such as roads, bridges, and water supply networks designed primarily for basic functionality and long-term durability. Smart city solutions integrate advanced technologies like IoT sensors, data analytics, and AI to optimize resource management, enhance real-time decision-making, and improve urban services efficiency. The key differences lie in adaptability, connectivity, and data-driven responsiveness, enabling smart cities to address dynamic urban challenges more effectively than traditional infrastructure.
The Evolution of Urban Development
Public infrastructure has traditionally centered on basic utilities such as roads, water supply, and sanitation systems, forming the backbone of urban development. Smart city solutions integrate advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and data analytics to enhance urban living through improved energy management, traffic control, and public safety. The evolution of urban development reflects a shift from conventional infrastructure to intelligent ecosystems designed for sustainability, efficiency, and citizen engagement.
Benefits of Upgrading to Smart City Technologies
Upgrading public infrastructure with smart city technologies enhances operational efficiency by integrating IoT sensors and AI-driven data analytics, leading to optimized traffic management and reduced energy consumption. Smart city solutions improve public safety through real-time surveillance and predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime and emergency response times. These innovations foster sustainable urban development by enabling adaptive resource allocation and reducing carbon footprints across transportation, utilities, and public services.
Challenges Faced in Modernizing Public Infrastructure
Modernizing public infrastructure encounters challenges such as aging assets, limited funding, and integrating advanced technologies with legacy systems. The complexity of coordinating multi-agency efforts and ensuring cybersecurity within smart city solutions further complicates upgrades. Balancing sustainability goals with the demand for real-time data and connectivity remains a critical hurdle.
Integration of IoT in Urban Environments
Integration of IoT in urban environments transforms public infrastructure by enabling real-time data collection and management of utilities such as traffic, water supply, and energy grids. Smart city solutions leverage interconnected sensors and devices to optimize resource allocation, reduce operational costs, and enhance public safety through predictive analytics and automated responses. This fusion of IoT technology with traditional infrastructure fosters sustainable urban development and improved quality of life for residents.
Cost Implications: Traditional vs. Smart City Investments
Traditional public infrastructure projects often involve high upfront capital costs and extended timelines, with recurring expenses for maintenance and limited scalability. Smart city solutions, while requiring significant initial investment in technology and integration, tend to offer long-term cost savings through improved energy efficiency, data-driven resource management, and reduced operational expenses. Investing in smart city technologies enhances economic sustainability by optimizing infrastructure performance and minimizing waste compared to conventional development approaches.
Case Studies: Cities Leading in Smart Infrastructure
Singapore's Smart Nation initiative showcases the integration of public infrastructure with IoT sensors, enabling real-time data collection for efficient traffic management and energy savings. Barcelona's smart city model leverages wireless sensor networks and open data platforms to optimize waste management and reduce water consumption. Amsterdam's smart grid system combines renewable energy with intelligent public infrastructure to enhance sustainability and urban resilience.
The Future of Public Infrastructure in Smart Cities
Public infrastructure in smart cities integrates IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and advanced communication networks to enhance urban efficiency and sustainability. Smart grid systems optimize energy distribution while real-time data monitoring improves transportation, water management, and emergency response. These innovations drive the future of public infrastructure by enabling adaptive, resilient, and citizen-centric urban environments.
Related Important Terms
Digital Twin Urbanism
Digital Twin Urbanism enhances public infrastructure by creating dynamic, real-time virtual models of urban environments to optimize resource management, reduce maintenance costs, and improve citizen engagement. Integrating digital twin technology within smart city solutions facilitates predictive analytics and efficient urban planning, transforming traditional infrastructure into adaptive, data-driven ecosystems.
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) provides scalable, on-demand computing resources essential for developing and managing both public infrastructure and smart city solutions. By leveraging virtualized hardware and cloud-based services, IaaS enables efficient data processing, real-time analytics, and seamless integration of IoT devices critical for urban planning and infrastructure optimization.
Urban Operating System (Urban OS)
Urban Operating System (Urban OS) serves as the central platform integrating data from public infrastructure to optimize city management, improve resource allocation, and enhance citizen services. Leveraging IoT sensors, real-time analytics, and AI, Urban OS enables smart city solutions such as traffic management, energy efficiency, and public safety, transforming traditional infrastructure into dynamic, responsive urban ecosystems.
Cognitive Infrastructure
Cognitive infrastructure integrates advanced AI, IoT, and data analytics to transform traditional public infrastructure into adaptive, intelligent systems that enhance urban efficiency and citizen services. Smart city solutions leverage cognitive technologies to optimize resource management, improve public safety, and enable real-time decision-making for sustainable urban development.
Sensor Fusion Networks
Sensor fusion networks integrate diverse data from public infrastructure components such as traffic lights, utilities, and transportation systems to enhance urban management and efficiency. This technology enables smart city solutions to optimize resource allocation, improve real-time monitoring, and support predictive maintenance for sustainable urban development.
Hyperconnected Mobility Corridors
Hyperconnected mobility corridors integrate advanced IoT sensors, real-time data analytics, and AI-driven traffic management systems to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion within public infrastructure. These smart city solutions enhance urban mobility by enabling seamless connectivity between autonomous vehicles, public transit, and pedestrian pathways, improving efficiency and sustainability in metropolitan environments.
Adaptive Streetscapes
Adaptive streetscapes integrate smart city solutions such as sensor networks, dynamic lighting, and real-time traffic management to enhance public infrastructure efficiency, safety, and sustainability. These technologies enable responsive urban environments that adjust to pedestrian flow, weather conditions, and energy consumption, fostering improved mobility and reduced carbon emissions.
Resilient Grid Microzones
Resilient grid microzones enhance public infrastructure by decentralizing energy distribution and integrating renewable resources, ensuring continuous power supply during outages and natural disasters. These microzones enable smart city solutions by supporting real-time energy management, reducing grid vulnerabilities, and promoting sustainability in urban environments.
Edge-Enabled Urban Infrastructure
Edge-enabled urban infrastructure integrates advanced Internet of Things (IoT) devices and real-time data processing at the network edge, enhancing the efficiency and responsiveness of public infrastructure such as traffic management, energy distribution, and public safety systems. This decentralized approach reduces latency, optimizes bandwidth usage, and enables scalable smart city solutions that adapt dynamically to urban demands while improving sustainability and citizen quality of life.
Data-Driven Public Realm
Data-driven public realm initiatives transform traditional public infrastructure by integrating IoT sensors, real-time analytics, and AI-powered platforms to enhance urban mobility, energy efficiency, and citizen engagement. Smart city solutions leverage big data and cloud computing to optimize resource allocation, improve public safety, and foster sustainable development within urban environments.
Public Infrastructure vs Smart City Solutions Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com