Public pet initiatives foster community engagement by integrating urban innovation labs that prioritize inclusive design and sustainability. Urban innovation labs serve as experimental spaces where public needs guide the development of cutting-edge solutions for pet welfare in city environments. Collaboration between public entities and innovation labs accelerates the creation of adaptable, scalable programs that enhance urban pet ownership experiences.
Table of Comparison
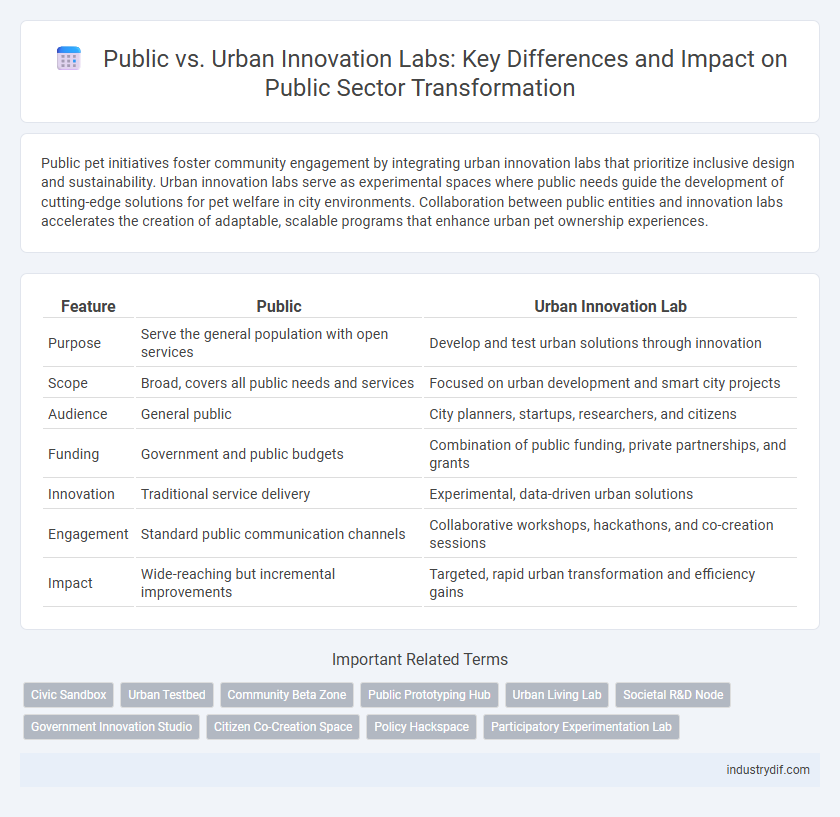
| Feature | Public | Urban Innovation Lab |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Serve the general population with open services | Develop and test urban solutions through innovation |
| Scope | Broad, covers all public needs and services | Focused on urban development and smart city projects |
| Audience | General public | City planners, startups, researchers, and citizens |
| Funding | Government and public budgets | Combination of public funding, private partnerships, and grants |
| Innovation | Traditional service delivery | Experimental, data-driven urban solutions |
| Engagement | Standard public communication channels | Collaborative workshops, hackathons, and co-creation sessions |
| Impact | Wide-reaching but incremental improvements | Targeted, rapid urban transformation and efficiency gains |
Understanding Public Innovation Labs
Public Innovation Labs serve as collaborative spaces where government entities, citizens, and private sectors co-create solutions to societal challenges, emphasizing transparency and inclusivity. Urban Innovation Labs, a subset of Public Innovation Labs, specifically address urban issues such as transportation, housing, and sustainability, leveraging smart city technologies and data analytics. Understanding Public Innovation Labs involves recognizing their role in fostering participatory governance, accelerating policy experimentation, and scaling impactful innovations across communities.
Defining Urban Innovation Labs
Urban Innovation Labs are specialized environments designed to foster collaborative problem-solving for complex city challenges, integrating technology, policy, and community engagement. These labs operate as experimental spaces where public sector entities, private companies, and civil society co-create innovative solutions to improve urban living conditions. Unlike broader public innovation initiatives, Urban Innovation Labs concentrate specifically on urban contexts, leveraging data-driven approaches and real-time testing to address transportation, sustainability, and social equity issues.
Key Differences: Public vs Urban Innovation Labs
Public Innovation Labs primarily focus on addressing broad societal challenges through collaborative governmental and community initiatives, leveraging public sector resources and policy frameworks. Urban Innovation Labs concentrate on city-specific problems, employing localized data, smart city technologies, and urban planning strategies to enhance urban living environments. The key difference lies in scope and scale: Public Labs operate on a wide societal level, while Urban Labs target urban-centric innovation for city development.
Core Objectives and Missions
Public Innovation Labs prioritize inclusive community engagement, aiming to address societal challenges through co-creation with diverse stakeholders. Urban Innovation Labs focus on leveraging data-driven solutions to optimize city infrastructure and enhance urban living conditions. Both entities emphasize sustainable development but differ in scope, with Public Labs targeting broader social impact and Urban Labs concentrating on smart city advancements.
Target Stakeholders and Communities
Public innovation initiatives prioritize broad-based stakeholder engagement, focusing on inclusive participation from government entities, local communities, and civil society organizations to drive social impact. Urban Innovation Labs target city-specific challenges by collaborating with municipal authorities, technology developers, and urban residents to co-create smart city solutions. Both models emphasize stakeholder co-creation but differ in scope, with Public labs addressing systemic governance issues and Urban labs concentrating on localized urban development and infrastructure optimization.
Funding and Governance Models
Public innovation labs often rely on government funding and operate under strict regulatory frameworks, ensuring accountability and alignment with public policy goals. Urban innovation labs typically secure diverse funding sources, including private investments, grants, and partnerships, allowing greater flexibility and rapid experimentation. Governance models in public labs emphasize transparency and stakeholder engagement, while urban labs adopt collaborative, multi-sector governance structures to drive localized innovation.
Scope of Innovation Outcomes
Public innovation initiatives typically target broad societal challenges, emphasizing scalable and inclusive solutions that impact diverse communities across regions. Urban Innovation Labs concentrate on localized problem-solving within city environments, generating data-driven, context-specific outcomes that enhance urban living conditions. Both approaches prioritize sustainable development but differ in scale and specificity, with Public efforts focusing on wide-reaching policies and Urban Labs driving tactical, neighborhood-level advancements.
Collaboration Methods and Partnerships
Public innovation labs emphasize open collaboration methods by engaging diverse community stakeholders through co-creation workshops and digital platforms, fostering inclusive problem-solving. Urban innovation labs prioritize strategic partnerships with local governments, private sectors, and academic institutions to drive data-driven urban solutions and policy development. Both models leverage cross-sector collaboration but differ in scale and stakeholder involvement, with Public labs focusing on grassroots engagement and Urban labs on institutional alliances.
Impact Measurement and Evaluation
Public innovation initiatives emphasize inclusive impact measurement frameworks that capture social equity, sustainability, and community engagement outcomes. Urban Innovation Labs prioritize data-driven evaluation methods using real-time sensors, geospatial analytics, and citizen feedback platforms to assess urban livability and infrastructure efficiency. Both approaches leverage qualitative and quantitative metrics to optimize policy interventions and enhance public value creation.
Future Trends in Public and Urban Innovation Labs
Future trends in public and urban innovation labs emphasize integrating artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT), and big data analytics to enhance civic engagement and urban planning. These labs increasingly prioritize collaborative ecosystems involving government agencies, private sector, and local communities to co-create scalable and sustainable solutions. Emphasis on digital twin technology and smart city frameworks drives real-time decision-making and adaptive urban infrastructure development.
Related Important Terms
Civic Sandbox
Civic Sandbox leverages Public's digital engagement platform to accelerate urban innovation through real-time community feedback and data-driven decision-making. Combining Public's scalable communication tools with Civic Sandbox's experimental urban projects fosters inclusive civic participation and drives sustainable city solutions.
Urban Testbed
Urban Innovation Labs provide controlled environments for experimenting with new technologies and policies, whereas Urban Testbeds offer real-world urban settings to validate and scale these innovations. By leveraging authentic city infrastructure, Urban Testbeds accelerate data-driven solutions that address complex urban challenges such as traffic congestion, energy efficiency, and public safety.
Community Beta Zone
The Public Community Beta Zone fosters inclusive collaboration by enabling diverse stakeholders to co-create innovative solutions within a real-world urban setting. This platform contrasts with traditional Urban Innovation Labs by emphasizing community-driven experimentation and iterative feedback to ensure scalable social impact.
Public Prototyping Hub
The Public Prototyping Hub accelerates civic innovation by providing open access to tools, resources, and collaborative spaces for rapid development of public solutions. Unlike Urban Innovation Labs, which often focus on experimental policy frameworks, the Public Prototyping Hub emphasizes hands-on, community-driven design and iterative testing of tangible prototypes to address urban challenges.
Urban Living Lab
Urban Living Labs serve as collaborative environments that engage public stakeholders, researchers, and local communities to co-create innovative solutions addressing urban challenges such as sustainability, mobility, and social inclusion. These labs integrate real-life urban settings with experimental methodologies, distinguishing them from traditional Public and Urban Innovation Labs by emphasizing participatory design and iterative testing within lived urban contexts.
Societal R&D Node
The Societal R&D Node in Public serves as a collaborative hub driving research and development focused on social impact, contrasting with Urban Innovation Labs that primarily target city-specific challenges through technological solutions. Public's Societal R&D Node integrates multidisciplinary expertise to create scalable social innovations addressing systemic issues across diverse communities.
Government Innovation Studio
Government Innovation Studios serve as collaborative hubs that enable public sector agencies to co-create innovative solutions tailored to complex governance challenges, leveraging multidisciplinary expertise and advanced technologies. Unlike urban innovation labs that primarily address city-specific issues, Government Innovation Studios operate at multiple jurisdictional levels, fostering policy development, digital transformation, and inclusive public service design to enhance government efficiency and civic engagement.
Citizen Co-Creation Space
Public innovation labs serve as inclusive citizen co-creation spaces designed to engage diverse community members in collaborative problem-solving, fostering participatory governance and social innovation. Urban innovation labs typically focus on city-scale challenges, leveraging advanced technologies and data-driven approaches to co-create solutions with urban stakeholders, emphasizing smart city development and sustainable urban planning.
Policy Hackspace
Policy Hackspace fosters collaborative policy development by leveraging diverse expertise within Public's open innovation framework, accelerating problem-solving beyond traditional Urban Innovation Labs. Integrating digital tools and community-driven insights, it enables scalable, adaptive governance models tailored to complex public sector challenges.
Participatory Experimentation Lab
The Participatory Experimentation Lab within Public emphasizes co-creating experimental solutions by actively involving diverse community members in the innovation process, fostering collaborative problem-solving and inclusive design. Unlike traditional Urban Innovation Labs that focus primarily on city infrastructure and technology, the Participatory Experimentation Lab prioritizes grassroots engagement and real-world testing of social innovations to address complex urban challenges.
Public vs Urban Innovation Lab Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com